| Tag | Content | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SG ID |
SG00000077 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
UniProt Accession |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Theoretical PI |
-
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Weight |
Da
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Genbank Nucleotide ID |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Genbank Protein ID |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Name |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Synonyms/Alias |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Name |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Synonyms/Alias |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Organism |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
NCBI Taxonomy ID |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Chromosome Location |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Function in Stage |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Function in Cell Type |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Description |
Temporarily unavailable |
||||||||||||||||||||||
The information of related literatures |
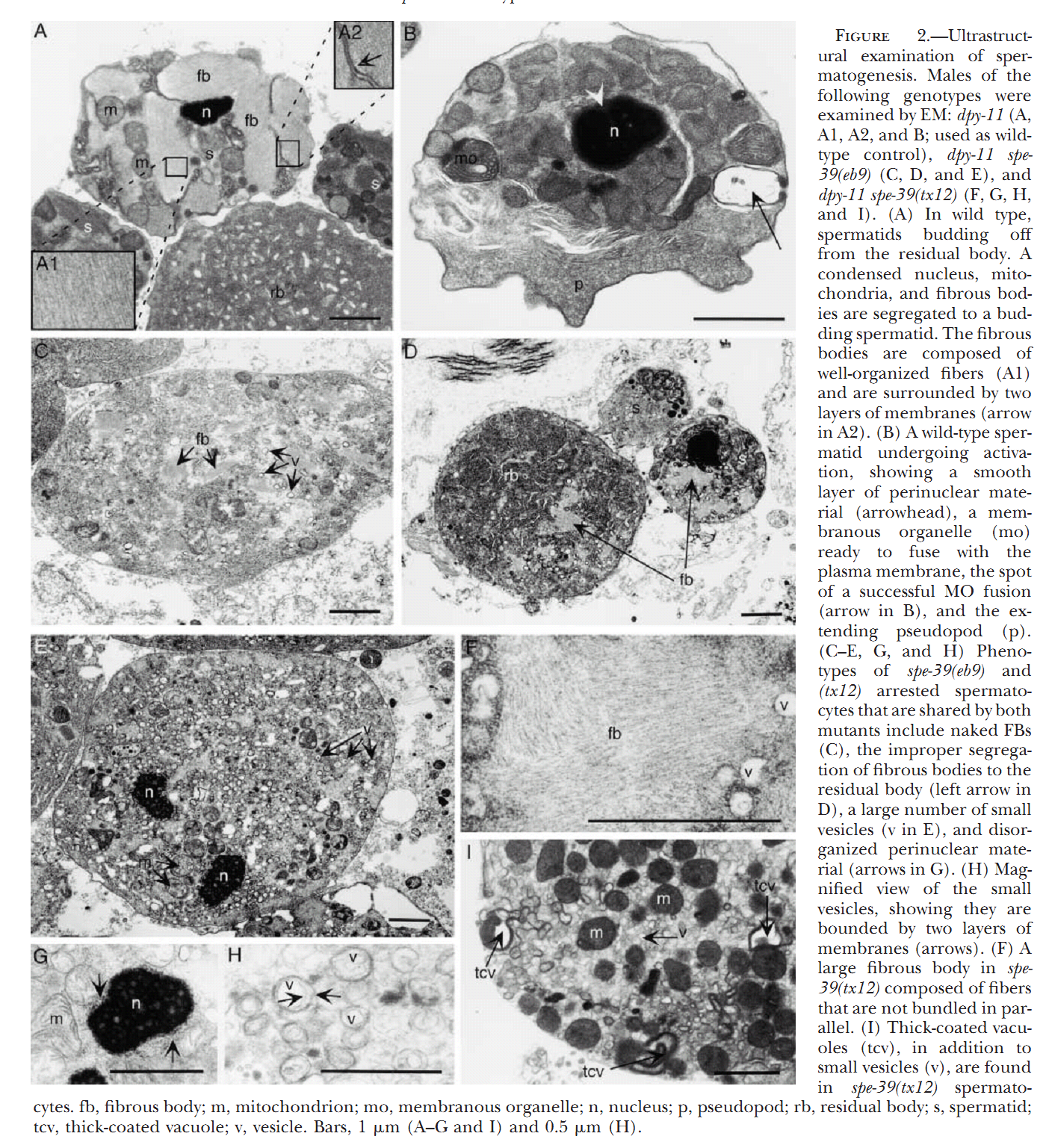
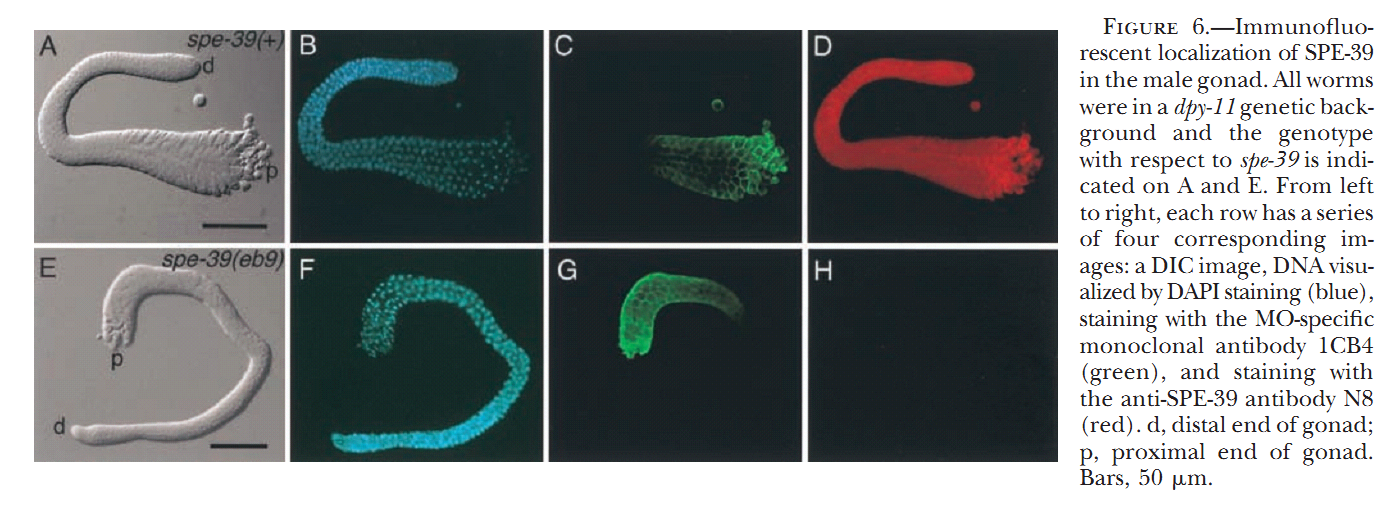
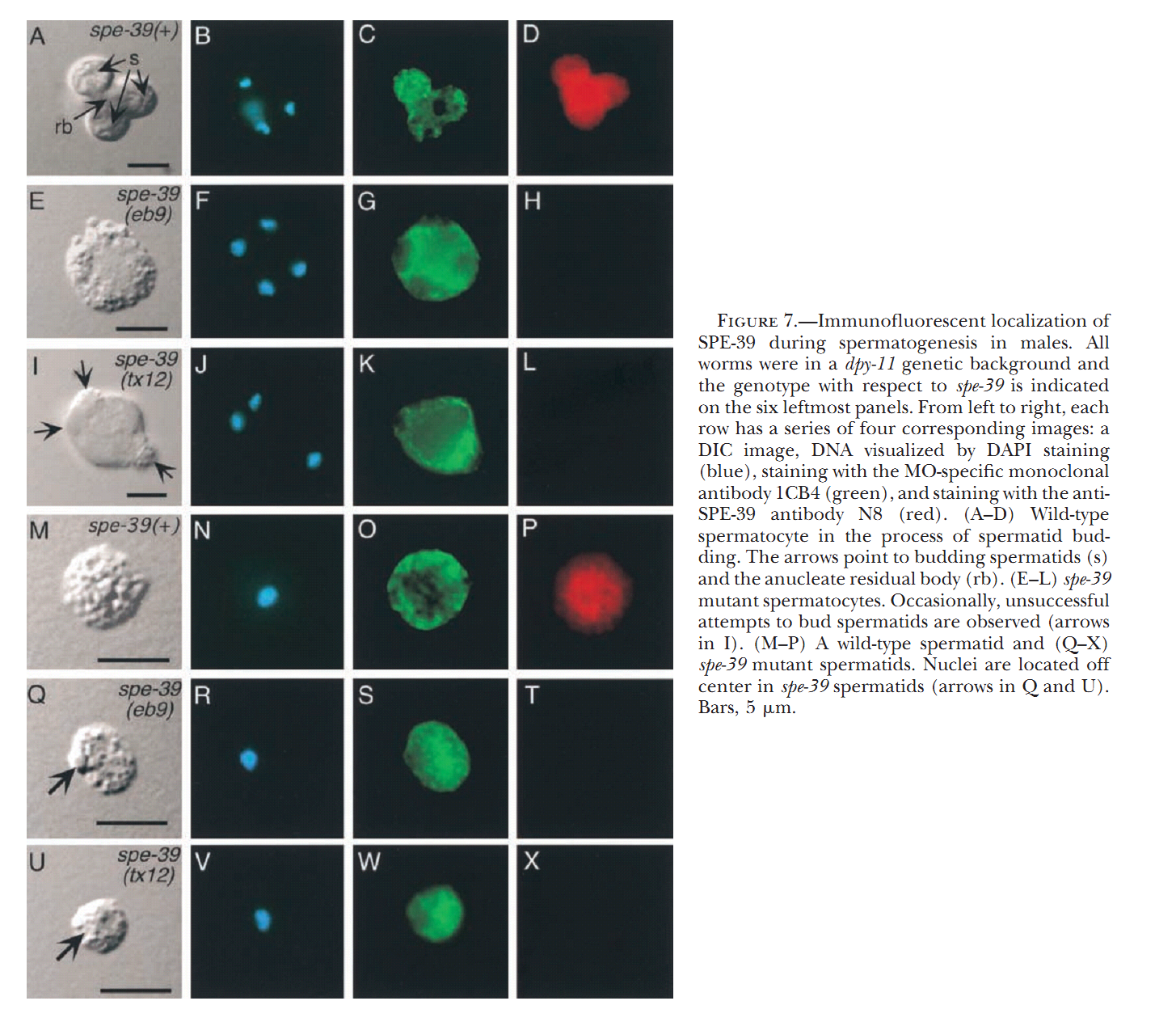
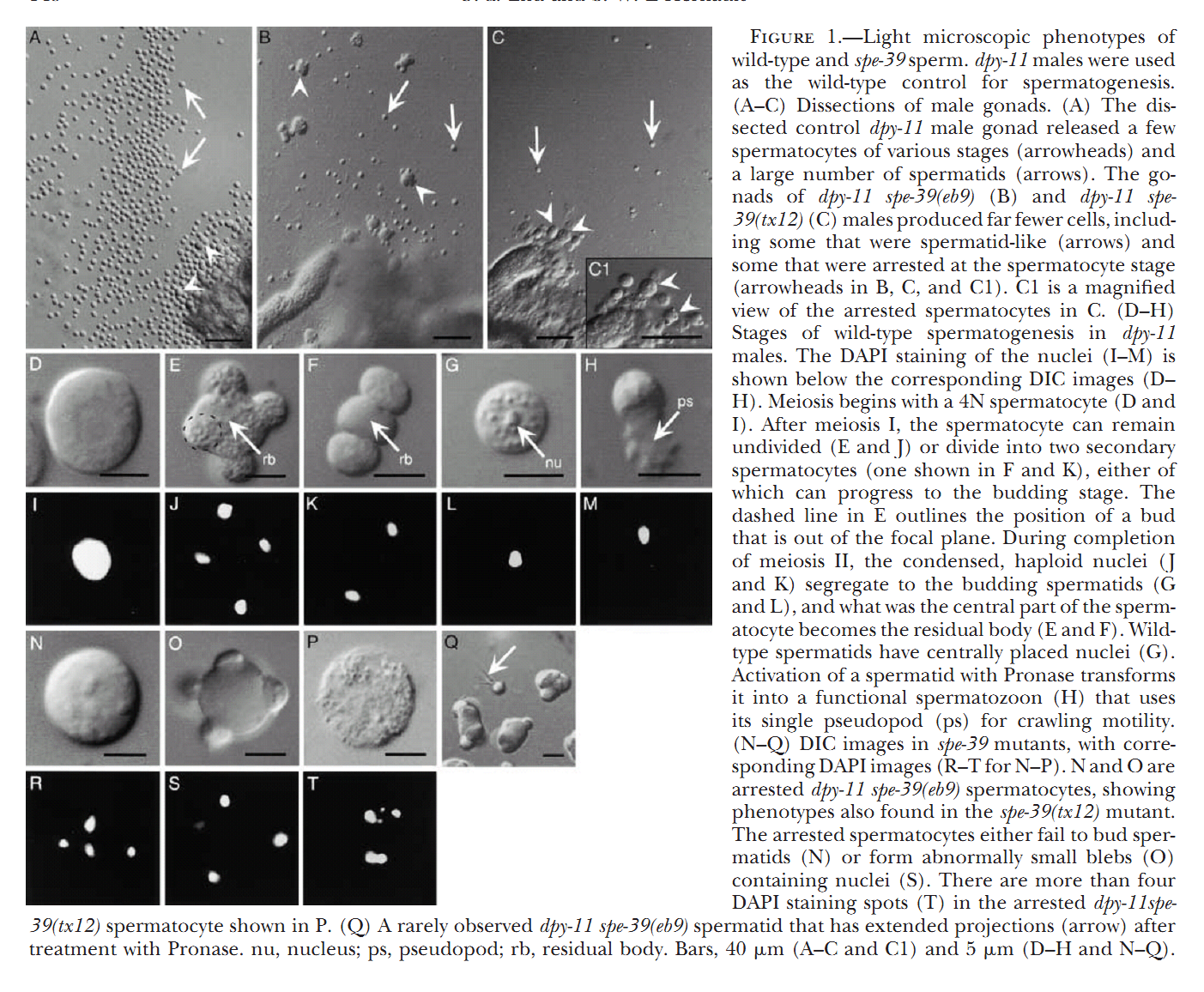
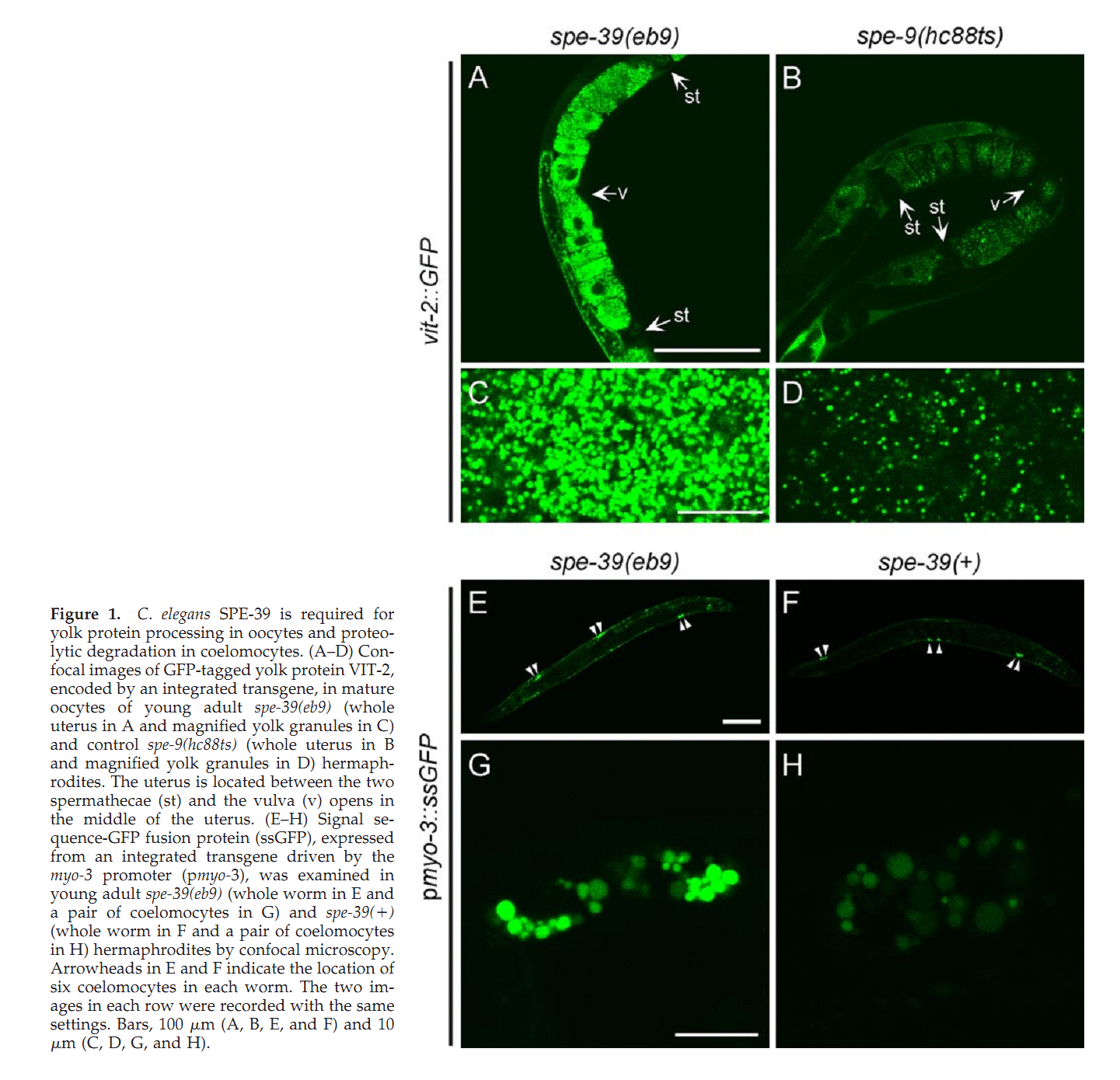
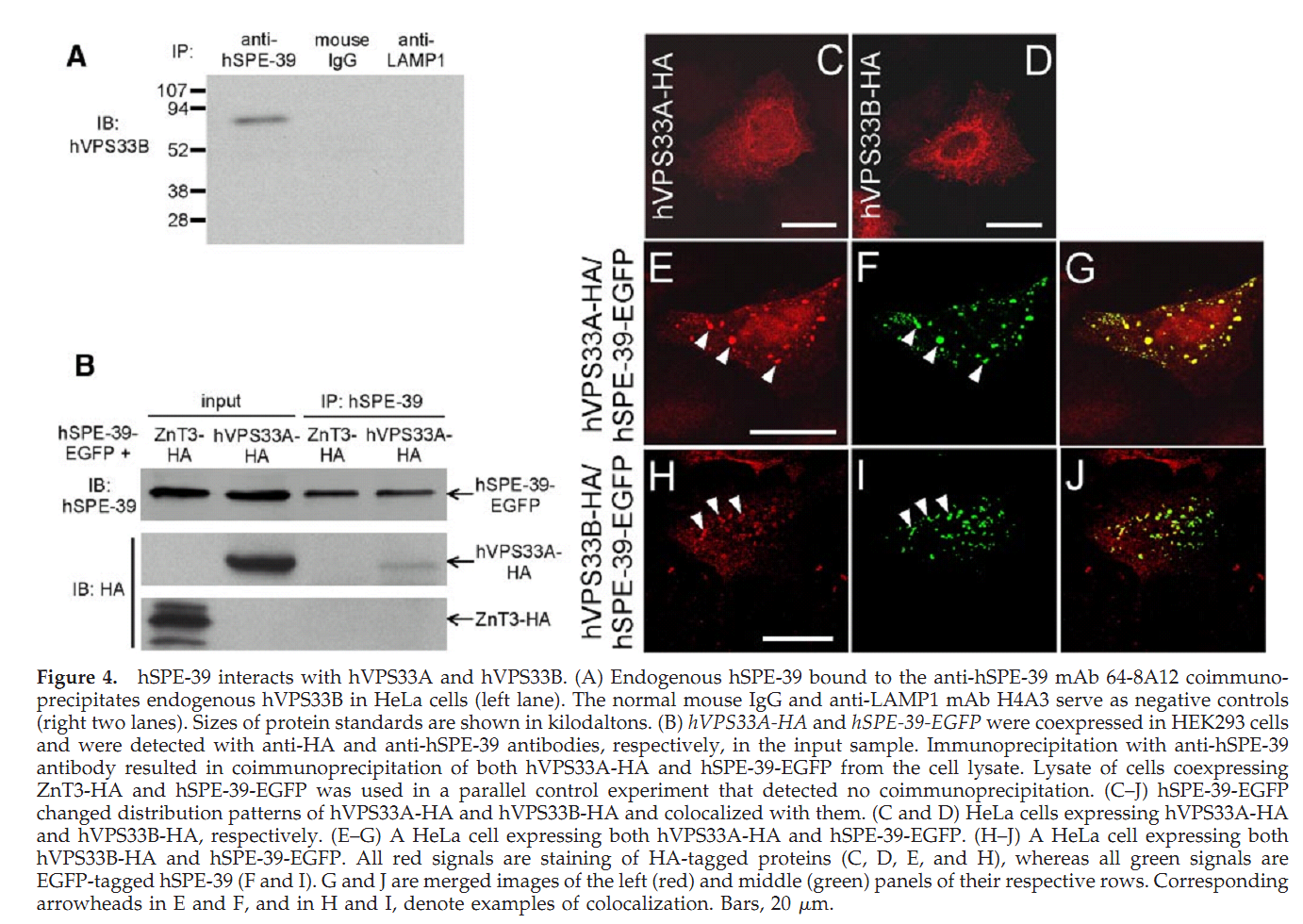
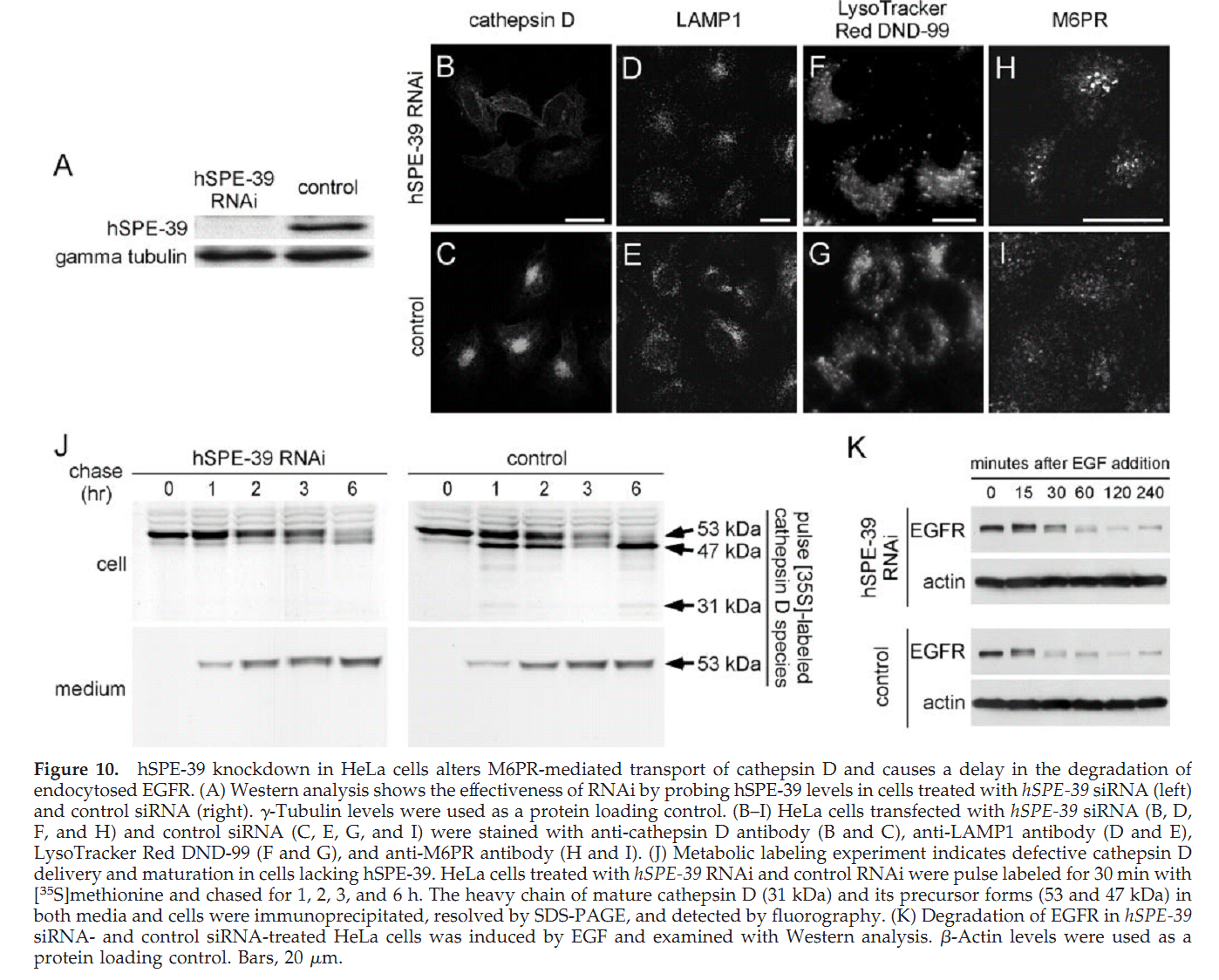
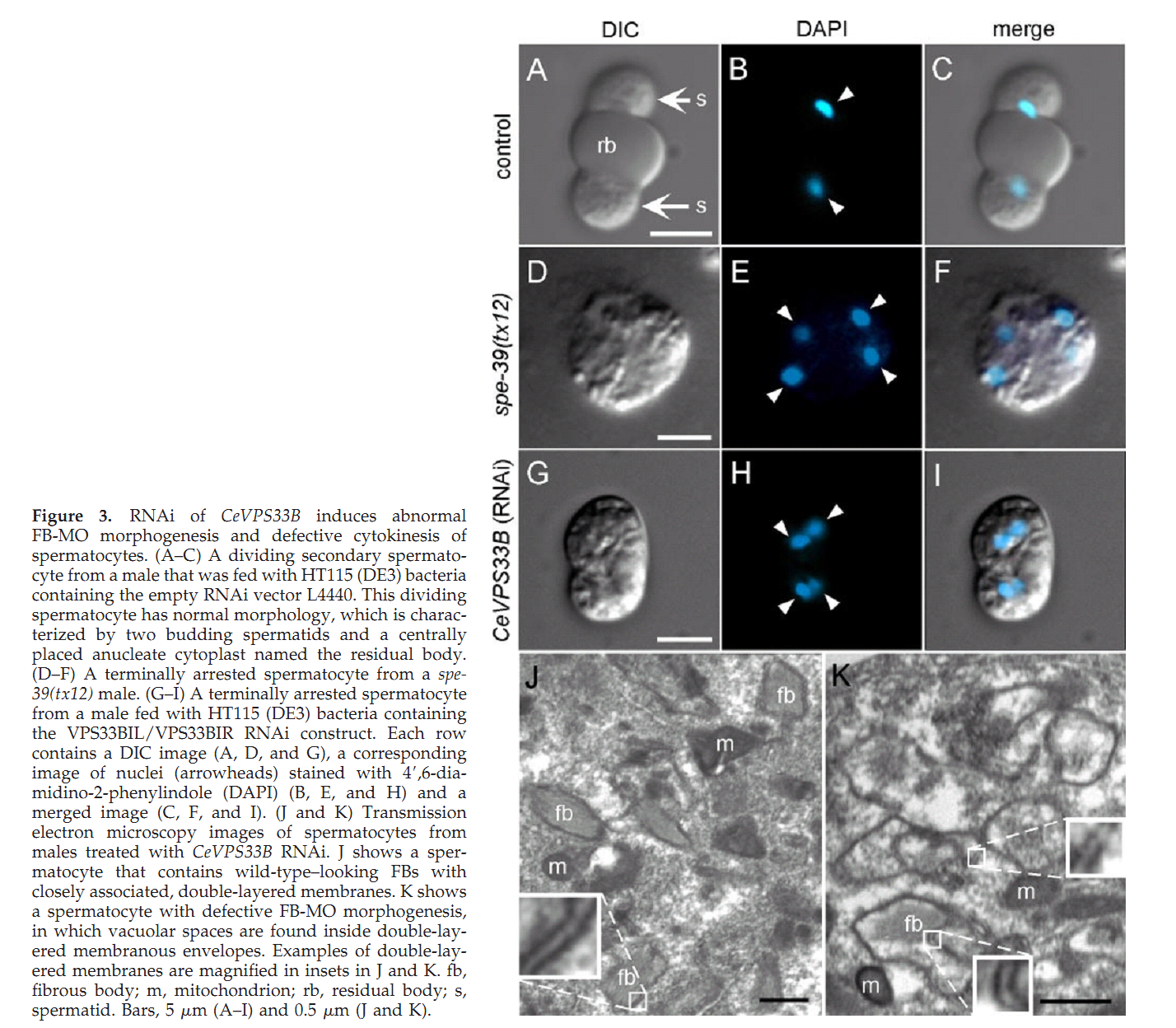
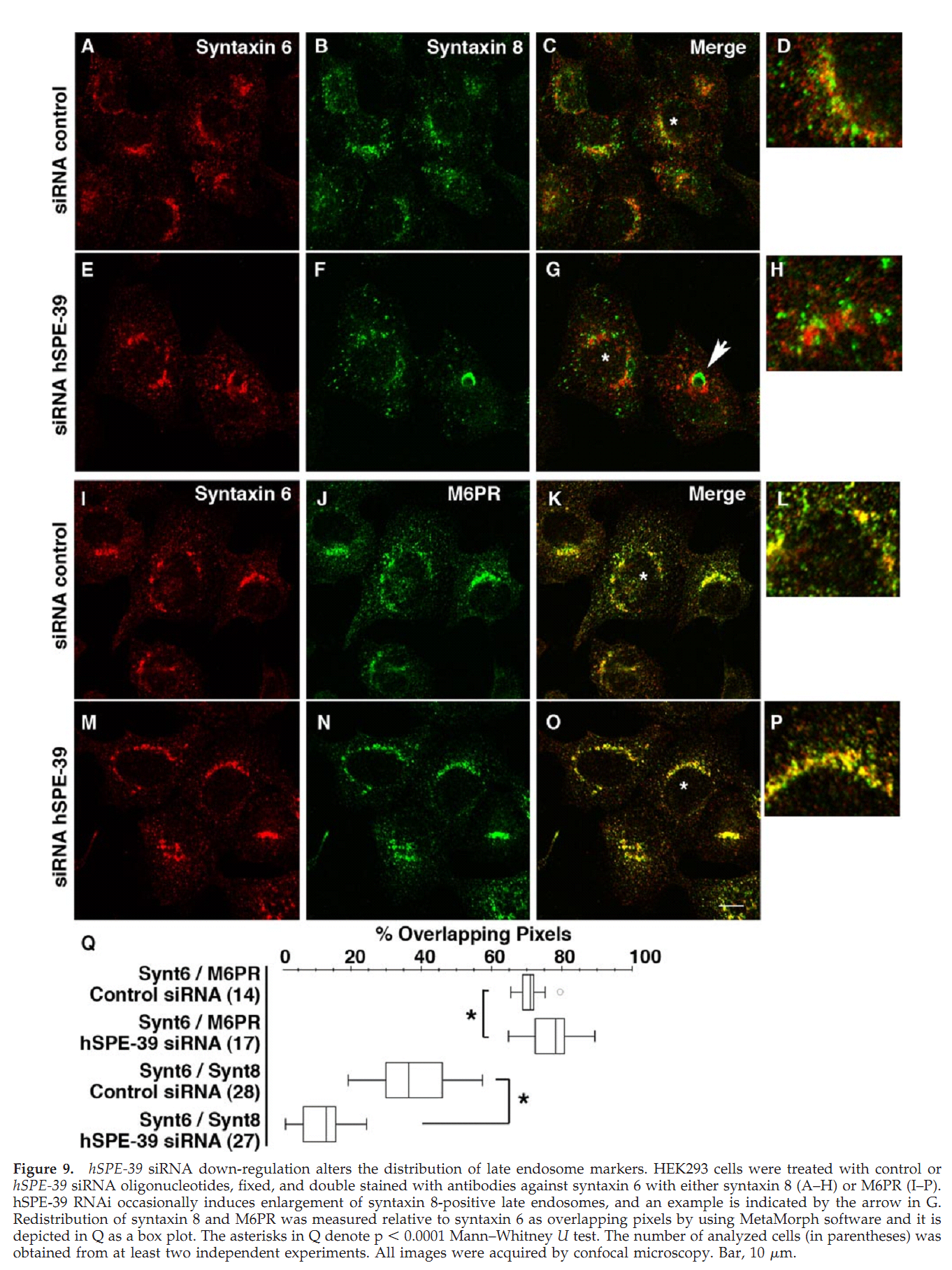
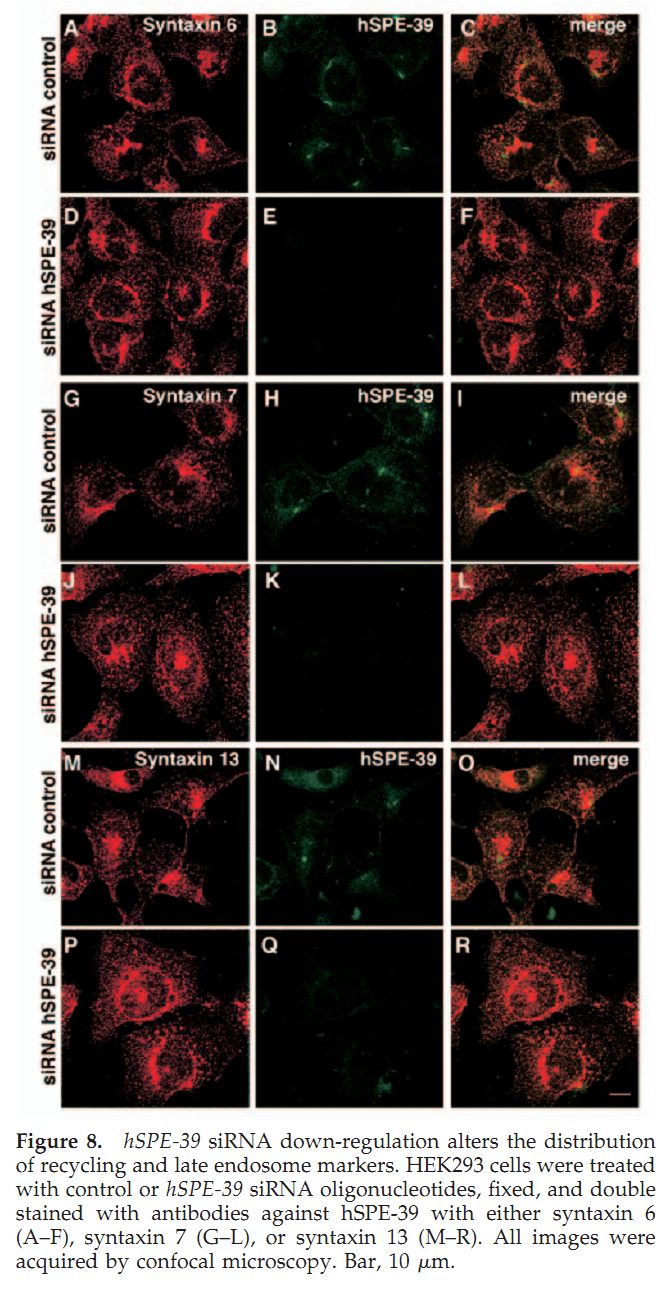
