| Tag | Content | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SG ID |
SG00000063 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
UniProt Accession |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Theoretical PI |
5.55
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Weight |
79780 Da
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Genbank Nucleotide ID |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Genbank Protein ID |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Name |
glh-1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Synonyms/Alias |
ORFNames=T21G5.3 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Name |
ATP-dependent RNA helicase glh-1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Synonyms/Alias |
EC=3.6.4.13 Germline helicase 1; |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Organism |
Caenorhabditis elegans |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NCBI Taxonomy ID |
6239 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Chromosome Location |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function in Stage |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function in Cell Type |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Description |
Temporarily unavailable |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The information of related literatures |
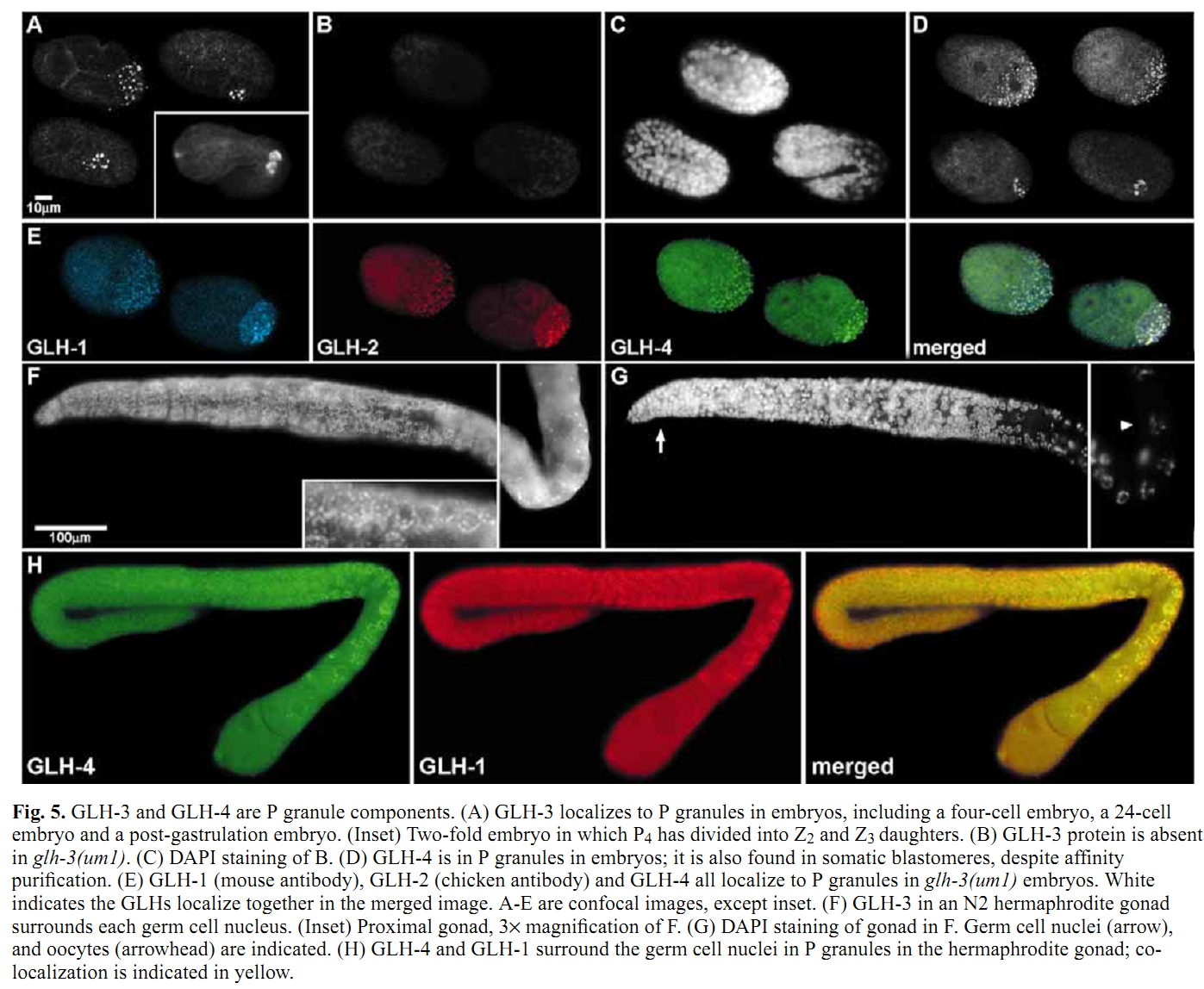
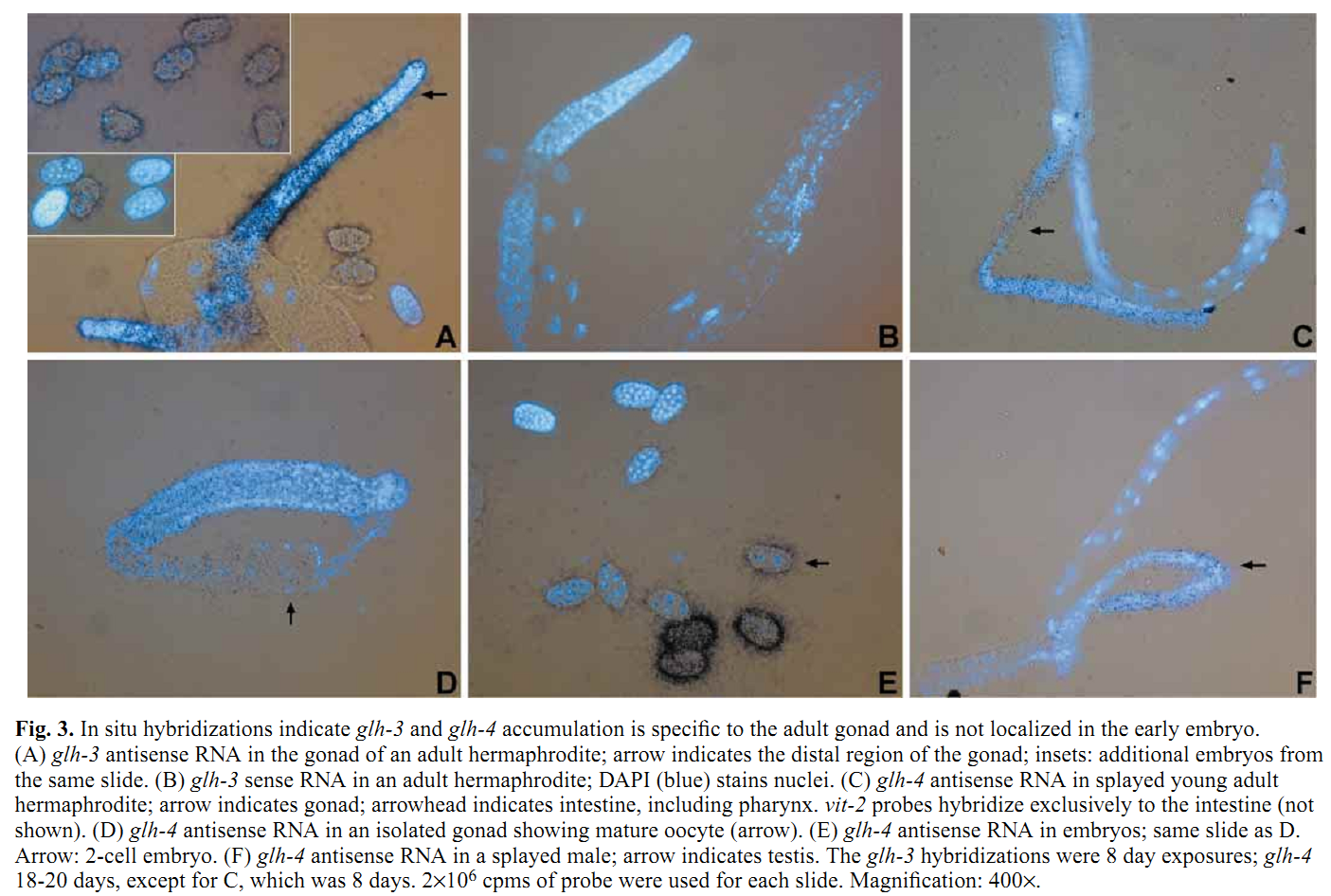
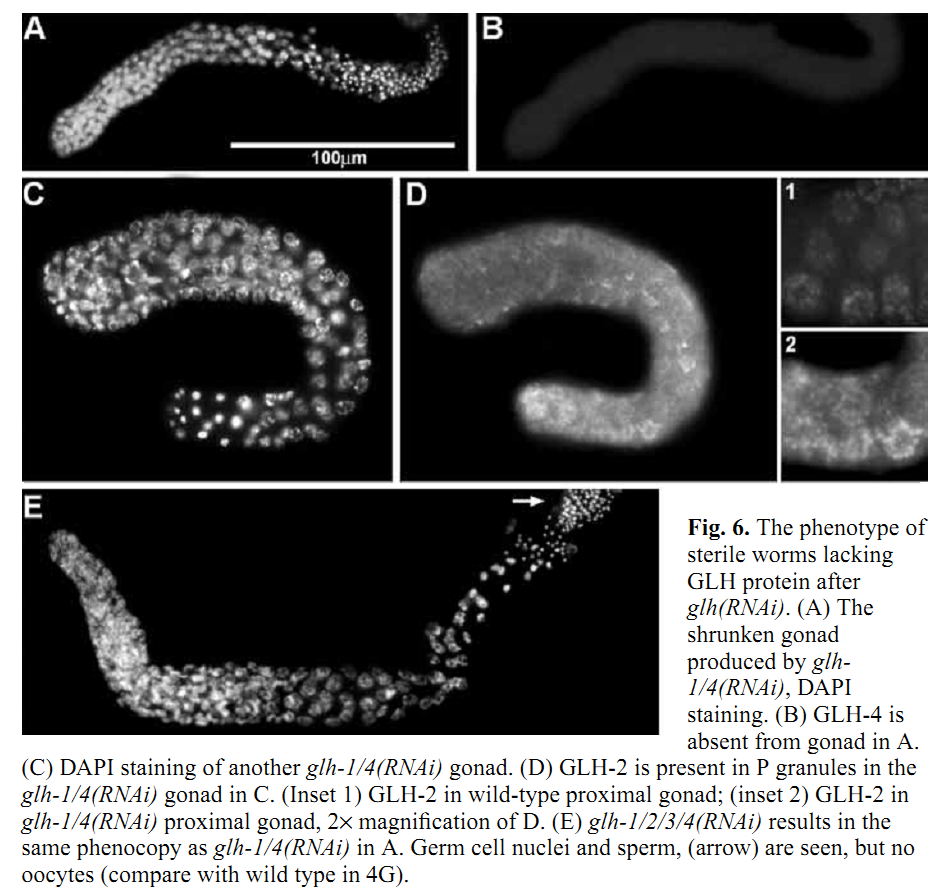
