| Tag | Content | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SG ID |
SG00000193 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
UniProt Accession |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Theoretical PI |
8.83
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Weight |
143299 Da
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Genbank Nucleotide ID |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Genbank Protein ID |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Name |
jar |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Synonyms/Alias |
Mhc95F |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Name |
Myosin heavy chain 95F |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Synonyms/Alias |
95F MHC; Protein jaguar; |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Organism |
Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NCBI Taxonomy ID |
7227 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Chromosome Location |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function in Stage |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function in Cell Type |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Description |
Temporarily unavailable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The information of related literatures |
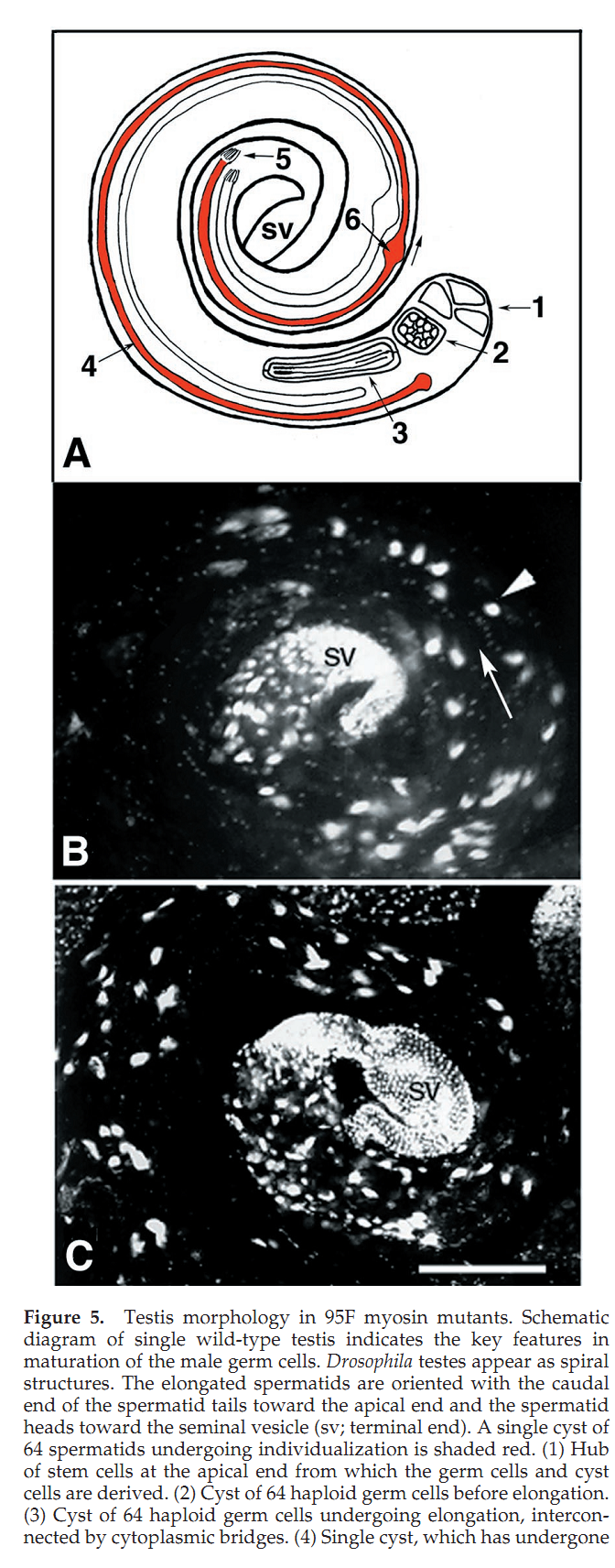
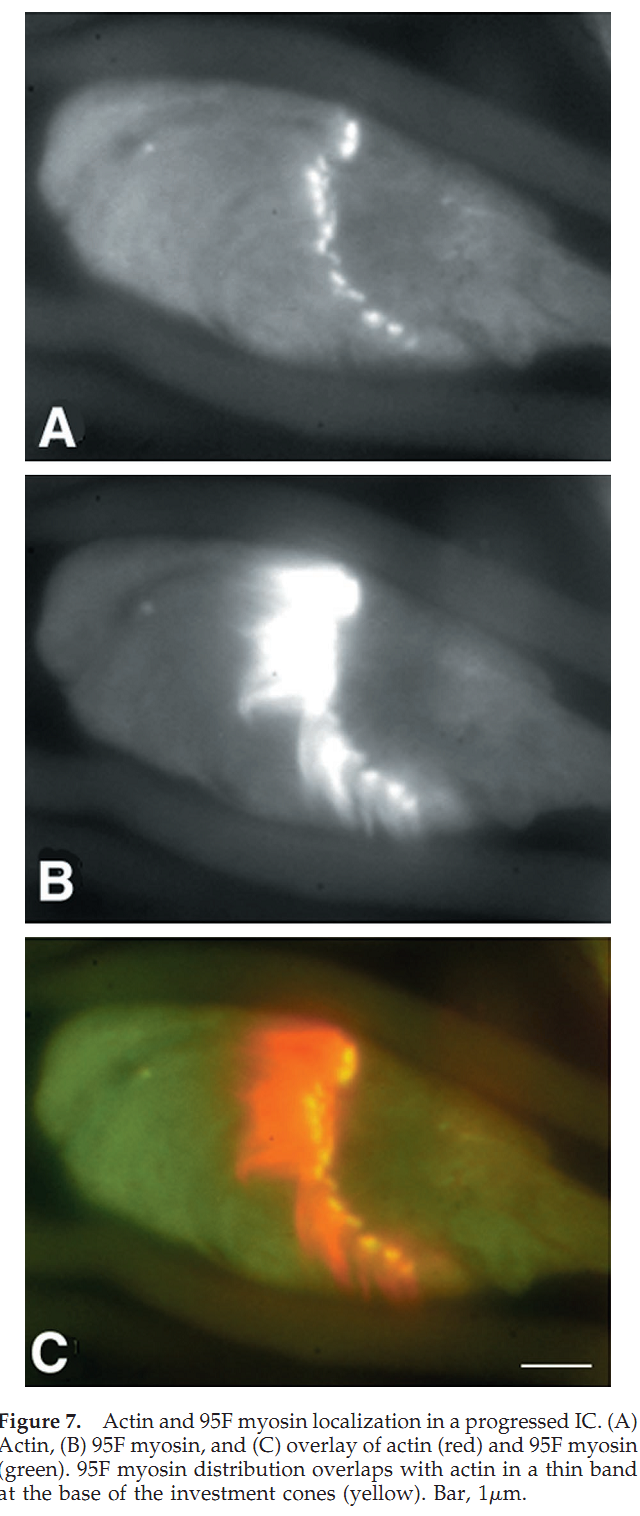
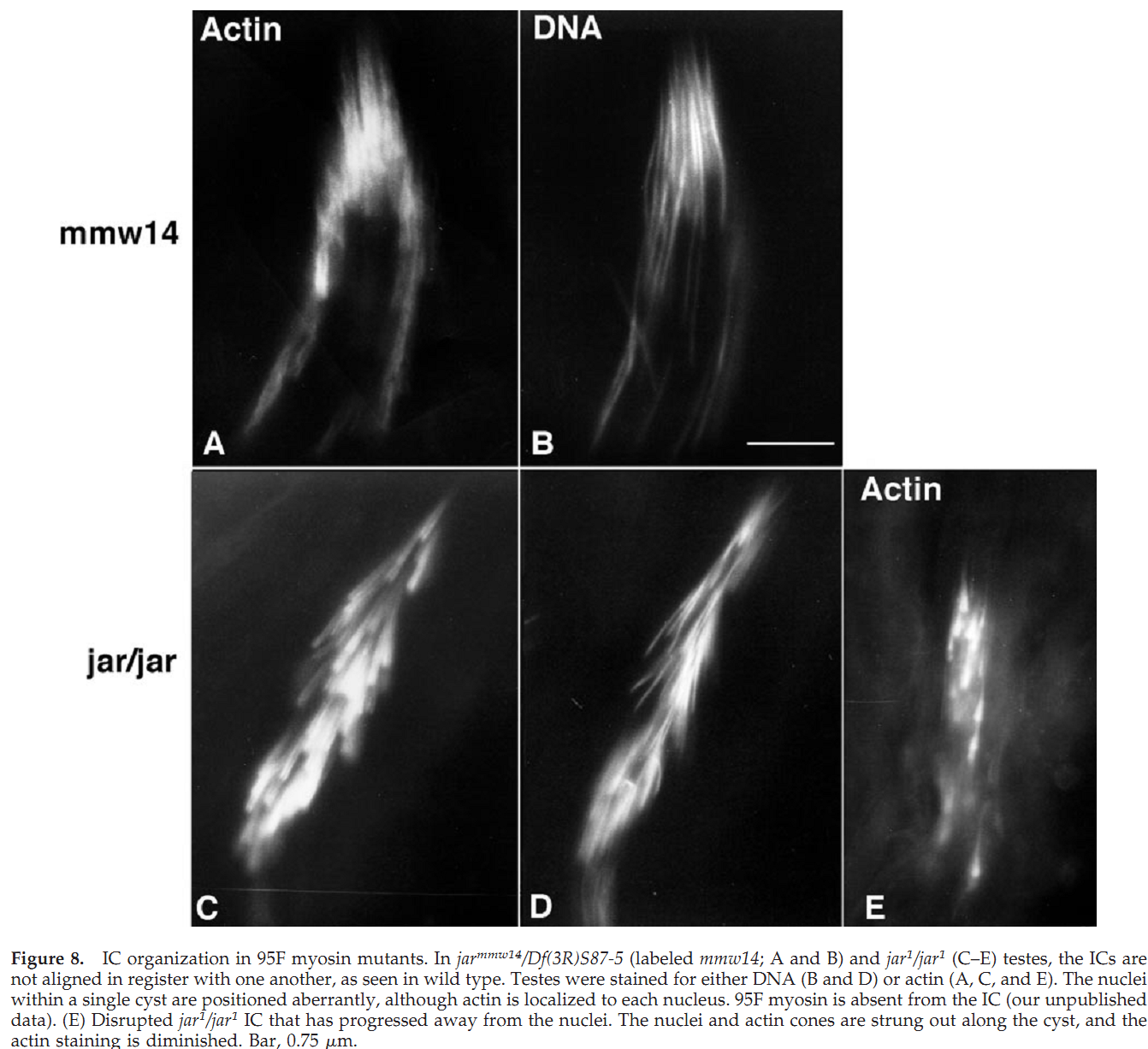
1. J. L. Hicks, W. M. Deng, A. D. Rogat, K. G. Miller and M. Bownes (1999) Class VI unconventional myosin is required for spermatogenesis in Drosophila. Mol Biol Cell 10(12): 4341-53. Abstract We have identified partial loss of function mutations in class VI unconventional myosin, 95F myosin, which results in male sterility. During spermatogenesis the germ line precursor cells undergo mitosis and meiosis to form a bundle of 64 spermatids. The spermatids remain interconnected by cytoplasmic bridges until individualization. The process of individualization involves the formation of a