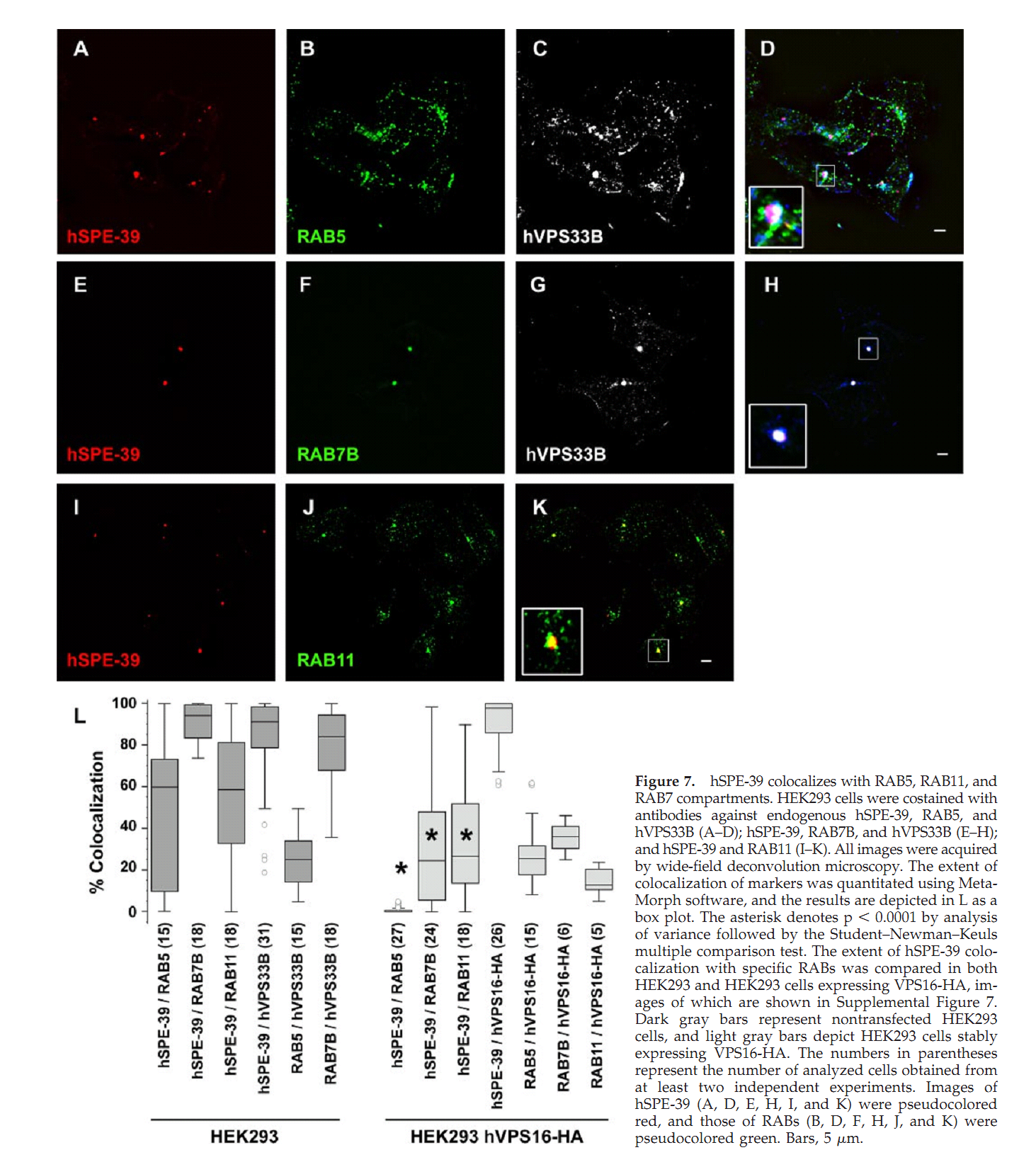
1. G. D. Zhu and S. W. L'Hernault (2003) The Caenorhabditis elegans spe-39 gene is required for intracellular membrane reorganization during spermatogenesis. Genetics 165(1): 145-57. Abstract Caenorhabditis elegans spermatid formation involves asymmetric partitioning of cytoplasm during the second meiotic division. This process is mediated by specialized ER/Golgi-derived fibrous body-membranous organelles (FB-MOs), which have a fibrous body (FB) composed of bundled major sperm protein filaments and a vesicular membranous organelle (MO). spe-39 mutant spermatocytes complete meiosis but do not usually form spermatids. Ultrastructural examination of spe-39 spermatocytes reveals that MOs are absent, while FBs are disorganized and not surrounded by the membrane envelope