| Tag | Content | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SG ID |
SG00000050 |
||||||||||||||
UniProt Accession |
|||||||||||||||
Theoretical PI |
-
|
||||||||||||||
Molecular Weight |
Da
|
||||||||||||||
Genbank Nucleotide ID |
|||||||||||||||
Genbank Protein ID |
|||||||||||||||
Gene Name |
|||||||||||||||
Gene Synonyms/Alias |
|||||||||||||||
Protein Name |
|||||||||||||||
Protein Synonyms/Alias |
|||||||||||||||
Organism |
|||||||||||||||
NCBI Taxonomy ID |
|||||||||||||||
Chromosome Location |
|
||||||||||||||
Function in Stage |
|||||||||||||||
Function in Cell Type |
|||||||||||||||
Description |
Temporarily unavailable |
||||||||||||||
The information of related literatures |
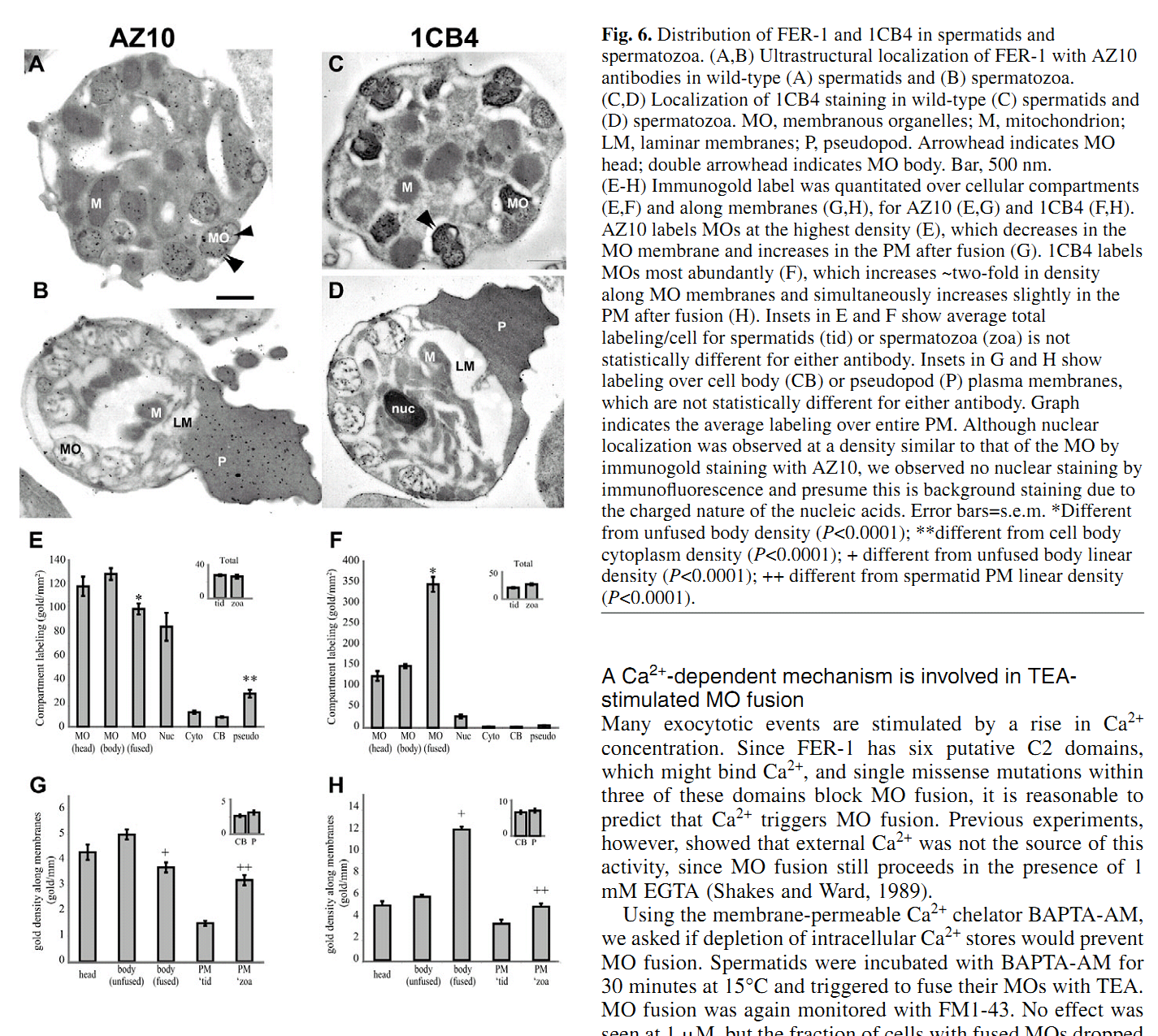
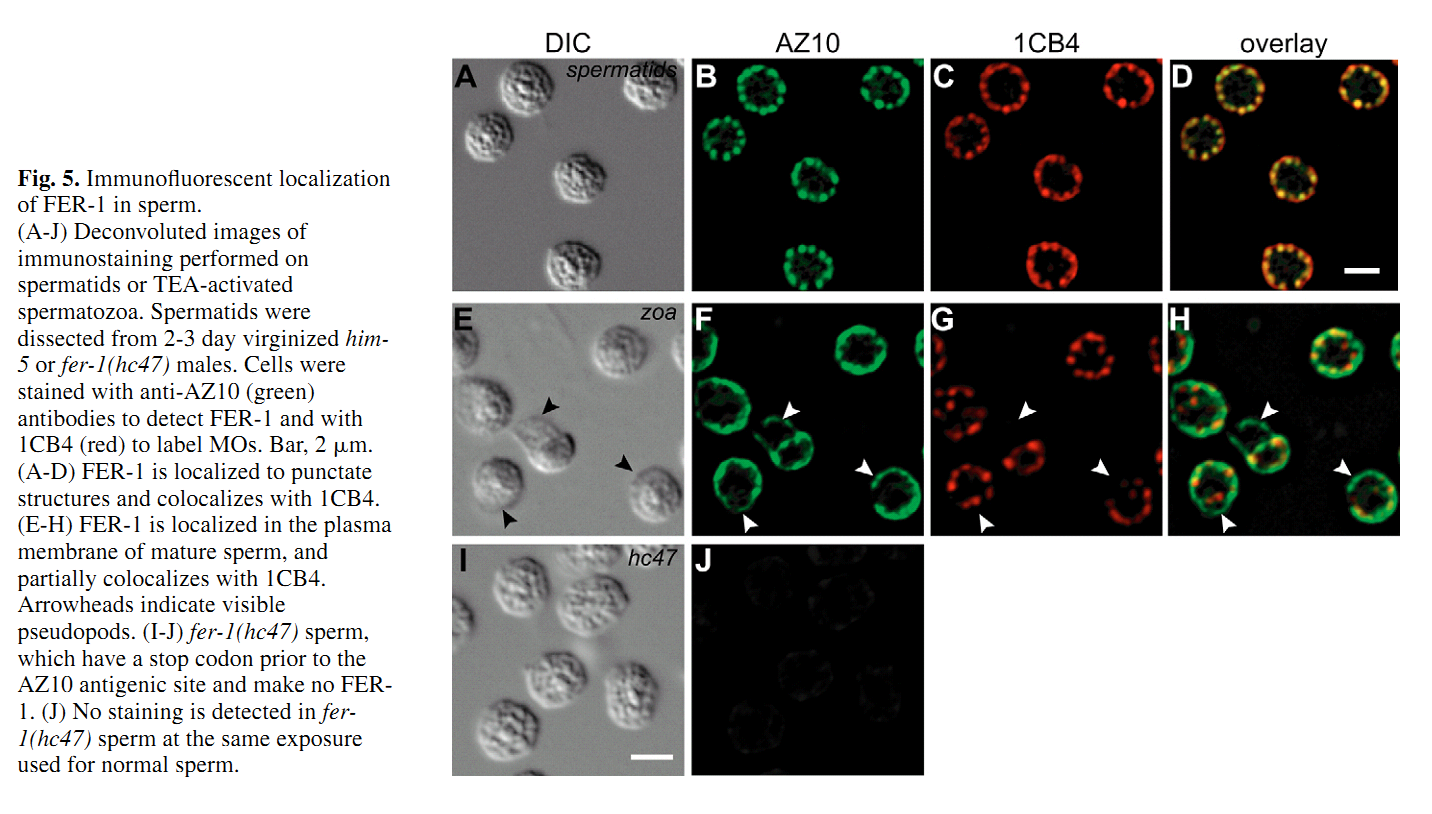
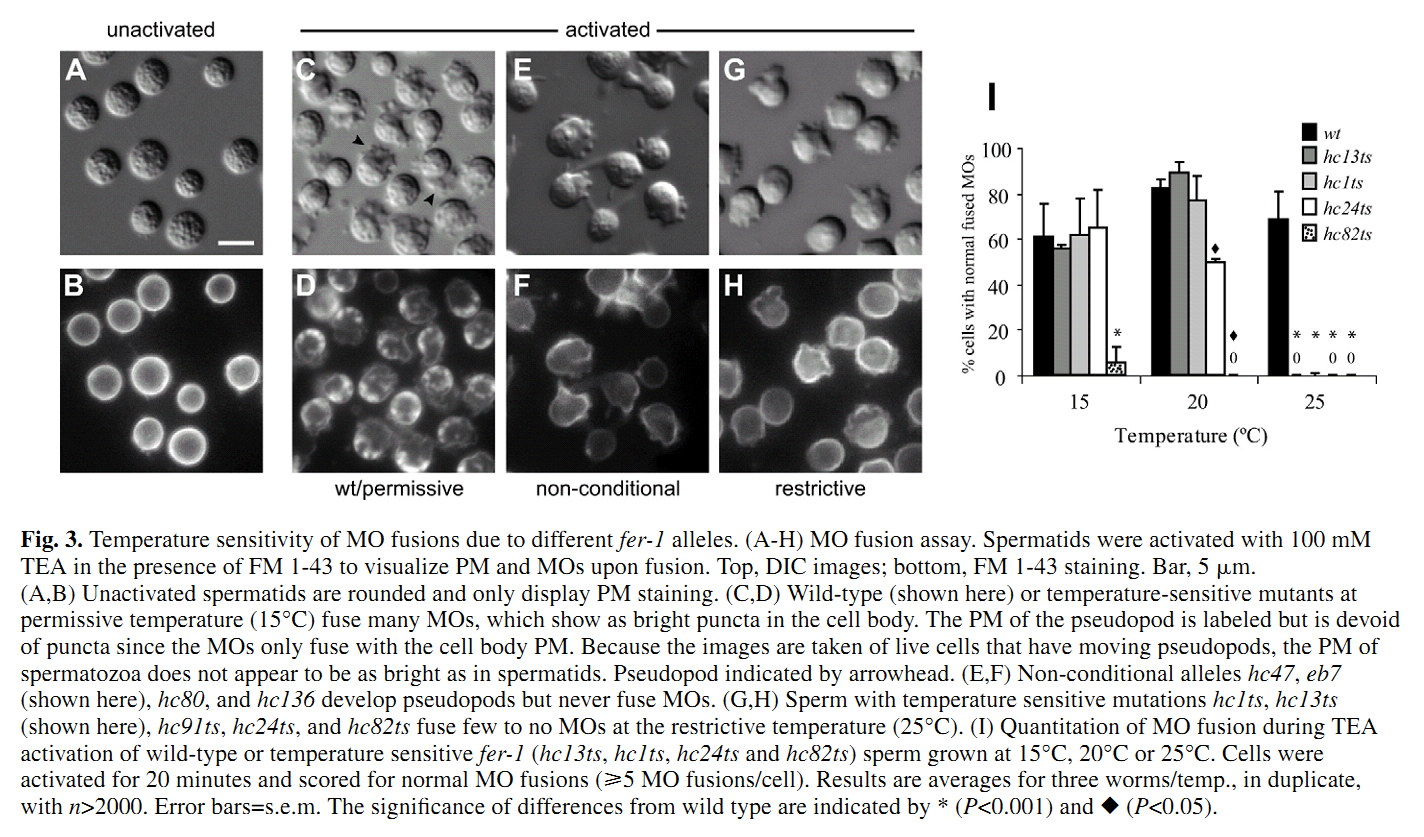
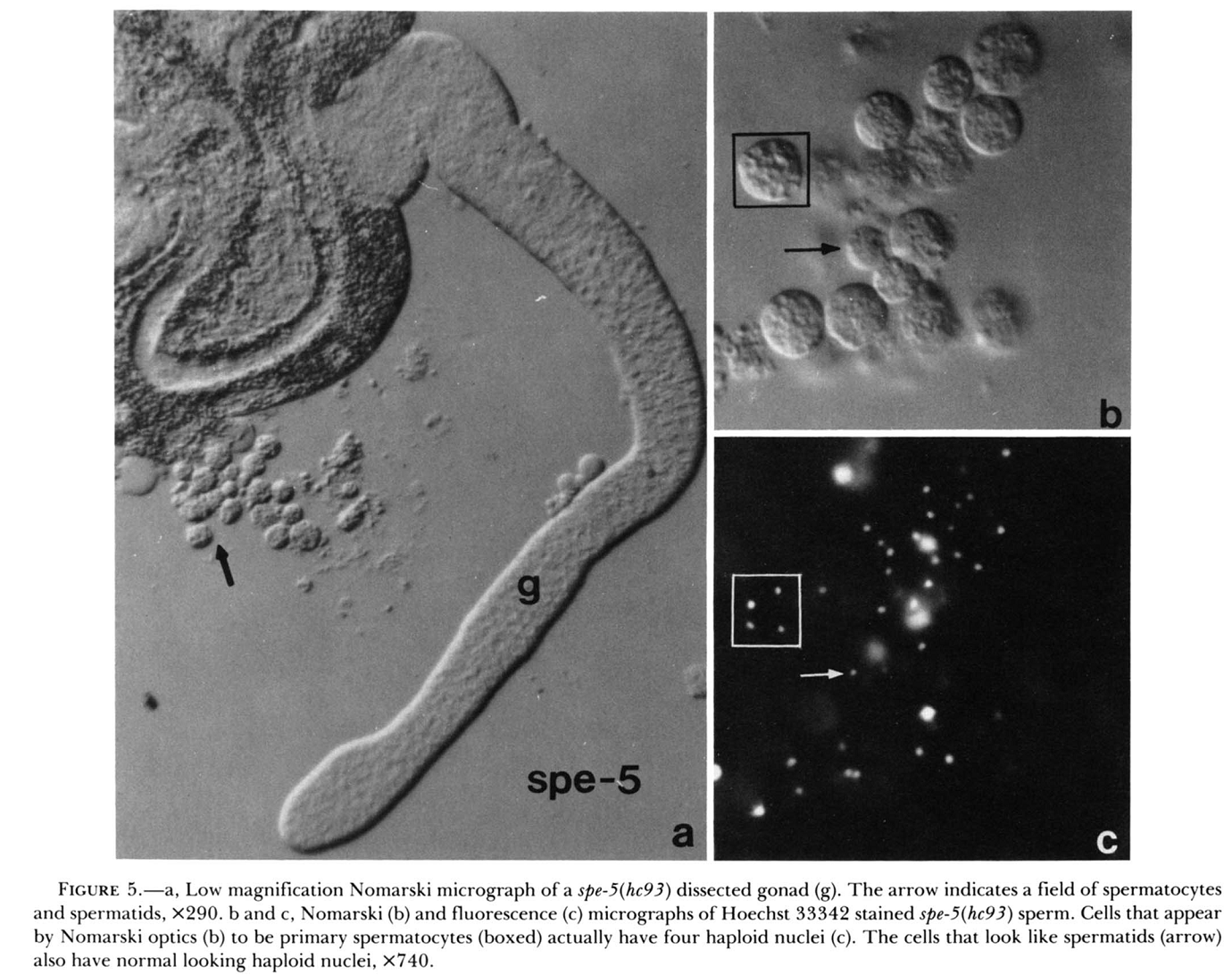
