| Tag | Content | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SG ID |
SG00001951 |
||||||||||||
UniProt Accession |
|||||||||||||
Theoretical PI |
8.92
|
||||||||||||
Molecular Weight |
23564 Da
|
||||||||||||
Genbank Nucleotide ID |
|||||||||||||
Genbank Protein ID |
|||||||||||||
Gene Name |
Gdnf |
||||||||||||
Gene Synonyms/Alias |
|||||||||||||
Protein Name |
|||||||||||||
Protein Synonyms/Alias |
SubName: Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor |
||||||||||||
Organism |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
||||||||||||
NCBI Taxonomy ID |
10116 |
||||||||||||
Chromosome Location |
|
||||||||||||
Function in Stage |
|||||||||||||
Function in Cell Type |
|||||||||||||
Description |
Temporarily unavailable |
||||||||||||
The information of related literatures |
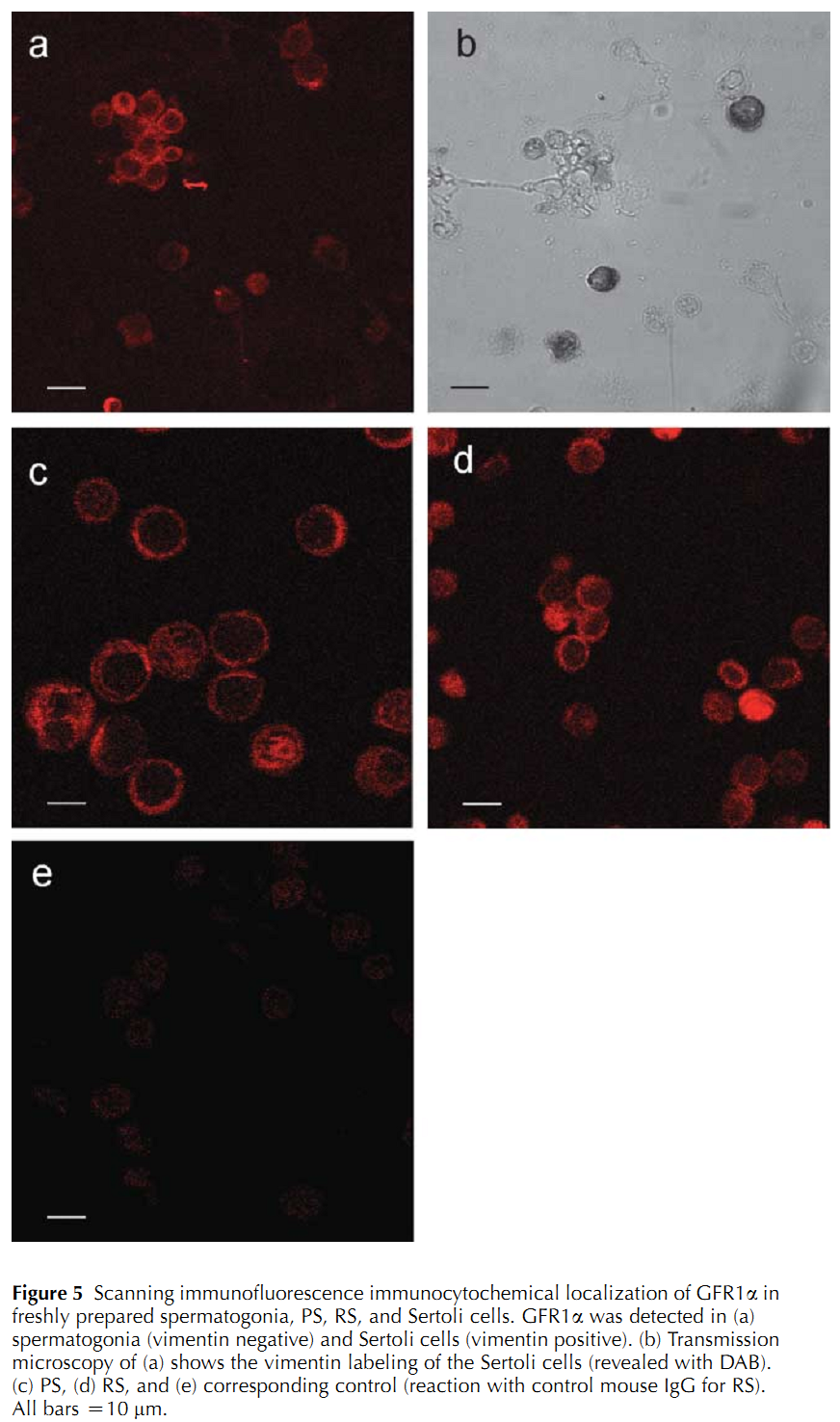
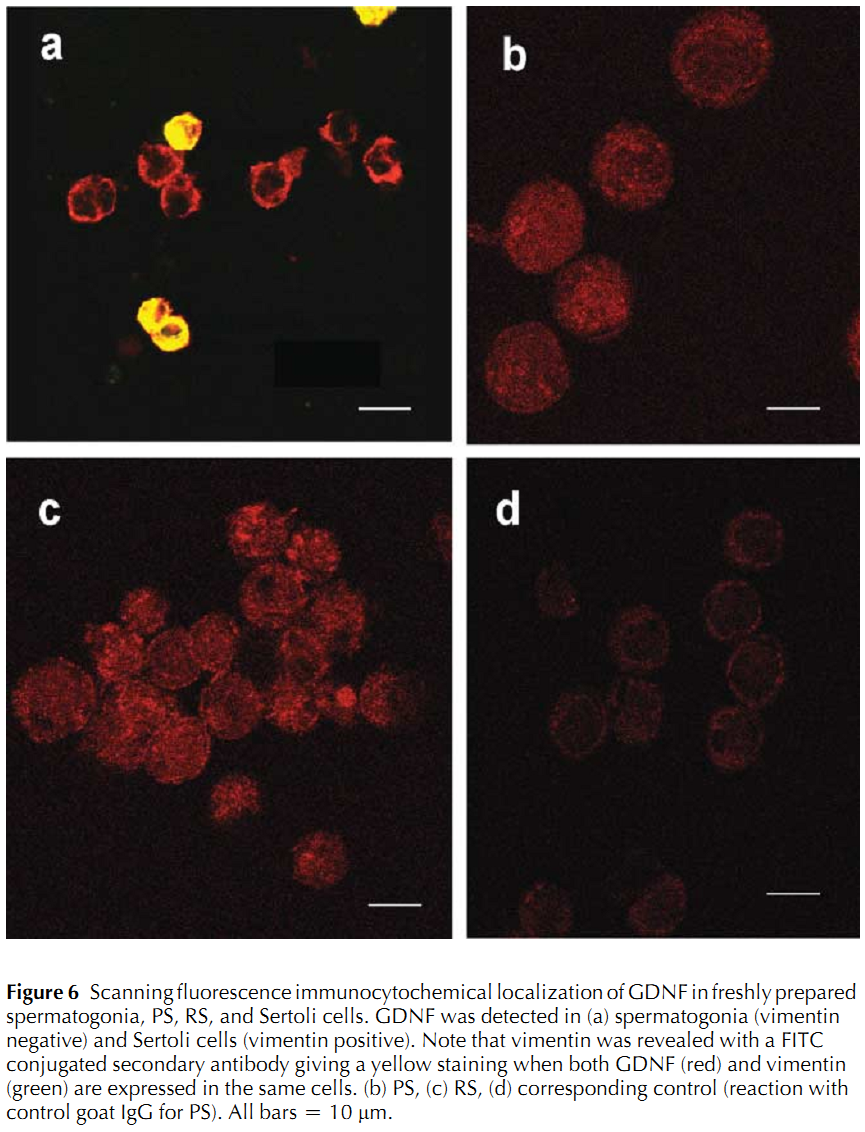
1. S. Fouchecourt, M. Godet, O. Sabido and P. Durand (2006) Glial cell-line-derived neurotropic factor and its receptors are expressed by germinal and somatic cells of the rat testis. J Endocrinol 190(1): 59-71. Abstract Glial cell-line-derived neurotropic factor (GDNF) and its receptors glial cell-line-derived neurotropic factor alpha (GFR1alpha) and rearranged during transformation (RET) have been localized in the rat testis during postnatal development. The three mRNAs, and GDNF and GFR1alpha proteins were detected in testis extracts from 1- to 90-day-old rats by reverse transcriptase PCR and Western blotting respectively. The three mRNAs were present in Sertoli cells from 20- and 55-day-old rats, pachytene spermatocytes (PS), and round spermatids (RS). The GDNF and GFR1alpha proteins were detected in PS, RS, and Sertoli cells. GDNF and GFR1alpha were also detected using flow cytometry in spermatogonia and preleptotene spermatocytes, and in secondary spermatocytes. The localization of GDNF and GFR1alpha in germ and Sertoli cells was confirmed by immunocytochemistry. The hypothesis that GDNF may control DNA synthesis of Sertoli cells and/or spermatogonia in the immature rat was addressed using cultures of seminiferous tubules from 7- to 8-day-old rats. Addition of GDNF for 48 h resulted in a twofold decrease in the percentage of spermatogonia able to duplicate DNA, whereas Sertoli cells were not affected. These results are consistent with a role of GDNF in inhibiting the S-phase entrance of a large subset of differentiated type A spermatogonia, together with an enhancing effect of the factor on a small population of undifferentiated (stem