usually observed in wild type. Instead, spe-39 spermatocytes contain many small vesicles with internal membranes, suggesting they are related to MOs. The spe-39 gene was identified and it encodes a novel hydrophilic protein. Immunofluorescence with a specific SPE-39 antiserum reveals that it is distributed through much of the cytoplasm and not specifically associated with FB-MOs in spermatocytes and spermatids. The spe-39 gene has orthologs in Drosophila melanogaster and humans but no homolog was identified in the yeast genome. This suggests that the specialized membrane biogenesis steps that occur during C. elegans spermatogenesis are part of a conserved process that requires SPE-39 homologs in other metazoan cell types. PMID: [14504223] 2. G. D. Zhu, G. Salazar, S. A. Zlatic, B. Fiza, M. M. Doucette, C. J. Heilman, A. I. Levey, V. Faundez and W. L'Hernault S (2009) SPE-39 family proteins interact with the HOPS complex and function in lysosomal delivery. Mol Biol Cell 20(4): 1223-40. Abstract Yeast and animal homotypic fusion and vacuole protein sorting (HOPS) complexes contain conserved subunits, but HOPS-mediated traffic in animals might require additional proteins. Here, we demonstrate that SPE-39 homologues, which are found only in animals, are present in RAB5-, RAB7-, and RAB11-positive endosomes where they play a conserved role in lysosomal delivery and probably function via their interaction with the core HOPS complex. Although Caenorhabditis elegans spe-39 mutants were initially identified as having abnormal vesicular biogenesis during spermatogenesis, we show that these mutants also have disrupted