1. N. L. Washington and S. Ward (2006) FER-1 regulates Ca2+ -mediated membrane fusion during C. elegans spermatogenesis. J Cell Sci 119(Pt 12): 2552-62. Abstract FER-1 is required for fusion of specialized vesicles, called membranous organelles, with the sperm plasma membrane during Caenorhabditis elegans spermiogenesis. To investigate its role in membranous organelle fusion, we examined ten fer-1 mutations and found that they all cause the same defect in membrane fusion. FER-1 and the ferlin protein family are membrane proteins with four to seven C2 domains. These domains commonly mediate Ca2+ -dependent lipid-processing events. Most of the fer-1 mutations fall within these C2 domains, showing that they have distinct, non-redundant functions. We found that membranous organelle fusion requires intracellular Ca2+ and that C2 domain mutations alter Ca2+ sensitivity. This suggests that the C2 domains are involved in Ca2+ sensing and further supports their independent function. Using two immunological approaches we found three FER-1 isoforms, two of which might arise from FER-1 by proteolysis. By both light and electron microscopy, these FER-1 proteins were found to be localized to membranous organelle membranes. Dysferlin, a human homologue of FER-1 involved in muscular dystrophy, is required for vesicle fusion during Ca2+ -induced muscle membrane repair. Our results suggest that the ferlin family members share a conserved mechanism to regulate cell-type-specific membrane fusion. PMID: [16735442] 2. S. W. L'Hernault, D. C. Shakes and S. Ward (1988) Developmental genetics of chromosome I spermatogenesis-defective mutants in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 120(2): 435-52. Abstract Mutations affecting Caenorhabditis elegans spermatogenesis can be used to dissect the processes of meiosis and spermatozoan morphological maturation. We have obtained 23 new chromosome I mutations that affect spermatogenesis (spe mutations). These mutations, together with six previously described