| Tag | Content | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SG ID |
SG00000339 |
||||||||||||||||||
UniProt Accession |
|||||||||||||||||||
Theoretical PI |
9.86
|
||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Weight |
24472 Da
|
||||||||||||||||||
Genbank Nucleotide ID |
|||||||||||||||||||
Genbank Protein ID |
|||||||||||||||||||
Gene Name |
Mst77F |
||||||||||||||||||
Gene Synonyms/Alias |
18c, anon-77F |
||||||||||||||||||
Protein Name |
Histone-like protein 18C |
||||||||||||||||||
Protein Synonyms/Alias |
|||||||||||||||||||
Organism |
Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) |
||||||||||||||||||
NCBI Taxonomy ID |
7227 |
||||||||||||||||||
Chromosome Location |
|
||||||||||||||||||
Function in Stage |
|||||||||||||||||||
Function in Cell Type |
|||||||||||||||||||
Description |
Temporarily unavailable |
||||||||||||||||||
The information of related literatures |
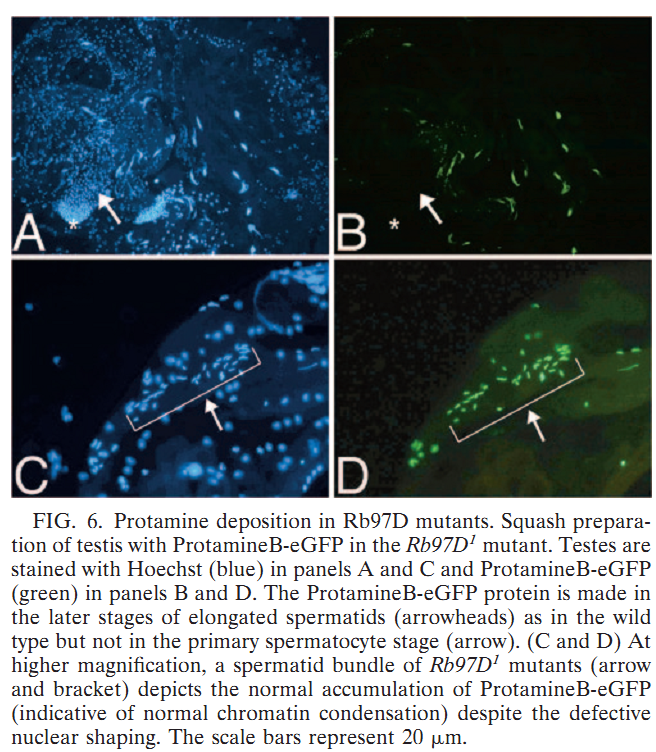
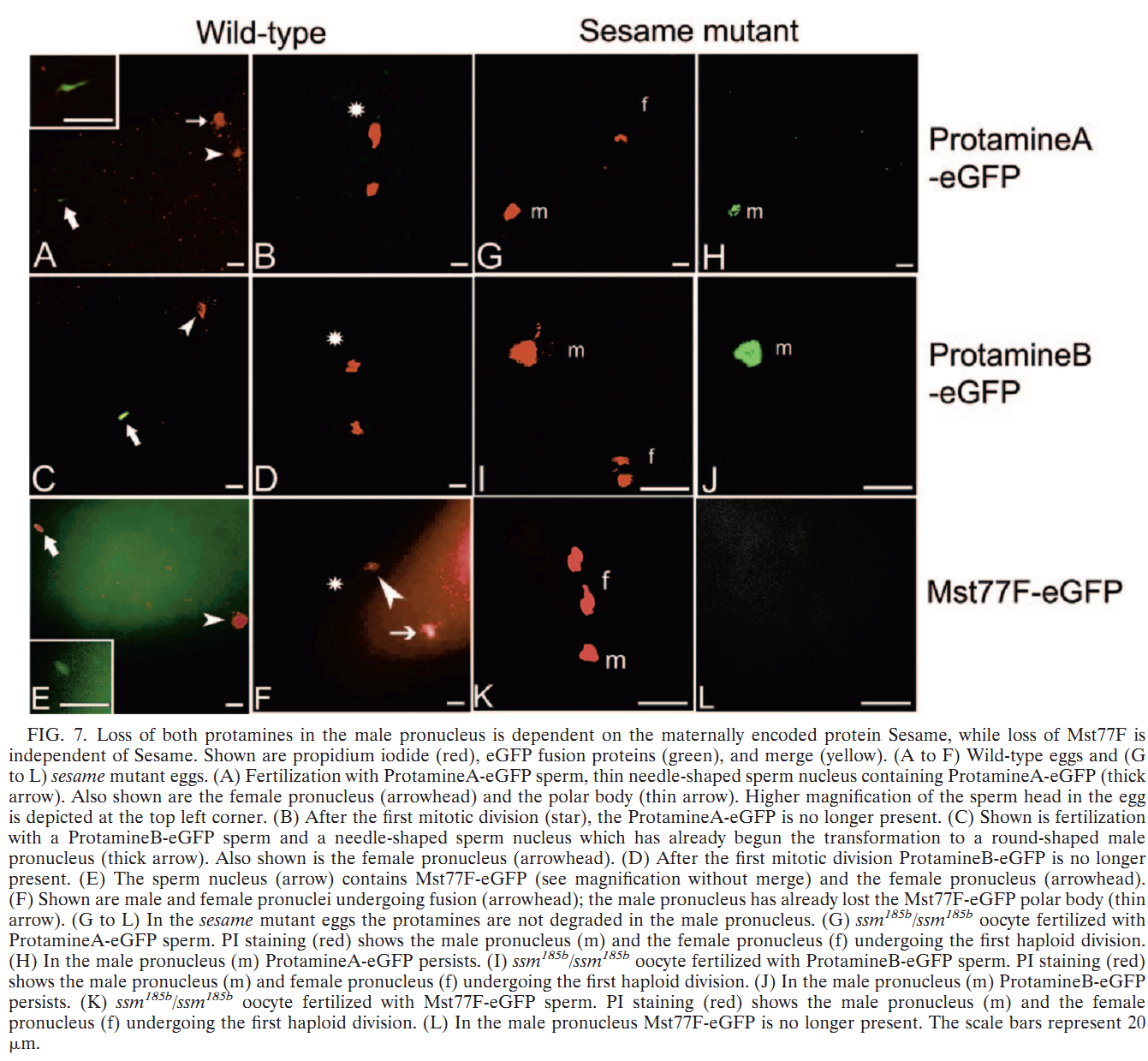
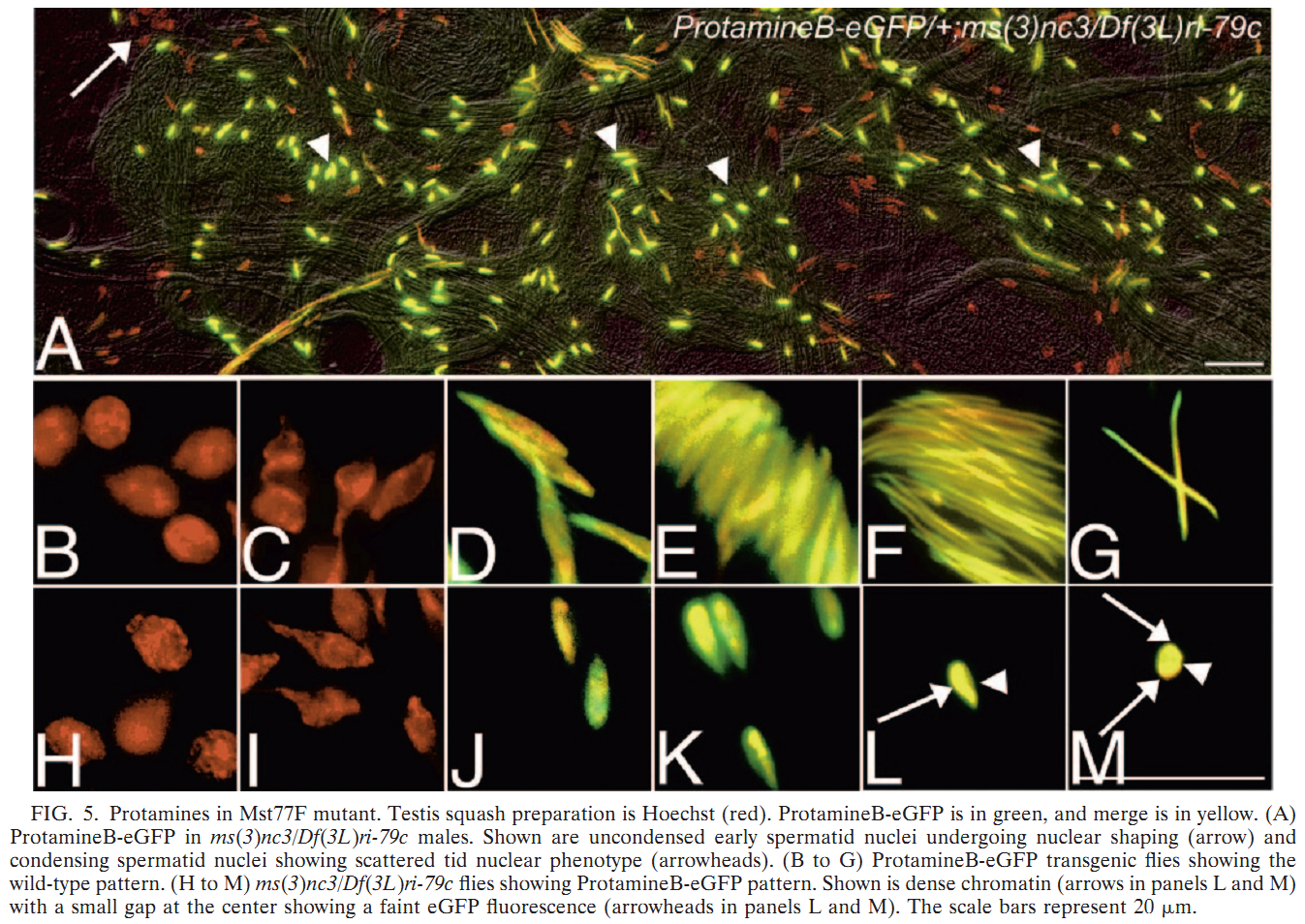
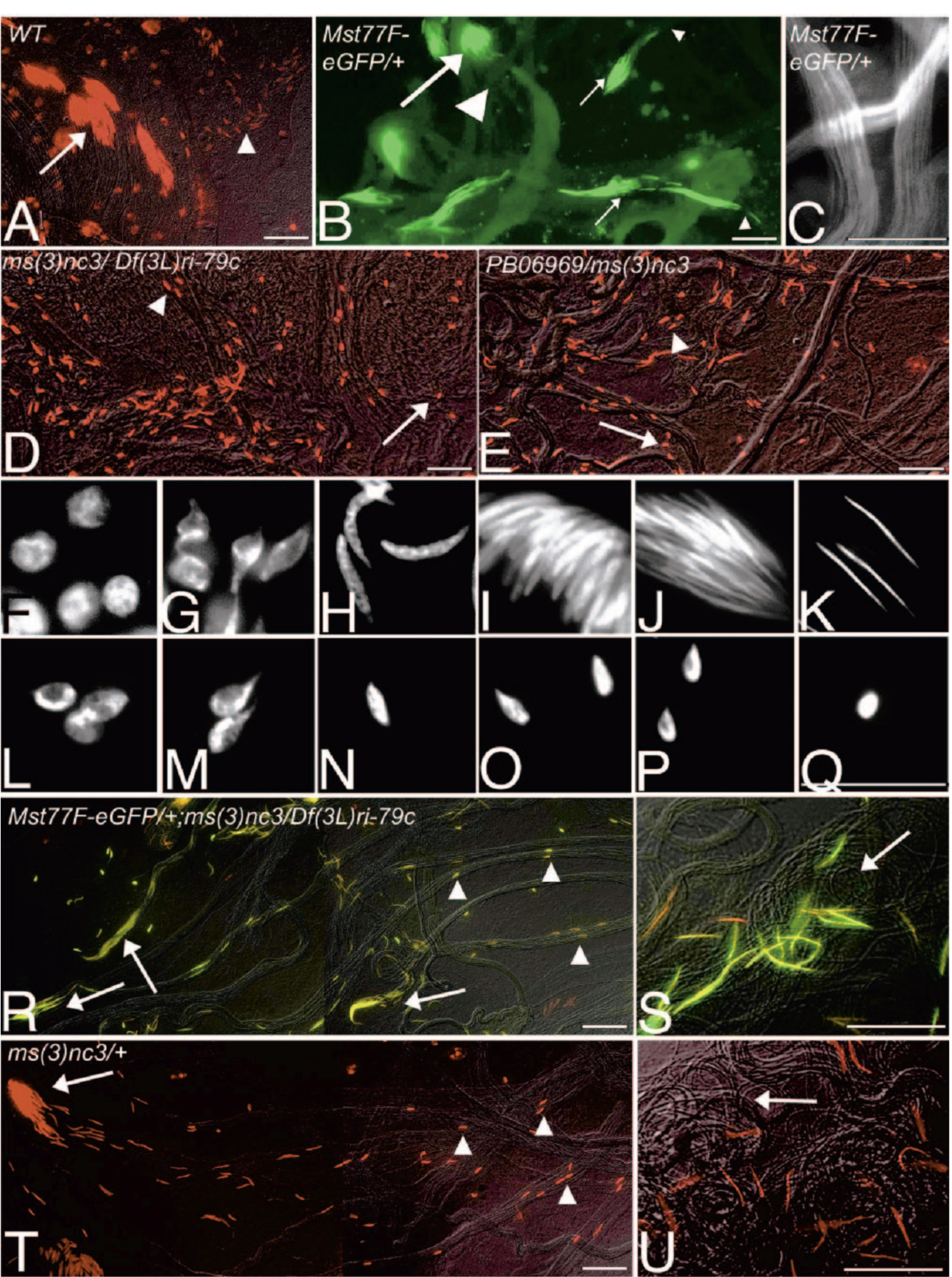
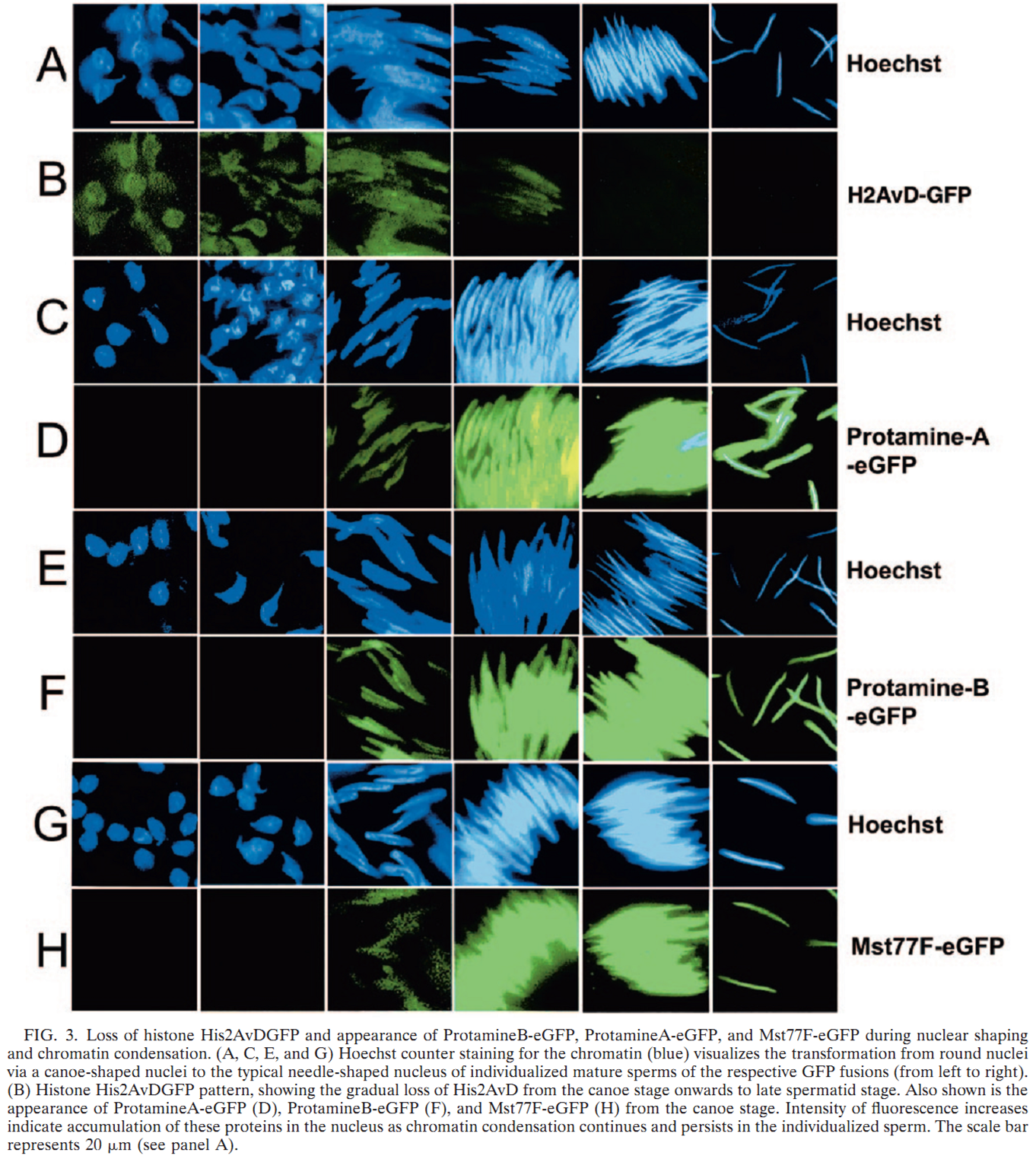
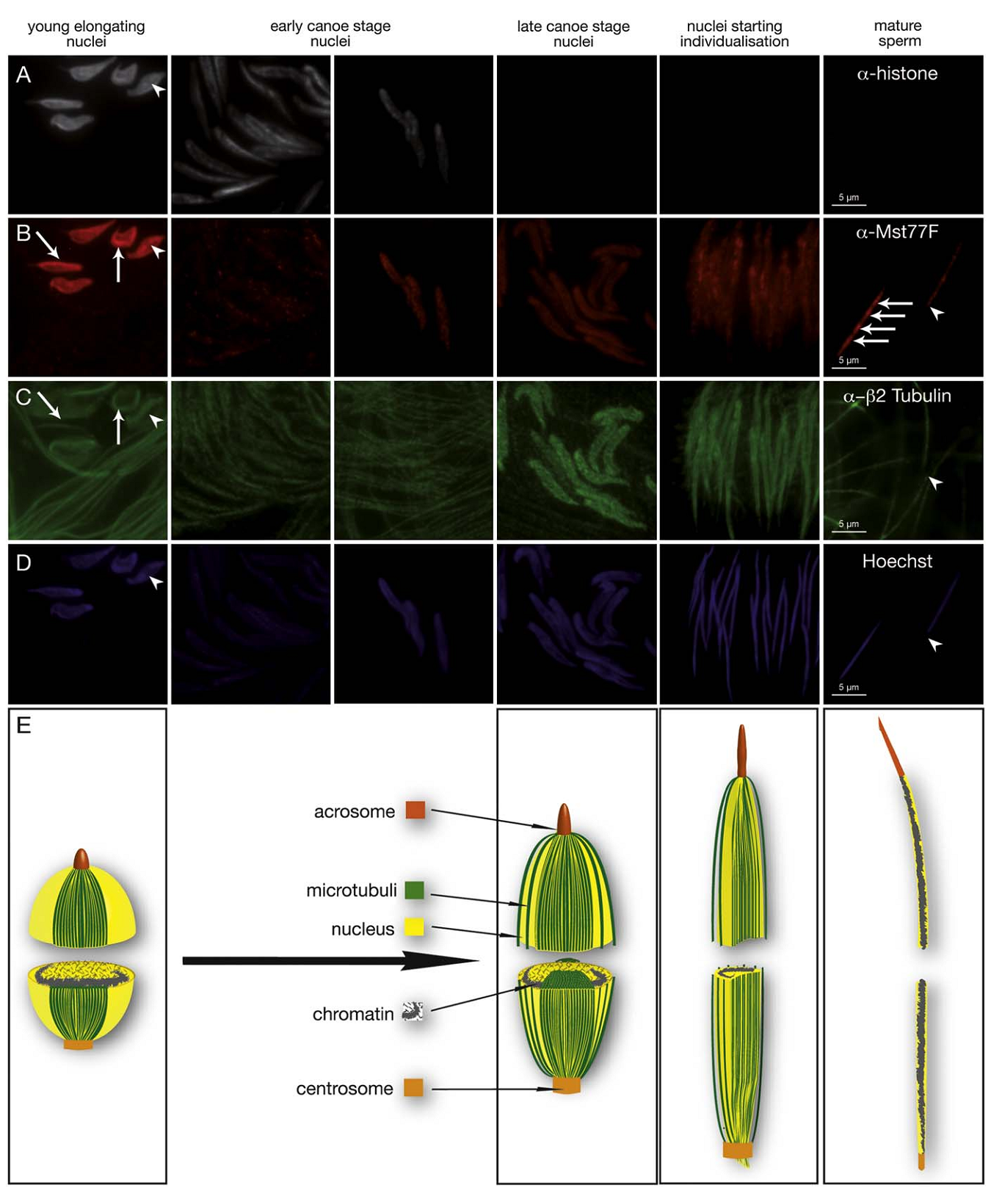
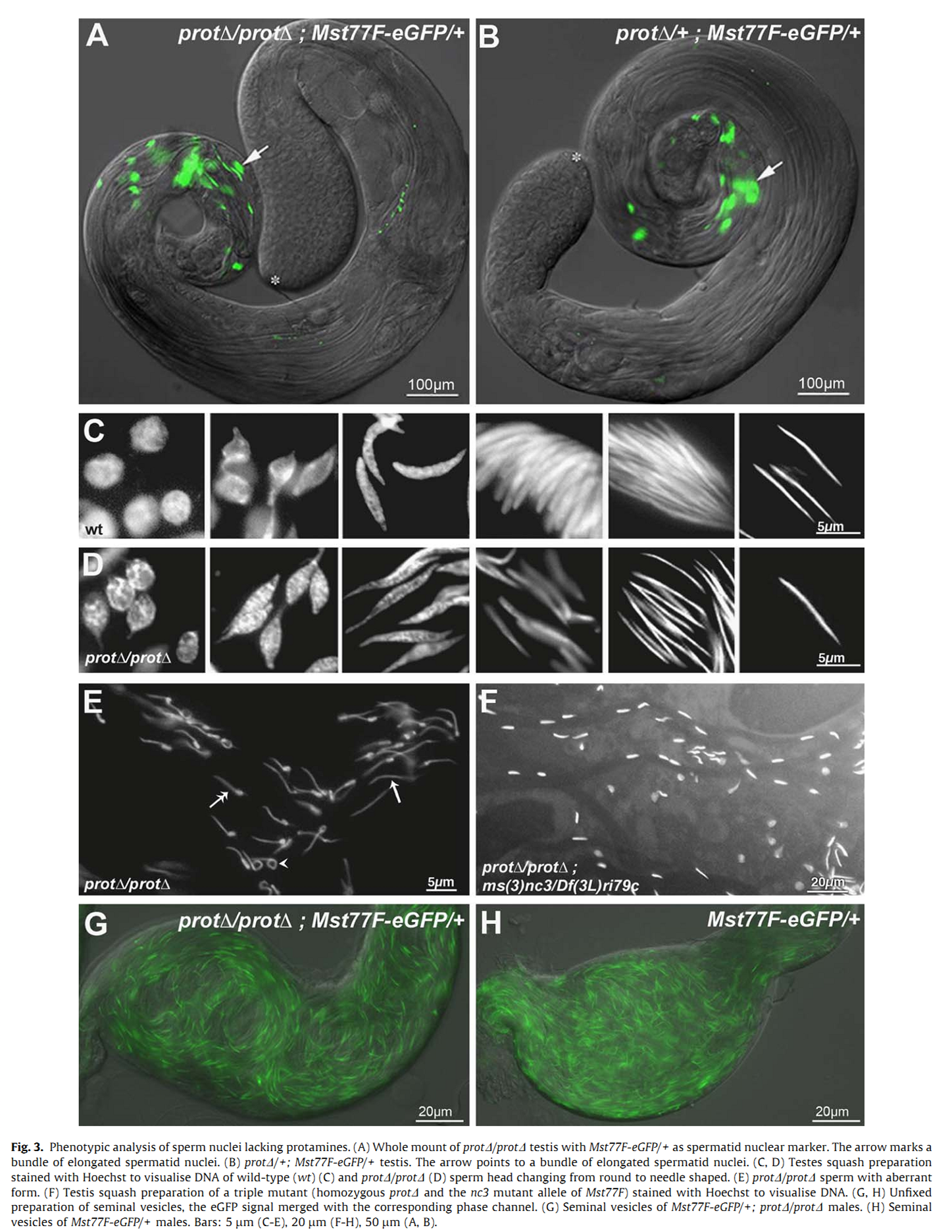
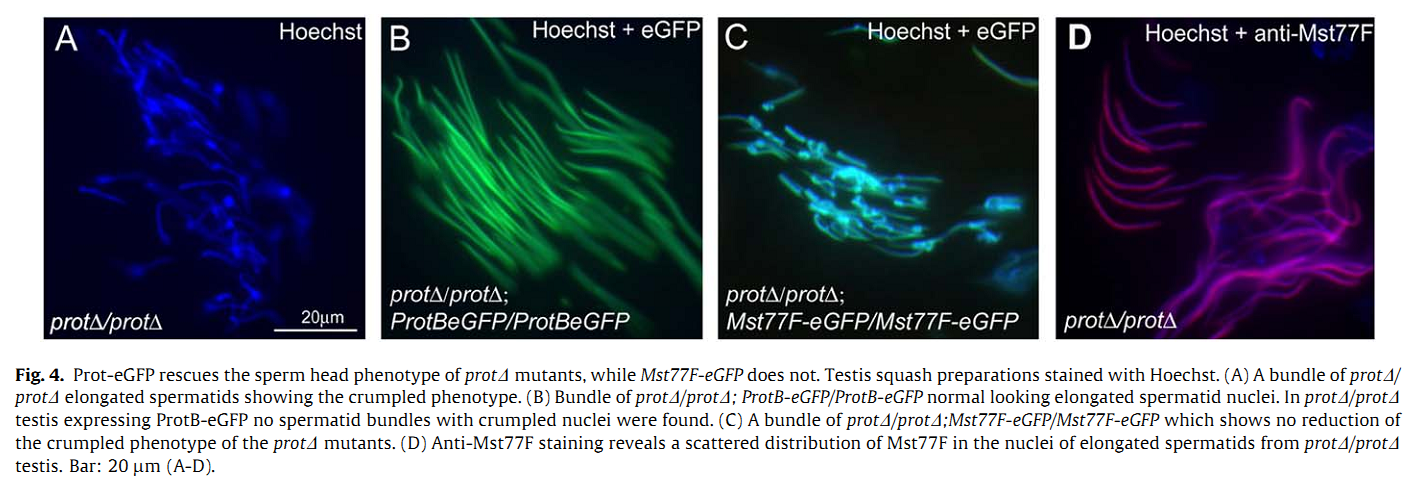
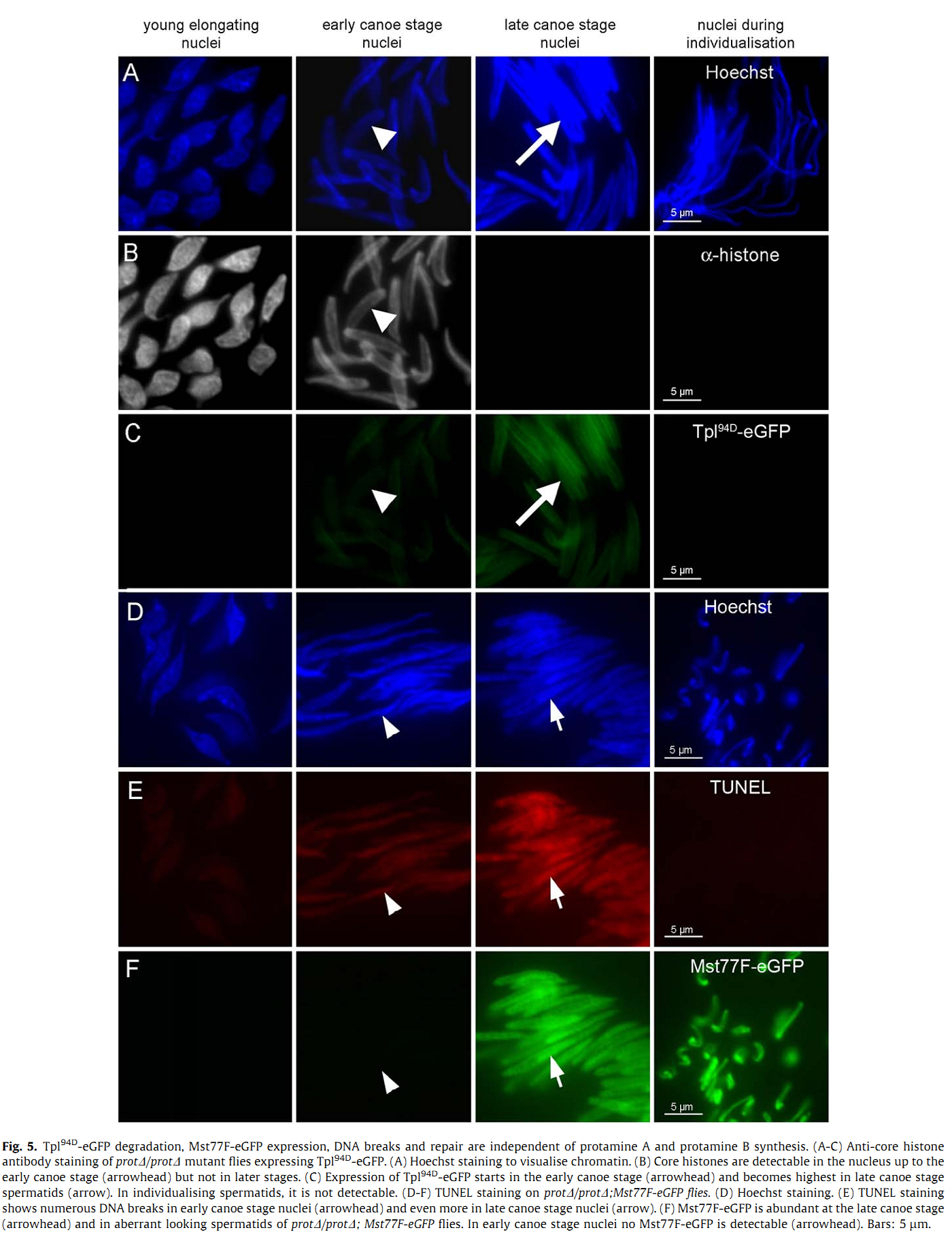
1. S. Jayaramaiah Raja and R. Renkawitz-Pohl (2005) Replacement by Drosophila melanogaster protamines and Mst77F of histones during chromatin condensation in late spermatids and role of sesame in the removal of these