| Tag | Content | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SG ID |
SG00000049 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
UniProt Accession |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Theoretical PI |
8.87
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Weight |
34368 Da
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Genbank Nucleotide ID |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Genbank Protein ID |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Name |
asb-1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Synonyms/Alias |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Name |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Synonyms/Alias |
SubName: Protein ASB-1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Organism |
Caenorhabditis elegans |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NCBI Taxonomy ID |
6239 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Chromosome Location |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function in Stage |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function in Cell Type |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Description |
Temporarily unavailable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The information of related literatures |
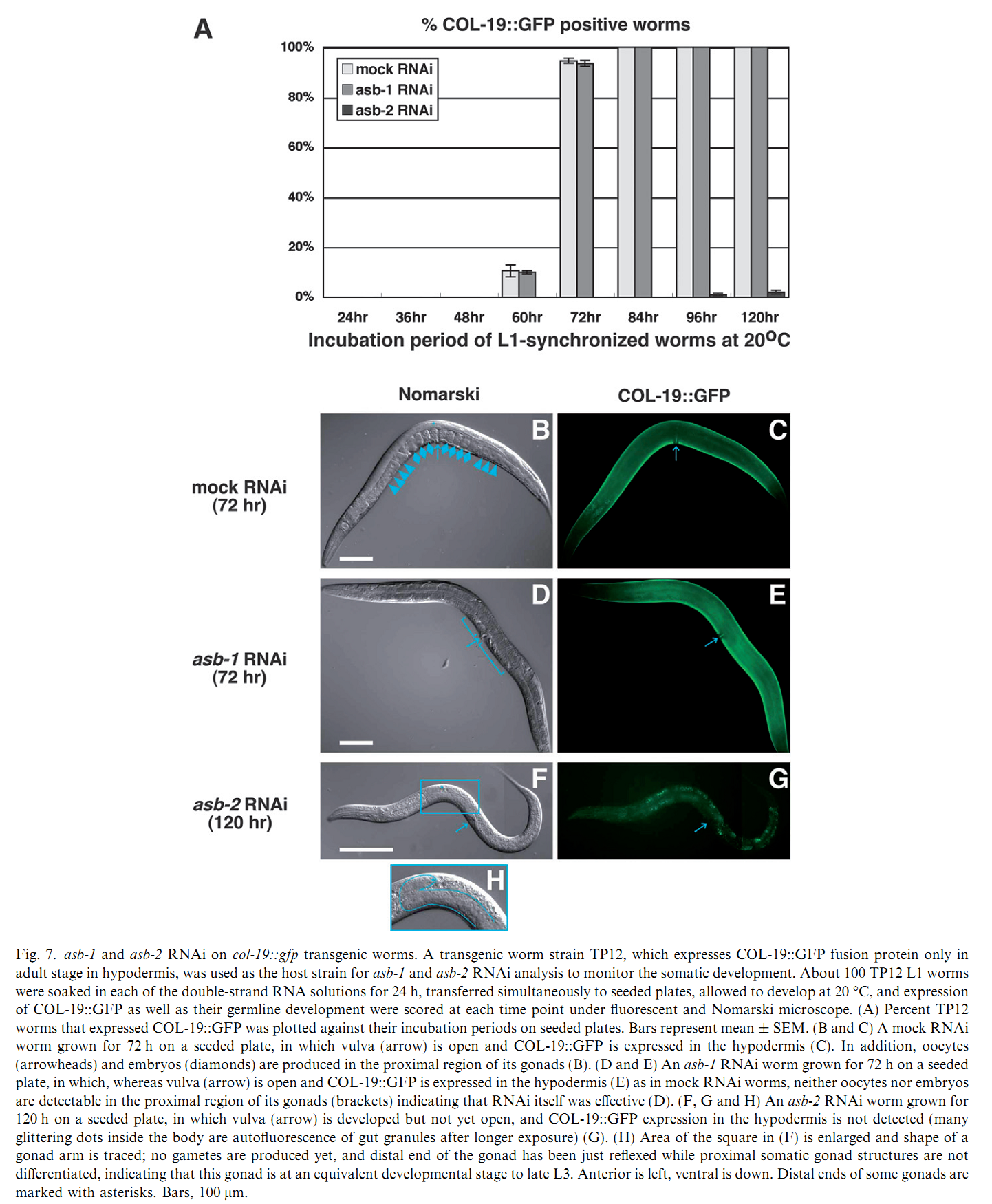
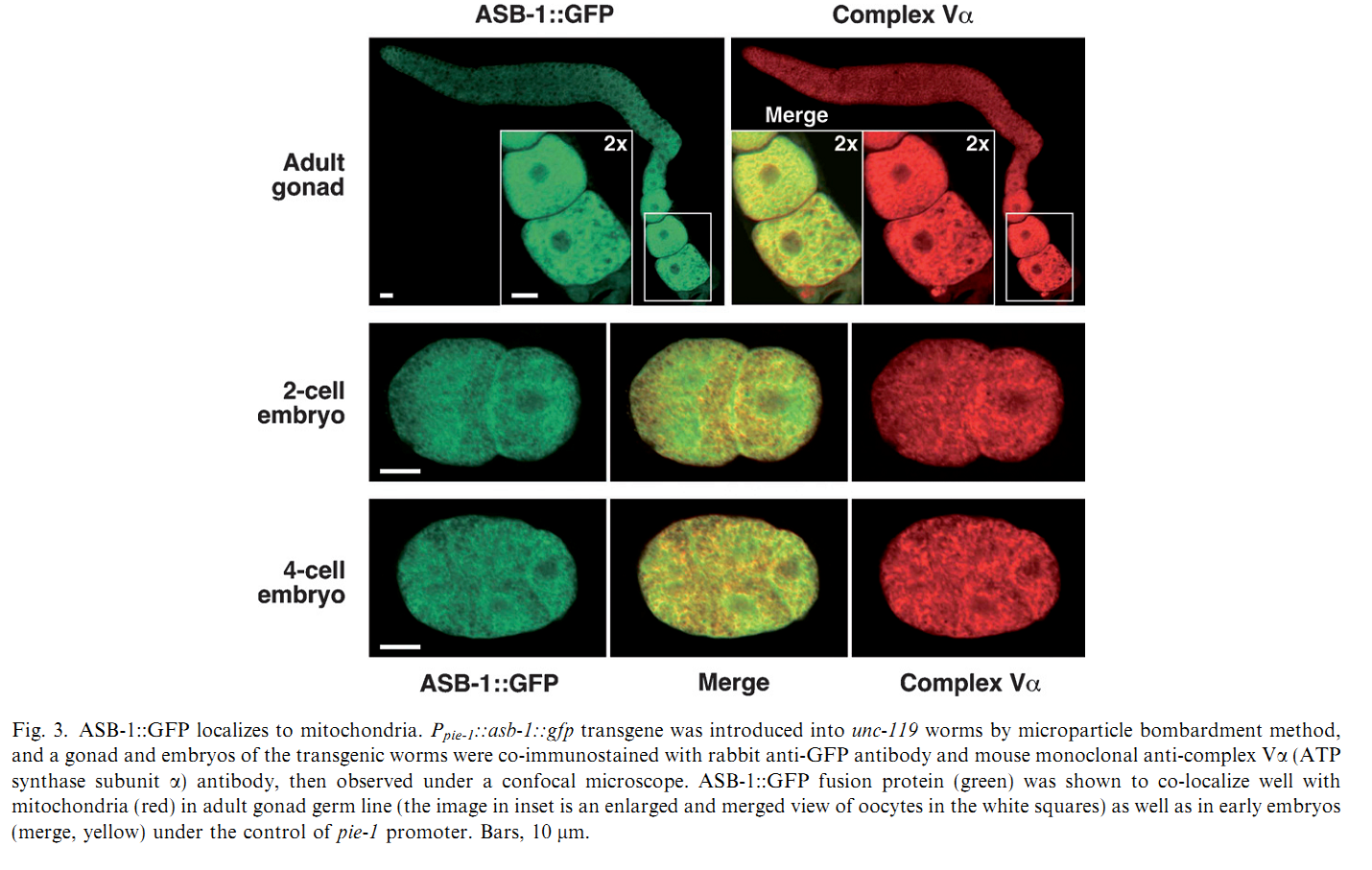
1. I. Kawasaki, M. Hanazawa, K. Gengyo-Ando, S. Mitani, I. Maruyama and Y. Iino (2007) ASB-1, a germline-specific isoform of mitochondrial ATP synthase b subunit, is required to maintain the rate of germline development in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mech Dev 124(3): 237-51. Abstract The developmental timing of all types of cells must be synchronized and spatially coordinated to achieve the organized development of a multicellular organism. Previously, we found RNAi of asb-1, encoding a germline-specific isoform of mitochondrial ATP synthase b subunit, caused 100% penetrant sterility in Caenorhabditis elegans. ATP synthase is one of the five complexes of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, and defects in some of the components of the chain are known to slow the growth and extend the lifespan of worms. We found that development of asb-1 mutant germ line was not arrested at any stage, but did slow to half the rate of wild type, whereas the