| Tag | Content | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SG ID |
SG00001039 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
UniProt Accession |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Theoretical PI |
9.25
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Weight |
25283 Da
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Genbank Nucleotide ID |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Genbank Protein ID |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Name |
Vegfa |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Synonyms/Alias |
Vegf |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Name |
Vascular endothelial growth factor A |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Synonyms/Alias |
VEGF-A Vascular permeability factor;VPFFlags: Precursor |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Organism |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NCBI Taxonomy ID |
10090 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Chromosome Location |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function in Stage |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function in Cell Type |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Description |
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a key regulator of endothelial growth and permeability. VEGF may play a potential role in regulating the initial stages of the process of spermatogonial proliferation through VEGFR-2 and spermiogenesis through VEGFR-1. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The information of related literatures |
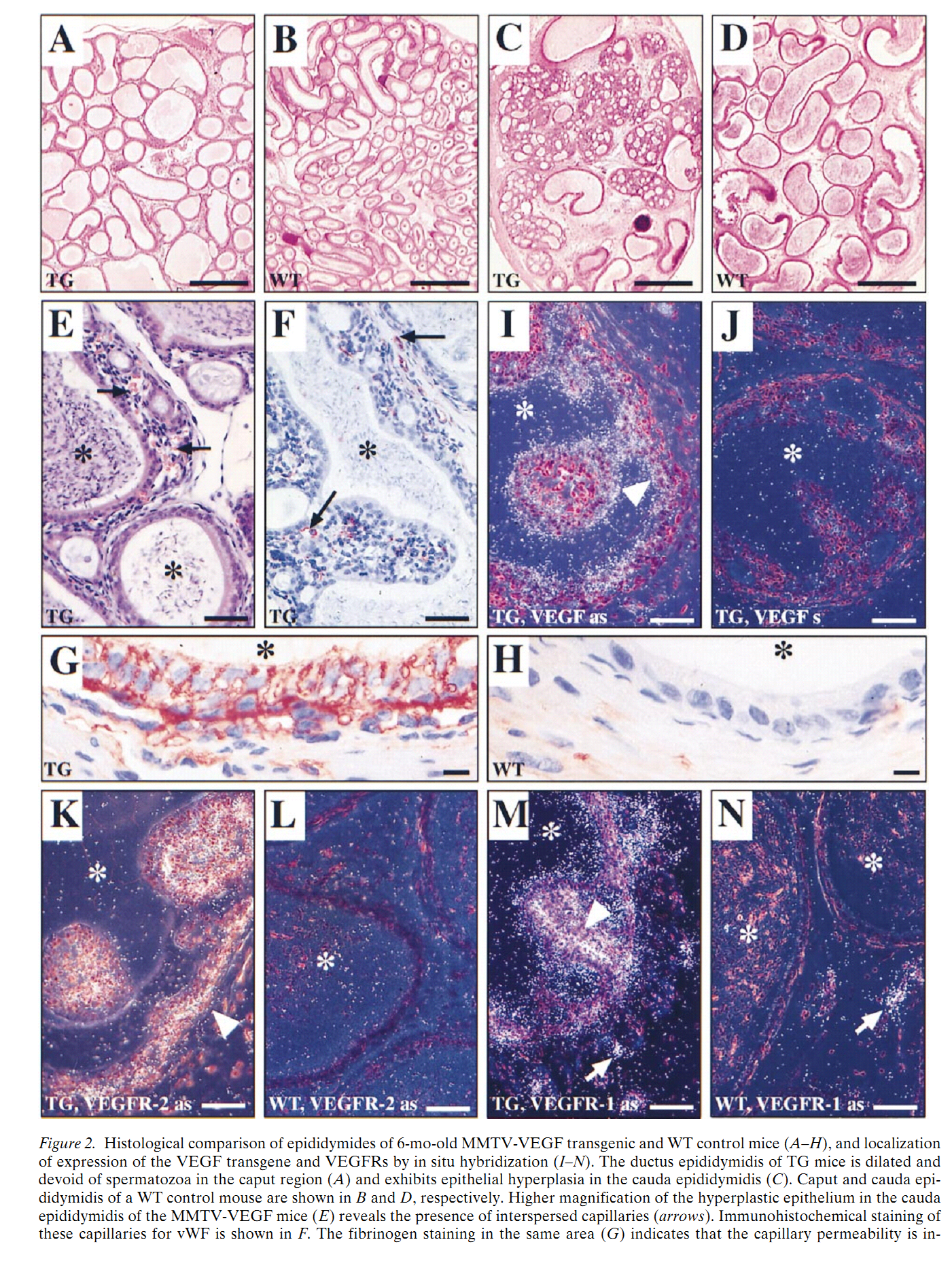
1. E. I. Korpelainen, M. J. Karkkainen, A. Tenhunen, M. Lakso, H. Rauvala, M. Vierula, M. Parvinen and K. Alitalo (1998) Overexpression of VEGF in testis and epididymis causes infertility in transgenic mice. J Cell Biol 143(6): 1705-12. Abstract Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a key regulator of endothelial growth and permeability. However, VEGF may also target nonendothelial cells, as VEGF receptors and responsiveness have been detected for example in monocytes, and high concentrations of VEGF have been reported in human semen. In this work we present evidence that overexpression of VEGF in the testis and epididymis of transgenic mice under the mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) LTR promoter causes infertility. The testes of the transgenic mice exhibited spermatogenic arrest and increased capillary density. The ductus epididymidis was dilated, containing areas of epithelial hyperplasia. The number of subepithelial capillaries in the epididymis was also increased and these vessels were highly permeable as judged by the detection of extravasated fibrinogen products. Intriguingly, the expression of VEGF receptor-1 (VEGFR-1) was detected in certain spermatogenic cells in addition to vascular endothelium, and both VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 were also found in the Leydig cells of the testis. The infertility of the MMTV-VEGF male mice could thus result from VEGF acting on both endothelial and nonendothelial cells of the male genital tract. Taken