complex of cytoskeletal proteins and membrane, the individualization complex (IC), around the spermatid nuclei. This complex traverses the length of each spermatid resolving the shared membrane into a single membrane enclosing each spermatid. We have determined that 95F myosin is a component of the IC whose function is essential for individualization. In wild-type testes, 95F myosin localizes to the leading edge of the IC. Two independent mutations in 95F myosin reduce the amount of 95F myosin in only a subset of tissues, including the testes. This reduction of 95F myosin causes male sterility as a result of defects in spermatid individualization. Germ line transformation with the 95F myosin heavy chain cDNA rescues the male sterility phenotype. IC movement is aberrant in these 95F myosin mutants, indicating a critical role for 95F myosin in IC movement. This report is the first identification of a component of the IC other than actin. We propose that 95F myosin is a motor that participates in membrane reorganization during individualization. PMID: [10588662] Back to Top |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figures for illustrating the function of this protein/gene |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function |
Myosin is a protein that binds to actin and has ATPaseactivity that is activated by actin. Together CLIP-190 and jar maycoordinate the interaction between the actin and microtubulecytoskeleton. May link endocytic vesicles to microtubules and maybe involved in transport in the early embryo and in the dynamicprocess of dorsal closure. It is believed that its functionchanges during the life cycle. Back to Top |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Subcellular Location |
Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Note=Microtubule-associated. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tissue Specificity |
