| Tag | Content | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SG ID |
SG00000244 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
UniProt Accession |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Theoretical PI |
6.24
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Weight |
84954 Da
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Genbank Nucleotide ID |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Genbank Protein ID |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Name |
fws |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Synonyms/Alias |
ORFNames=CG6549 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Name |
Conserved oligomeric Golgi complex subunit 5 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Synonyms/Alias |
COG complex subunit 5 Component of oligomeric Golgi complex 5; Protein four way stop; |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Organism |
Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NCBI Taxonomy ID |
7227 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Chromosome Location |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function in Stage |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function in Cell Type |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Description |
Temporarily unavailable |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The information of related literatures |
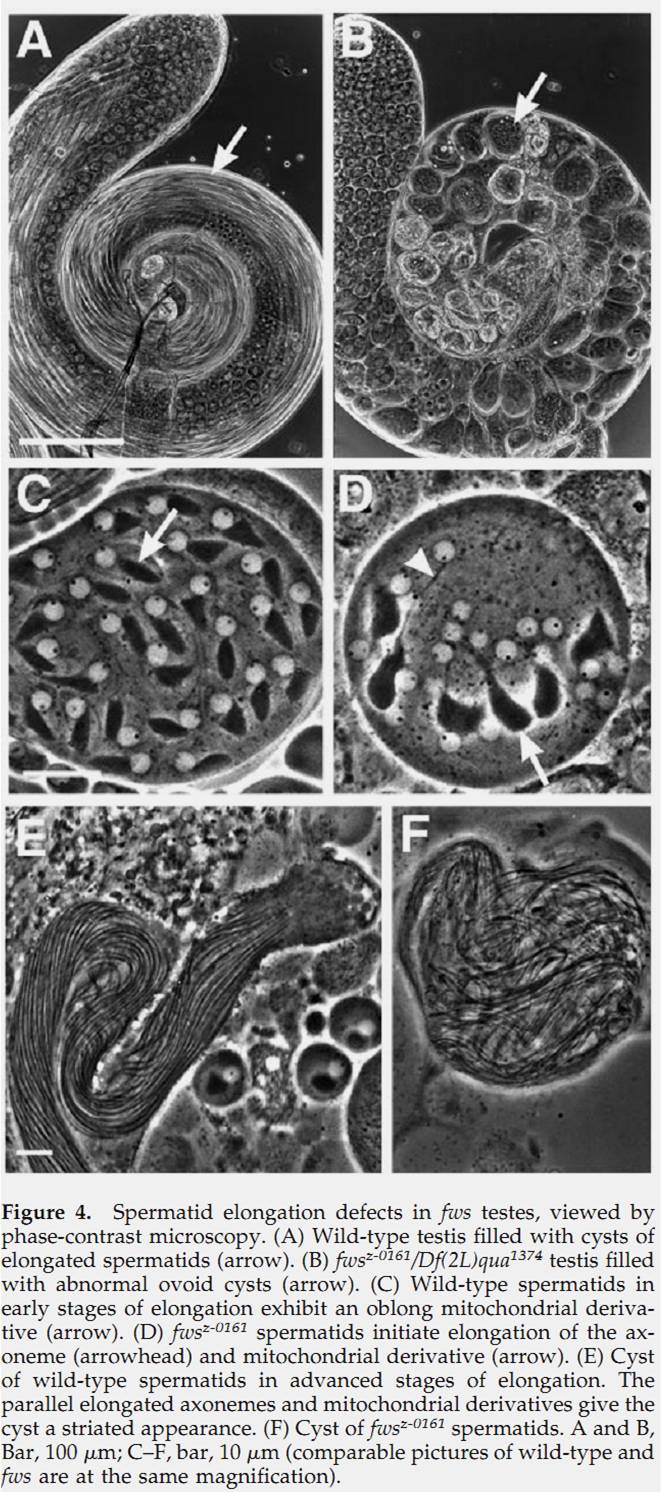
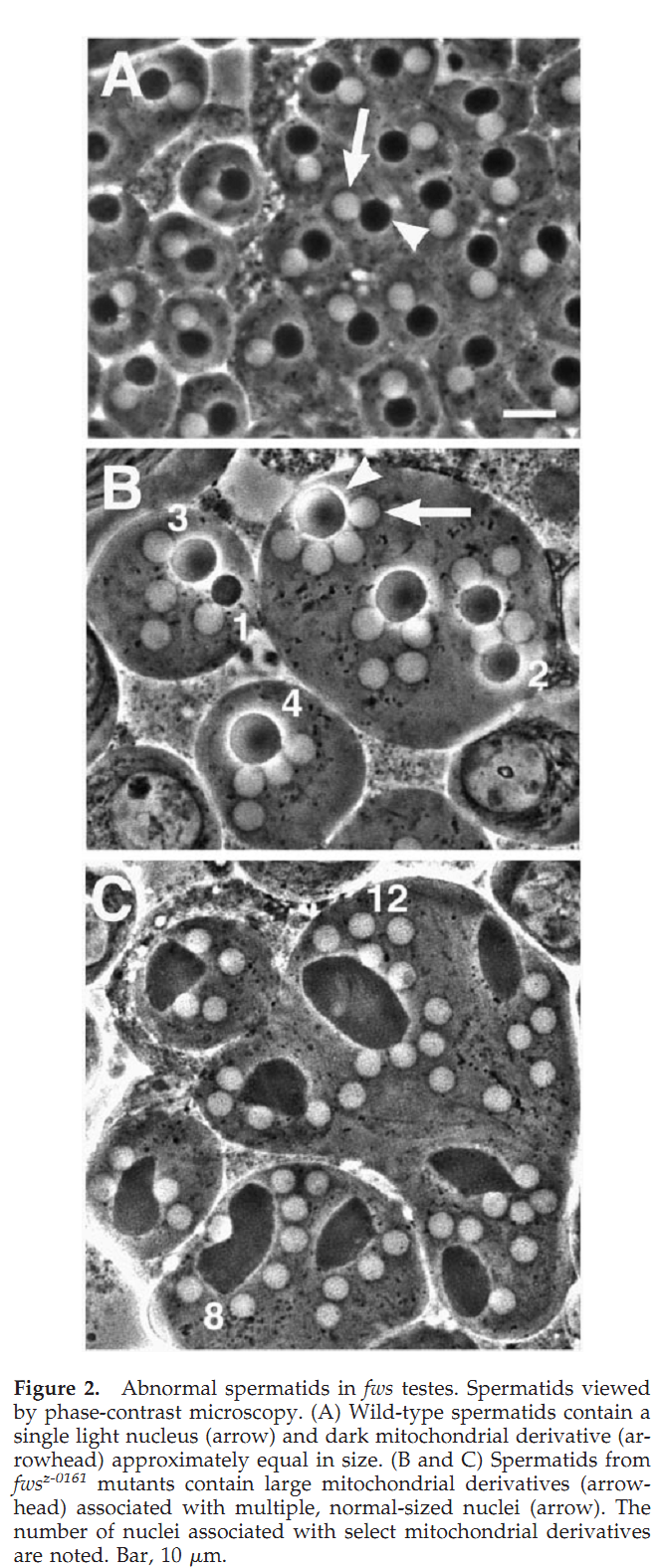
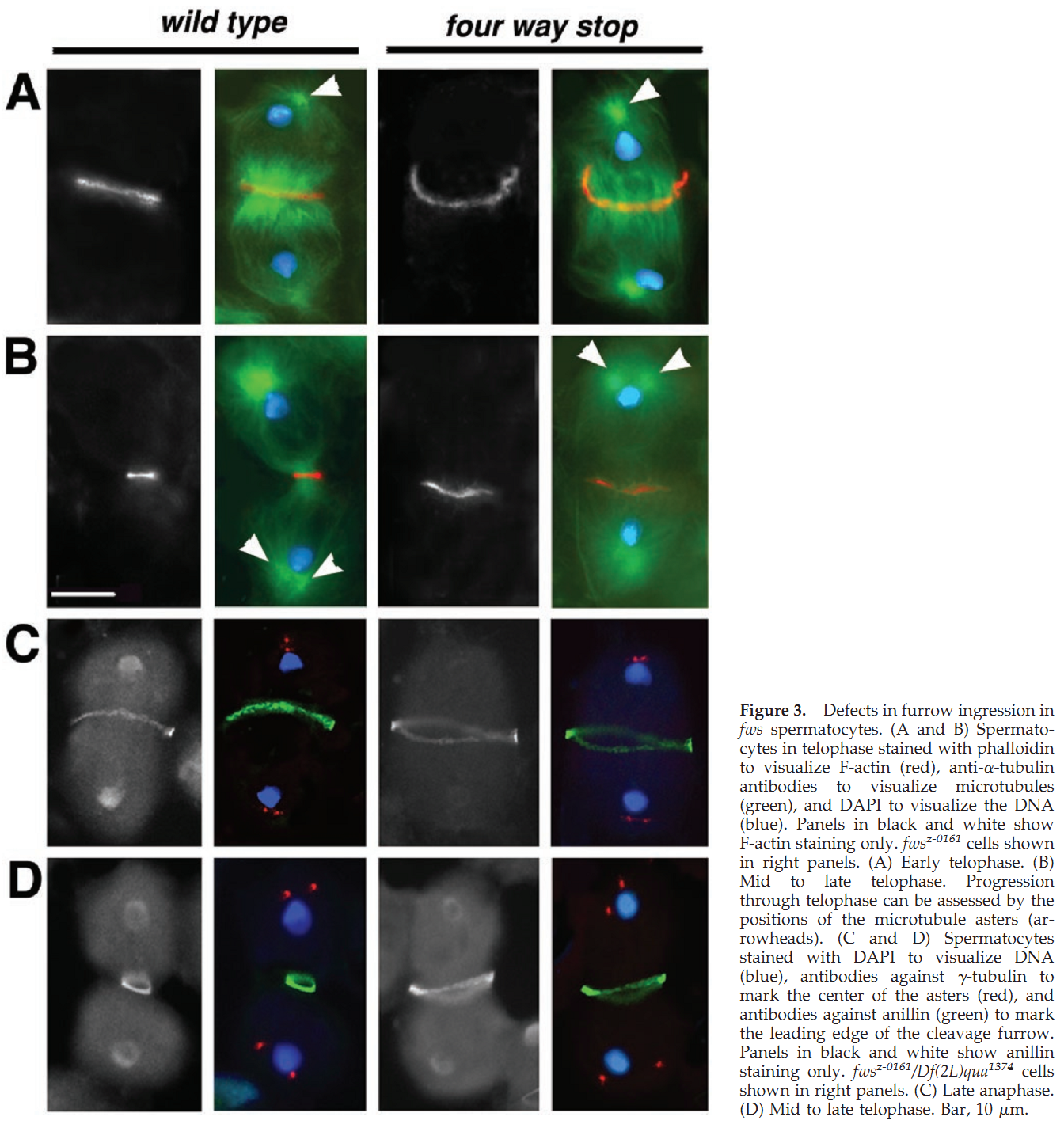
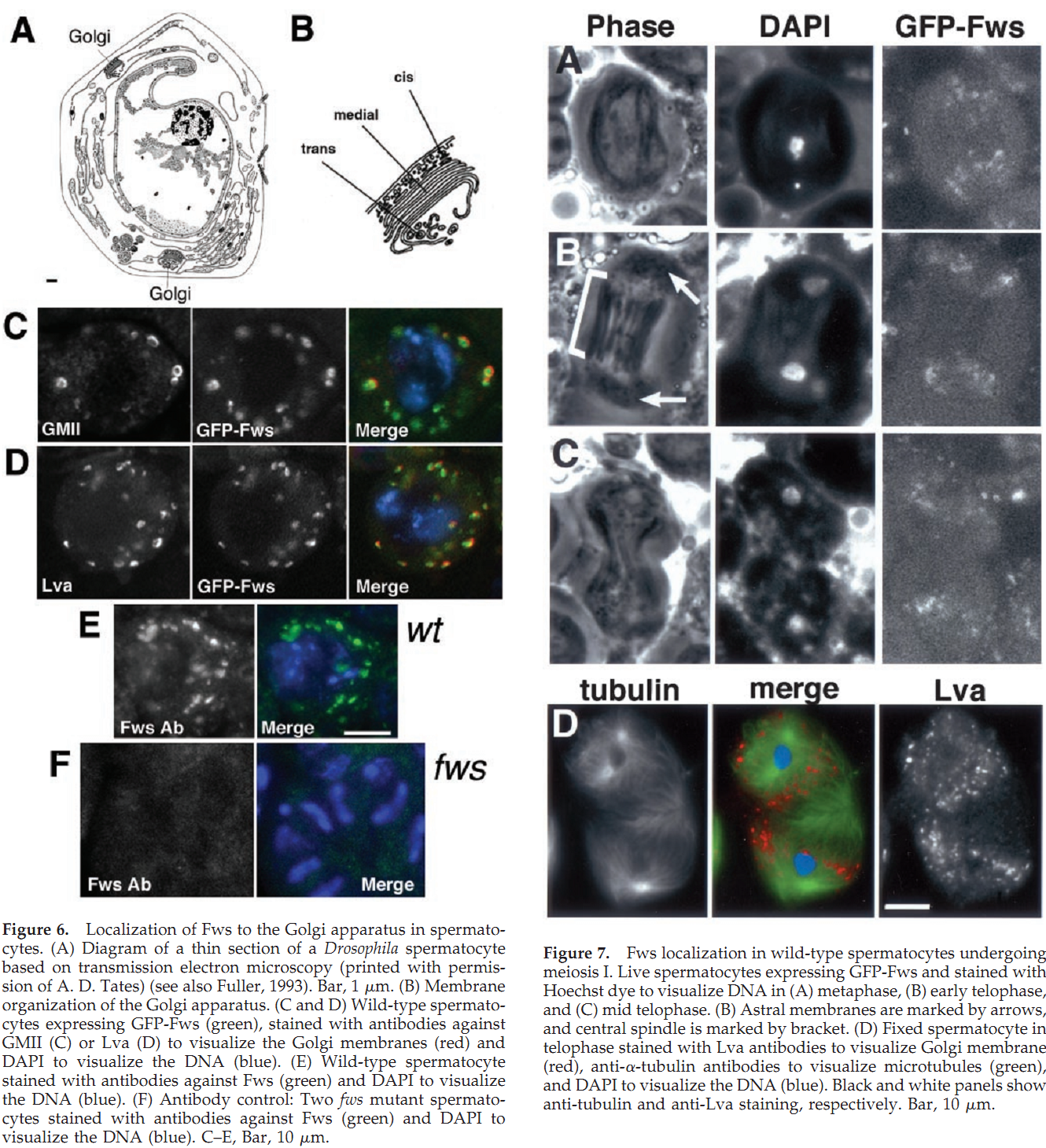
1. R. M. Farkas, M. G. Giansanti, M. Gatti and M. T. Fuller (2003) The Drosophila Cog5 homologue is required for cytokinesis, cell elongation, and assembly of specialized Golgi architecture during spermatogenesis. Mol Biol Cell 14(1): 190-200. Abstract The multisubunit conserved oligomeric Golgi (COG) complex has been shown previously to be involved in Golgi function in yeast and mammalian tissue culture cells. Despite this broad conservation, several subunits, including Cog5, were not essential for growth and showed only mild effects on secretion when mutated in yeast, raising questions about what functions these COG complex subunits play in the life of the cell. Here, we show that function of the gene four way stop (fws), which encodes the Drosophila Cog5 homologue, is necessary for dramatic changes in cellular and subcellular morphology during spermatogenesis. Loss-of-function mutations in fws caused failure of cleavage furrow ingression in dividing spermatocytes and failure of cell elongation in differentiating spermatids and disrupted the formation and/or stability of the Golgi-based spermatid