together, these findings suggest that the VEGF transgene has nonendothelial target cells in the testis and that VEGF may regulate male fertility. PMID: [9852161] 2. A. Nalbandian, L. Dettin, M. Dym and N. Ravindranath (2003) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors during male germ cell differentiation in the mouse. Biol Reprod 69(3): 985-94. Abstract Overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the testis of transgenic mice induces infertility, suggesting a potential role for VEGF in the process of spermatogenesis. Spermatogenesis occurs within the confines of the seminiferous tubules, and the seminiferous epithelium lining these tubules consists of Sertoli cells and germ cells in various stages of maturation. We investigated the source of VEGF and VEGF-target cells within the seminiferous tubules of the normal mouse testis. Sections of testes fixed in Bouin solution and embedded in paraffin were subjected to immunofluorescent staining with specific antibodies against VEGF, and its receptors, VEGFR-1 (Flt-1) and VEGFR-2 (Flk-1). Total RNA was extracted from isolated populations of Sertoli cells, type A spermatogonia, pachytene spermatocytes, and spermatids. Primer pairs specific for VEGF and its receptors were designed and reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was performed. Immunofluorescent studies indicated that VEGF is strongly expressed in the cytoplasm of Sertoli cells. VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 were not expressed by the Sertoli cell. In contrast, a differential expression of VEGF receptors was observed in germ cells. Although VEGFR-2 was expressed in the cytoplasm of type A spermatogonia, VEGFR-1 was expressed in the acrosomal region of spermatids and spermatozoa. Pachytene spermatocytes did not exhibit any staining. Further, we examined the transcription of VEGF and its receptors by RT-PCR. VEGF was actively transcribed only in Sertoli cells. The transcription of VEGFR-2 was confined to type A spermatogonia. Interestingly, VEGFR-1 was transcribed both in pachytene spermatocytes and round spermatids. The mRNA expression of VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 in germ cells was inversely correlated during postnatal development of the mouse testis. Thus, VEGF may play a potential role in regulating the initial stages of the process of spermatogonial proliferation through VEGFR-2 and spermiogenesis through VEGFR-1. PMID: [12773425] Back to Top |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figures for illustrating the function of this protein/gene |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function |
Growth factor active in angiogenesis, vasculogenesis andendothelial cell growth. Induces endothelial cell proliferation,promotes cell migration, inhibits apoptosis and inducespermeabilization of blood vessels. Binds to the FLT1/VEGFR1 andKDR/VEGFR2 receptors, heparan sulfate and heparin. May play a rolein increasing vascular permeability during lactation, whenincreased transport of molecules from the blood is required forefficient milk protein synthesis (By similarity). Back to Top |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Subcellular Location |