Isoform B is present at a higher level in thehead and gonads than in the thoraxes. Isoform 145 kDa is foundonly in the head. CLIP-190 and jar are coexpressed at severaltimes in development and in a number of tissues, includingembryonic axonal neuron processes and posterior pole. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Ontology |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interpro |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pfam |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SMART |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PROSITE |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PRINTS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Created Date |
18-Oct-2012 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Record Type |
Experiment identified |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein sequence Annotation |
CHAIN 1 1253 Myosin heavy chain 95F. /FTId=PRO_0000123389. DOMAIN 1 807 Myosin head-like. DOMAIN 808 837 IQ. NP_BIND 151 158 ATP. REGION 647 666 Actin-binding. REGION 1187 1193 Hydrophobic region. COILED 900 1022 Potential. VAR_SEQ 1047 1047 R -> SFSQVVSNIASRYLNK (in isoform H). /FTId=VSP_003343. VAR_SEQ 1048 1073 SENVRAQQQALGKQKYDLSKWKYSEL -> YSTLYELPMST TLVNFVNLFLLSQKH (in isoform I). /FTId=VSP_003344. VAR_SEQ 1074 1253 Missing (in isoform I). /FTId=VSP_003345. CONFLICT 220 220 V -> M (in Ref. 1; CAA47462). CONFLICT 1051 1051 V -> L (in Ref. 1; CAA47462). CONFLICT 1121 1121 R -> P (in Ref. 1; CAA47462). Back to Top |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nucleotide Sequence |
Length: 4280 bp Go to nucleotide: FASTA |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Sequence |
Length: 1253 bp Go to amino acid: FASTA |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The verified Protein-Protein interaction information |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other Protein-Protein interaction resources |
String database |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
View Microarray data |
Temporarily unavailable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Comments |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||