processing of endocytosed proteins in oocytes and coelomocytes. C. elegans SPE-39 interacts in vitro with both VPS33A and VPS33B, whereas RNA interference of VPS33B causes spe-39-like spermatogenesis defects. The human SPE-39 orthologue C14orf133 also interacts with VPS33 homologues and both coimmunoprecipitates and cosediments with other HOPS subunits. SPE-39 knockdown in cultured human cells altered the morphology of syntaxin 7-, syntaxin 8-, and syntaxin 13-positive endosomes. These effects occurred concomitantly with delayed mannose 6-phosphate receptor-mediated cathepsin D delivery and degradation of internalized epidermal growth factor receptors. Our findings establish that SPE-39 proteins are a previously unrecognized regulator of lysosomal delivery and that C. elegans spermatogenesis is an experimental system useful for identifying conserved regulators of metazoan lysosomal biogenesis. PMID: [19109425] Back to Top |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Figures for illustrating the function of this protein/gene |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Function |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Subcellular Location |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Tissue Specificity |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Ontology |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Interpro |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Pfam |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
SMART |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
PROSITE |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
PRINTS |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Created Date |
18-Oct-2012 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Record Type |
Experiment identified |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein sequence Annotation |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Nucleotide Sequence |
Length: bp Go to nucleotide: FASTA |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Sequence |
Length: bp Go to amino acid: FASTA |
||||||||||||||||||||||
The verified Protein-Protein interaction information |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
Other Protein-Protein interaction resources |
String database |
||||||||||||||||||||||
View Microarray data |
Temporarily unavailable |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Comments |
|||||||||||||||||||||||