Isoform VEGF-3: Cell membrane; Peripheralmembrane protein. Note=Remains cell-surface associated unlessreleased by heparin. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tissue Specificity |
In developing embryos, expressed mainly in thechoroid plexus, paraventricular neuroepithelium, placenta andkidney glomeruli. Also found in bronchial epithelium, adrenalgland and in seminiferous tubules of testis. High expression ofVEGF continues in kidney glomeruli and choroid plexus in adults. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Ontology |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interpro |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pfam |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SMART |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PROSITE |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PRINTS |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Created Date |
18-Oct-2012 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Record Type |
Experiment identified |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein sequence Annotation |
SIGNAL 1 26 By similarity. CHAIN 27 214 Vascular endothelial growth factor A. /FTId=PRO_0000023388. MOD_RES 146 146 N6-acetyllysine (By similarity). MOD_RES 148 148 N6-acetyllysine (By similarity). MOD_RES 151 151 N6-acetyllysine (By similarity). CARBOHYD 100 100 N-linked (GlcNAc...) (Probable). DISULFID 51 93 By similarity. DISULFID 76 76 Interchain (By similarity). DISULFID 82 127 By similarity. DISULFID 85 85 Interchain (By similarity). DISULFID 86 129 By similarity. VAR_SEQ 1 1 M -> MTDRQTDTAPSPSAHLLAGGLPTVDAAASREEPKPA PGGGVEGVGARGIARKLFVQLLGSSRSVVAVVCAAGDKPIG AGRSASSGLEKPGPEKRGEEEKEEERGPQWALGSQEPSSWT GEAAVCADSAPAARAPQAPARASVPEGRGARQGAQESGLPR SPSRRGSASRAGPGRASETM (in isoform L-VEGF- 1). /FTId=VSP_038746. VAR_SEQ 105 141 IMRIKPHQSQHIGEMSFLQHSRCECRPKKDRTKPEKK -> VGTCGTGDGAGAGGGRRTVVQGGALEGCLGLCLGNFW (in isoform VEGF-4). /FTId=VSP_016418. VAR_SEQ 105 128 IMRIKPHQSQHIGEMSFLQHSRCE -> VGTCGTGDGAGAG GAGGQWYKEGH (in isoform VEGF-5). /FTId=VSP_016419. VAR_SEQ 129 214 Missing (in isoform VEGF-5). /FTId=VSP_016420. VAR_SEQ 140 140 K -> N (in isoform VEGF-1 and isoform L- VEGF-1). /FTId=VSP_004626. VAR_SEQ 141 208 Missing (in isoform VEGF-2). /FTId=VSP_004628. VAR_SEQ 141 164 Missing (in isoform VEGF-1 and isoform L- VEGF-1). /FTId=VSP_004627. VAR_SEQ 142 214 Missing (in isoform VEGF-4). /FTId=VSP_016421. CONFLICT 61 61 F -> I (in Ref. 3; AAC05442). CONFLICT 117 118 GE -> ER (in Ref. 2; AAA40547). Back to Top |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nucleotide Sequence |
Length: 661 bp Go to nucleotide: FASTA |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Sequence |
Length: 214 bp Go to amino acid: FASTA |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The verified Protein-Protein interaction information |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other Protein-Protein interaction resources |
String database |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
View Microarray data |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Comments |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||