mutations, identify 11 complementation groups, of which six are defined by multiple alleles. These spe mutations are all recessive and cause normally self-fertile hermaphrodites to produce unfertilized oocytes that can be fertilized by wild-type male sperm. Five chromosome I mutation/deficiency heterozygotes have similar phenotypes to the homozygote showing that the probable null phenotype of these genes is defective sperm. Spermatogenesis is disrupted at different steps by mutations in these genes. The maturation of 1 degree spermatocytes is disrupted by mutations in spe-4 and spe-5. Spermatids from spe-8 and spe-12 mutants develop into normal spermatozoa in males, but not in hermaphrodites. fer-6 spermatids are abnormal, and fer-1 spermatids look normal but subsequently become abnormal spermatozoa. Mutations in five genes (fer-7, spe-9, spe-11, spe-13 and spe-15) allow formation of normal looking motile spermatozoa that appear to be defective in either sperm-spermathecal or sperm-oocyte interactions. PMID: [3197956] Back to Top |
||||||||||||||
Figures for illustrating the function of this protein/gene |
|
||||||||||||||
Function |
|||||||||||||||
Subcellular Location |
|||||||||||||||
Tissue Specificity |
|||||||||||||||
Gene Ontology |
|
||||||||||||||
Interpro |
|||||||||||||||
Pfam |
|||||||||||||||
SMART |
|||||||||||||||
PROSITE |
|||||||||||||||
PRINTS |
|||||||||||||||
Created Date |
18-Oct-2012 |
||||||||||||||
Record Type |
Experiment identified |
||||||||||||||
Protein sequence Annotation |
|||||||||||||||
Nucleotide Sequence |
Length: bp Go to nucleotide: FASTA |
||||||||||||||
Protein Sequence |
Length: bp Go to amino acid: FASTA |
||||||||||||||
The verified Protein-Protein interaction information |
| ||||||||||||||
Other Protein-Protein interaction resources |
String database |
||||||||||||||
View Microarray data |
Temporarily unavailable |
||||||||||||||
Comments |
|||||||||||||||