| Tag | Content | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SG ID |
SG00000066 |
||||||||||||||||||
UniProt Accession |
|||||||||||||||||||
Theoretical PI |
6.14
|
||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Weight |
56035 Da
|
||||||||||||||||||
Genbank Nucleotide ID |
|||||||||||||||||||
Genbank Protein ID |
|||||||||||||||||||
Gene Name |
spe-5 |
||||||||||||||||||
Gene Synonyms/Alias |
atpB2, tag-300 |
||||||||||||||||||
Protein Name |
V-type ATP synthase beta chain 2 |
||||||||||||||||||
Protein Synonyms/Alias |
V-ATPase subunit B 2; |
||||||||||||||||||
Organism |
Caenorhabditis elegans |
||||||||||||||||||
NCBI Taxonomy ID |
6239 |
||||||||||||||||||
Chromosome Location |
|
||||||||||||||||||
Function in Stage |
|||||||||||||||||||
Function in Cell Type |
|||||||||||||||||||
Description |
Temporarily unavailable |
||||||||||||||||||
The information of related literatures |
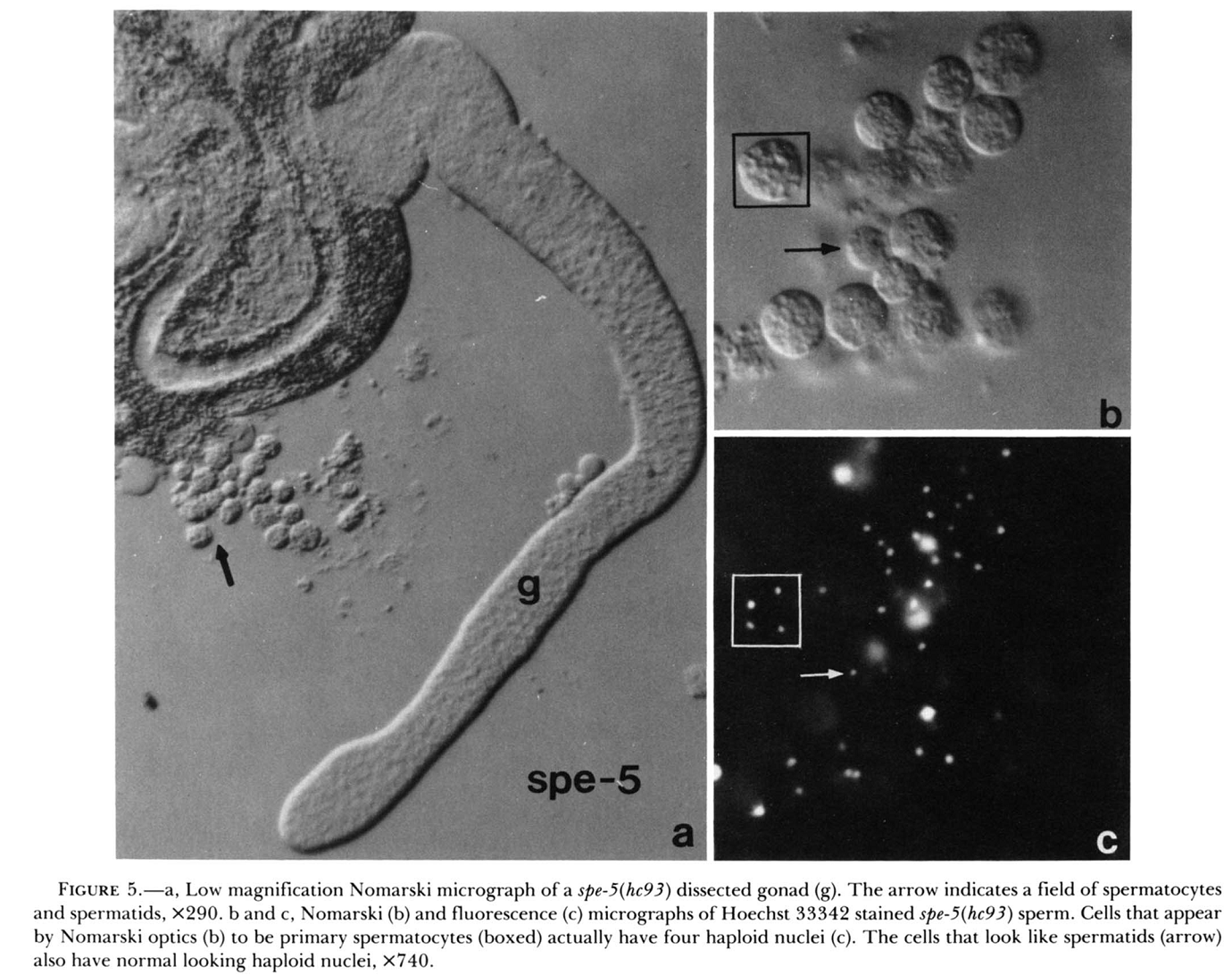
1. K. Machaca and S. W. L'Hernault (1997) The Caenorhabditis elegans spe-5 gene is required for morphogenesis of a sperm-specific organelle and is associated with an inherent cold-sensitive phenotype. Genetics 146(2): 567-81. Abstract The nonrandom segregation of organelles to the appropriate compartment during asymmetric cellular division is observed in many developing systems. Caenorhabditis elegans spermatogenesis is an excellent system to address this issue genetically. The proper progression of spermatogenesis requires specialized intracellular organelles, the fibrous body-membranous organelle complexes (FB-MOs). The FB-MOs play a critical role in cytoplasmic partitioning during the asymmetric cellular division associated with sperm meiosis II. Here we show that spe-5 mutants contain defective, vacuolated FB-MOs and usually arrest spermatogenesis at the spermatocyte stage. Occasionally, spe-5 mutants containing defective FB-MOs will form spermatids that are capable of differentiating into functional spermatozoa. These spe-5 spermatids exhibit an incomplete penetrance for tubulin mis-segregation during the second meiotic division. In addition to morphological and FB-MO segregation defects, all six spe-5 mutants are cold-sensitive, exhibiting a more penetrant sterile phenotype at 16 degrees than 25 degrees. This cold sensitivity could be an inherent property of FB-MO morphogenesis. PMID: [9178007] 2. S. W. L'Hernault, D. C. Shakes and S. Ward (1988) Developmental