proteins from the male pronucleus. Mol Cell Biol 25(14): 6165-77. Abstract Chromatin condensation is a typical feature of sperm cells. During mammalian spermiogenesis, histones are first replaced by transition proteins and then by protamines, while little is known for Drosophila melanogaster. Here we characterize three genes in the fly genome, Mst35Ba, Mst35Bb, and Mst77F. The results indicate that Mst35Ba and Mst35Bb encode dProtA and dProtB, respectively. These are considerably larger than mammalian protamines, but, as in mammals, both protamines contain typical cysteine/arginine clusters. Mst77F encodes a linker histone-like protein showing significant similarity to mammalian HILS1 protein. ProtamineA-enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP), ProtamineB-eGFP, and Mst77F-eGFP carrying Drosophila lines show that these proteins become the important chromosomal protein components of elongating spermatids, and His2AvDGFP vanishes. Mst77F mutants [ms(3)nc3] are characterized by small round nuclei and are sterile as males. These data suggest the major features of chromatin condensation in Drosophila spermatogenesis correspond to those in mammals. During early fertilization steps, the paternal pronucleus still contains protamines and Mst77F but regains a nucleosomal conformation before zygote formation. In eggs laid by sesame-deficient females, the paternal pronucleus remains in a protamine-based chromatin status but Mst77F-eGFP is removed, suggesting that the sesame