rate of somatic development was the same in asb-1 mutants as that of wild type, indicating that asb-1 is required to maintain the rate of germline development but has no effect on somatic development. Among ATP synthase subunit genes, RNAi of asg-1, encoding a germline-specific isoform of the g subunit, also caused asb-1-like sterility, indicating that some other germline-specific components are also required to maintain the rate of germline development. Both asb-1 and asg-1 are located on autosomes while they possess counterparts, asb-2 and asg-2, respectively, on X chromosome, which are both required for somatic development. Chromosomal locations of the genes may be the basis of the segregation of germline/somatic functions of each gene, as were demonstrated for other autosomal/X-linked duplicated gene pairs. PMID: [17223323] Back to Top |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figures for illustrating the function of this protein/gene |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Subcellular Location |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tissue Specificity |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Ontology |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interpro |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pfam |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SMART |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PROSITE |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PRINTS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Created Date |
18-Oct-2012 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Record Type |
Experiment identified |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein sequence Annotation |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nucleotide Sequence |
Length: 39709 bp Go to nucleotide: FASTA |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Sequence |
Length: 301 bp Go to amino acid: FASTA |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The verified Protein-Protein interaction information |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other Protein-Protein interaction resources |
String database |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
View Microarray data |
Temporarily unavailable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Comments |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||