genetics of chromosome I spermatogenesis-defective mutants in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 120(2): 435-52. Abstract Mutations affecting Caenorhabditis elegans spermatogenesis can be used to dissect the processes of meiosis and spermatozoan morphological maturation. We have obtained 23 new chromosome I mutations that affect spermatogenesis (spe mutations). These mutations, together with six previously described mutations, identify 11 complementation groups, of which six are defined by multiple alleles. These spe mutations are all recessive and cause normally self-fertile hermaphrodites to produce unfertilized oocytes that can be fertilized by wild-type male sperm. Five chromosome I mutation/deficiency heterozygotes have similar phenotypes to the homozygote showing that the probable null phenotype of these genes is defective sperm. Spermatogenesis is disrupted at different steps by mutations in these genes. The maturation of 1 degree spermatocytes is disrupted by mutations in spe-4 and spe-5. Spermatids from spe-8 and spe-12 mutants develop into normal spermatozoa in males, but not in hermaphrodites. fer-6 spermatids are abnormal, and fer-1 spermatids look normal but subsequently become abnormal spermatozoa. Mutations in five genes (fer-7, spe-9, spe-11, spe-13 and spe-15) allow formation of normal looking motile spermatozoa that appear to be defective in either sperm-spermathecal or sperm-oocyte interactions. PMID: [3197956] Back to Top |
||||||||||||||||||
Figures for illustrating the function of this protein/gene |
|
||||||||||||||||||
Function |
|||||||||||||||||||
Subcellular Location |
|||||||||||||||||||
Tissue Specificity |
|||||||||||||||||||
Gene Ontology |
|
||||||||||||||||||
Interpro |
|||||||||||||||||||
Pfam |
|||||||||||||||||||
SMART |
|||||||||||||||||||
PROSITE |
|||||||||||||||||||
PRINTS |
|||||||||||||||||||
Created Date |
18-Oct-2012 |
||||||||||||||||||
Record Type |
Experiment identified |
||||||||||||||||||
Protein sequence Annotation |
|||||||||||||||||||
Nucleotide Sequence |
Length: bp Go to nucleotide: FASTA |
||||||||||||||||||
Protein Sequence |
Length: 501 bp Go to amino acid: FASTA |
||||||||||||||||||
The verified Protein-Protein interaction information |
|||||||||||||||||||
Other Protein-Protein interaction resources |
String database |
||||||||||||||||||
View Microarray data |
Temporarily unavailable |
||||||||||||||||||
Comments |
|||||||||||||||||||