gene product is essential for removal of protamines while Mst77F removal is independent of Sesame. PMID: [15988027] 2. C. Rathke, B. Barckmann, S. Burkhard, S. Jayaramaiah-Raja, J. Roote and R. Renkawitz-Pohl (2010) Distinct functions of Mst77F and protamines in nuclear shaping and chromatin condensation during Drosophila spermiogenesis. Eur J Cell Biol 89(4): 326-38. Abstract Chromatin reorganisation is a major event towards the end of mammalian and Drosophila spermatogenesis. In Drosophila, we previously identified protamine A, protamine B and Mst77F as major chromatin components of the mature sperm. Here, an antibody against Mst77F reveals a dual expression pattern of Mst77F as a chromatin component and in association with microtubules during nuclear shaping. Spermatids of ms(3)nc3 (Mst77F(1)) mutants show disturbed nuclear shaping, instability of perinuclear microtubules but no obvious chromatin condensation defects. Furthermore, we generated a deletion including both protamine genes (prot Delta) and observed that in Drosophila, protamine genes are not haploinsufficient in contrast to those of mice and humans. Moreover, we show that in prot Delta mutants, histone degradation, distribution of DNA breaks and Tpl(94D)-eGFP and Mst77F expression proceed as in wild-type males. Surprisingly, in homozygous prot Delta mutants, males are fertile and sperm are motile, while about 20% of sperm show abnormally shaped nuclei. The latter phenotype can be rescued by supplying protamine-eGFP