cells) spermatogonia. Moreover, the wide temporal and spatial expression of GDNF and its receptors in the rat testis suggest that it might act at several stages of spermatogenesis. PMID: [16837611] 2. W. M. Yang, H. Y. Kim, S. Y. Park, H. M. Kim, M. S. Chang and S. K. Park (2010) Cynomorium songaricum induces spermatogenesis with glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) enhancement in rat testes. J Ethnopharmacol 128(3): 693-6. Abstract AIM OF THE STUDY PMID: [20219665] 3. G. Akkoyunlu, T. Erdogru, Y. Seval, I. Ustunel, T. Koksal, M. F. Usta, M. Baykara and R. Demir (2007) Immunolocalization of glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) and its receptor GFR-alpha1 in varicocele-induced rat testis. Acta Histochem 109(2): 130-7. Abstract The aim of the study was to determine the immunolocalisation of glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) and its receptor (GFRalpha1) in testicular dysfunction induced by experimental left varicocele. Male Wistar rats were divided randomly into two groups PMID: [17240430] 4. J. A. Schmidt, M. R. Avarbock, J. W. Tobias and R. L. Brinster (2009) Identification of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor-regulated genes important for spermatogonial stem cell self-renewal in the rat. Biol Reprod 81(1): 56-66. Abstract Spermatogonial stem cells (SSCs) provide the foundation for spermatogenesis throughout the life of a male. Because SSCs of many species can colonize the mouse testis, and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is responsible for stimulating SSC self-renewal in rodents, we reasoned that molecular mechanisms of SSC self-renewal are similar across species. GDNF-regulated genes have been identified in mouse SSCs; however, downstream targets of GDNF are unknown in other species. The objective of this work was to identify GDNF-regulated genes in rat SSCs and to define the biological significance of these genes for rat SSC self-renewal. We conducted microarray analysis on cultured rat germ cells enriched for SSCs in the presence and absence of GDNF. Many GDNF-regulated genes were identified, most notably, Bcl6b and Etv5, which are important for mouse SSC self-renewal. Bcl6b was the most highly regulated gene in both the rat and mouse. Additionally, we identified three novel GDNF-regulated genes in rat SSCs PMID: [19339709] 5. D. S. Johnston, E. Olivas, P. Dicandeloro and W. W. Wright (2011) Stage-Specific Changes in GDNF Expression by Rat Sertoli Cells. Biol Reprod (): . Abstract In the adult testis, the precise control of the self-renewing