1. K. A. Kuznicki, P. A. Smith, W. M. Leung-Chiu, A. O. Estevez, H. C. Scott and K. L. Bennett (2000) Combinatorial RNA interference indicates GLH-4 can compensate for GLH-1; these two P granule components are critical for fertility in C. elegans. Development 127(13): 2907-16. Abstract We report that four putative germline RNA helicases, GLHs, are components of the germline-specific P granules in Caenorhabditis elegans. GLH-3 and GLH-4, newly discovered, belong to a multi-gene glh family. Although GLHs are homologous to Drosophila VASA, a polar granule component necessary for oogenesis and embryonic pattern formation, the GLHs are distinguished by containing multiple CCHC zinc fingers. RNA-mediated interference (RNAi) reveals the GLHs are critical for oogenesis. By RNAi at 20 degrees C, when either loss of GLH-1 or GLH-4 alone has no effect, loss of both GLH-1 and GLH-4 results in 97% sterility in the glh-1/4(RNAi) offspring of injected hermaphrodites. glh-1/4(RNAi) germlines are under-proliferated and are without oocytes. glh-1/4(RNAi) animals produce sperm; however, spermatogenesis is delayed and the sperm are defective. P granules are still present in glh-1/4(RNAi) sterile worms as revealed with antibodies against the remaining GLH-2 and GLH-3 proteins, indicating the GLHs function independently in P granule assembly. These studies reveal that C.elegans can use GLH-1 or GLH-4 to promote germline development. PMID: [10851135] Back to Top |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figures for illustrating the function of this protein/gene |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function |
Probable ATP-binding RNA helicase. Back to Top |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Subcellular Location |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tissue Specificity |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Ontology |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interpro |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pfam |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SMART |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PROSITE |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PRINTS |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Created Date |
18-Oct-2012 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Record Type |
Experiment identified |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein sequence Annotation |
CHAIN 1 763 ATP-dependent RNA helicase glh-1. /FTId=PRO_0000055089. REPEAT 24 33 1. REPEAT 34 43 2. REPEAT 44 53 3. REPEAT 54 63 4. REPEAT 64 73 5. REPEAT 74 83 6. REPEAT 84 93 7. DOMAIN 372 556 Helicase ATP-binding. DOMAIN 592 739 Helicase C-terminal. ZN_FING 158 175 CCHC-type 1. ZN_FING 183 200 CCHC-type 2. ZN_FING 242 259 CCHC-type 3. ZN_FING 262 279 CCHC-type 4. NP_BIND 385 392 ATP (By similarity). REGION 24 93 7 X 10 AA tandem repeats, Gly-rich. MOTIF 341 369 Q motif. MOTIF 499 502 DEAD box. COMPBIAS 207 236 Gly-rich. CONFLICT 69 69 T -> A (in Ref. 3; AAB04136). CONFLICT 621 621 T -> I (in Ref. 1; AAC27384). Back to Top |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nucleotide Sequence |
Length: 2436 bp Go to nucleotide: FASTA |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Sequence |
Length: 763 bp Go to amino acid: FASTA |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The verified Protein-Protein interaction information |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other Protein-Protein interaction resources |
String database |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
View Microarray data |
Temporarily unavailable |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Comments |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||