but not by supplying Mst77F-eGFP. Finally, we demonstrate a 21% increase in X-ray-induced mutation rate of prot Delta sperm. These data support the long-standing hypothesis that the switch from a histone- to protamine-based chromatin protects the paternal genome from mutagens. PMID: [20138392] Back to Top |
||||||||||||||||||
Figures for illustrating the function of this protein/gene |
|
||||||||||||||||||
Function |
Not known. Encoded in the intron of cAMP-dependentprotein kinase regulatory chain type I. Back to Top |
||||||||||||||||||
Subcellular Location |
|||||||||||||||||||
Tissue Specificity |
|||||||||||||||||||
Gene Ontology |
|
||||||||||||||||||
Interpro |
|||||||||||||||||||
Pfam |
|||||||||||||||||||
SMART |
|||||||||||||||||||
PROSITE |
|||||||||||||||||||
PRINTS |
|||||||||||||||||||
Created Date |
18-Oct-2012 |
||||||||||||||||||
Record Type |
Experiment identified |
||||||||||||||||||
Protein sequence Annotation |
CHAIN 1 215 Histone-like protein 18C. /FTId=PRO_0000064354. CONFLICT 130 130 T -> N (in Ref. 4; AAO45196). Back to Top |
||||||||||||||||||
Nucleotide Sequence |
Length: 1620 bp Go to nucleotide: FASTA |
||||||||||||||||||
Protein Sequence |
Length: 215 bp Go to amino acid: FASTA |
||||||||||||||||||
The verified Protein-Protein interaction information |
| ||||||||||||||||||
Other Protein-Protein interaction resources |
String database |
||||||||||||||||||
View Microarray data |
Temporarily unavailable |
||||||||||||||||||
Comments |
|||||||||||||||||||