replication and differentiation of stem spermatogonia is fundamental to male fertility. Previous studies have shown that the replication of A single (A(s)) spermatogonia, a population that includes the stem cells, is maximal at stage I of the cycle of the rat seminiferous epithelium and minimal at stage VII, while the ratio of A paired spermatogonia to A(s) spermatogonia increases from stages I to VII. It has been hypothesized that these changes in A(s) spermatogonia replication and differentiation result from changes in the expression of glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) by Sertoli cells. To directly test this hypothesis, we used immunocytochemistry and confocal microscopy to demonstrate that within intact seminiferous tubules, GDNF is only detectable in Sertoli cells and that its amount and its location within these cells changes with progression of the stages of the cycle. The identification of Sertoli cells as the primary source of GDNF was confirmed by RT-PCR analysis of RNA isolated from purified populations of Sertoli cells, pachytene spermatocytes and round spermatids. Stage-specific changes in GDNF expression were confirmed by quantifying GDNF mRNA in seminiferous tubules at defined stages of the cycle. Expression of this transcript was maximal at stage I, fell 14-fold by stage VIIc,d and then increased 12-fold by stages XIII-XIV. This pattern of expression was the opposite of the control, cathepsin L mRNA. Taken together, these data support the hypothesis that cyclical changes in GDNF expression by Sertoli cells are responsible for the stage-specific replication and differentiation of stem spermatogonia, the foundational cells of spermatogenesis. PMID: [21653894] Back to Top |
||||||||||||
Figures for illustrating the function of this protein/gene |
|
||||||||||||
Function |
|||||||||||||
Subcellular Location |
|||||||||||||
Tissue Specificity |
|||||||||||||
Gene Ontology |
|
||||||||||||
Interpro |
|||||||||||||
Pfam |
|||||||||||||
SMART |
|||||||||||||
PROSITE |
|||||||||||||
PRINTS |
|||||||||||||
Created Date |
18-Oct-2012 |
||||||||||||
Record Type |
Experiment identified |
||||||||||||
Protein sequence Annotation |
|||||||||||||
Nucleotide Sequence |
Length: bp Go to nucleotide: FASTA |
||||||||||||
Protein Sequence |
Length: 211 bp Go to amino acid: FASTA |
||||||||||||
The verified Protein-Protein interaction information |
| ||||||||||||
Other Protein-Protein interaction resources |
String database |
||||||||||||
View Microarray data |
Temporarily unavailable |
||||||||||||
Comments |
|||||||||||||