acroblast. Consistent with the lack of a growth defect in yeast lacking Cog5, animals lacking fws function were viable, although males were sterile. Fws protein localized to Golgi structures throughout spermatogenesis. We propose that Fws may directly or indirectly facilitate efficient vesicle traffic through the Golgi to support rapid and extensive increases in cell surface area during spermatocyte cytokinesis and polarized elongation of differentiating spermatids. Our study suggests that Drosophila spermatogenesis can be an effective sensitized genetic system to uncover in vivo functions for proteins involved in Golgi architecture and/or vesicle transport. PMID: [12529436] Back to Top |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figures for illustrating the function of this protein/gene |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function |
Required for normal Golgi function and necessary duringspermatogenesis. Required for cleavage furrow ingression duringcytokinesis in dividing spermatocytes and for the extensivepolarized cell growth that accompanies spermatid elongation. Back to Top |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Subcellular Location |
Golgi apparatus membrane; Peripheralmembrane protein. Note=Localized to Golgi membrane throughoutspermatogenesis, as seen in spermatocytes and differentiatingspermatids. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tissue Specificity |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Ontology |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interpro |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pfam |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SMART |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PROSITE |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PRINTS |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Created Date |
18-Oct-2012 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Record Type |
Experiment identified |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein sequence Annotation |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nucleotide Sequence |
Length: bp Go to nucleotide: FASTA |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Sequence |
Length: 751 bp Go to amino acid: FASTA |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The verified Protein-Protein interaction information |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other Protein-Protein interaction resources |
String database |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
View Microarray data |
Temporarily unavailable |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Comments |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||