| Tag | Content | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SG ID |
SG00002116 |
|||||||||
UniProt Accession |
||||||||||
Theoretical PI |
8.58
|
|||||||||
Molecular Weight |
84149 Da
|
|||||||||
Genbank Nucleotide ID |
||||||||||
Genbank Protein ID |
||||||||||
Gene Name |
GN ORFNames=Smp_149460 |
|||||||||
Gene Synonyms/Alias |
||||||||||
Protein Name |
||||||||||
Protein Synonyms/Alias |
SubName: Tyrosine kinase |
|||||||||
Organism |
Schistosoma mansoni (Blood fluke) |
|||||||||
NCBI Taxonomy ID |
6183 |
|||||||||
Chromosome Location |
|
|||||||||
Function in Stage |
||||||||||
Function in Cell Type |
||||||||||
Description |
Temporarily unavailable |
|||||||||
The information of related literatures |
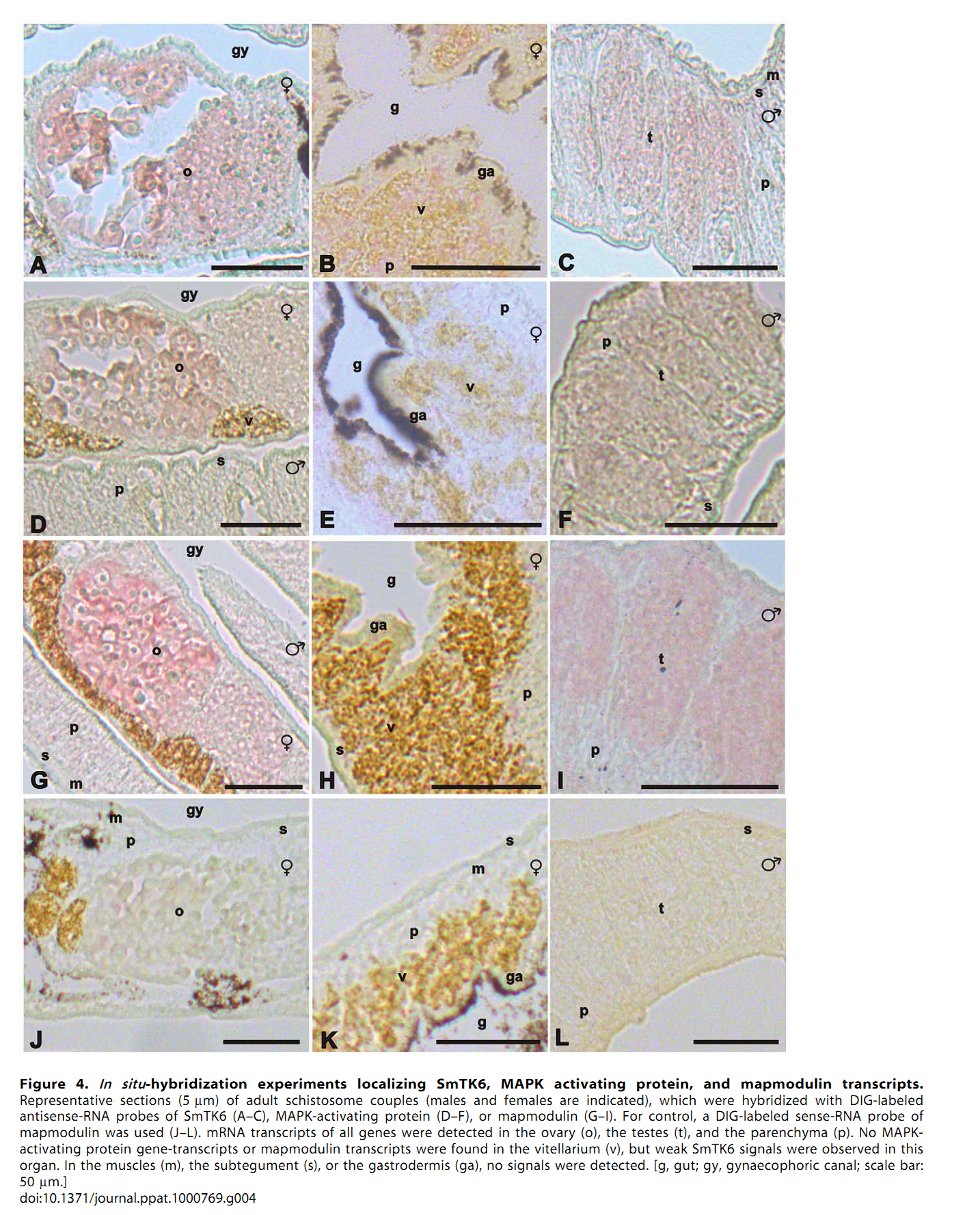
1. S. Beckmann, C. Buro, C. Dissous, J. Hirzmann and C. G. Grevelding (2010) The Syk kinase SmTK4 of Schistosoma mansoni is involved in the regulation of spermatogenesis and oogenesis. PLoS Pathog 6(2): e1000769. Abstract The signal transduction protein SmTK4 from Schistosoma mansoni belongs to the family of Syk kinases. In vertebrates, Syk kinases are known to play specialized roles in signaling pathways in cells of the hematopoietic system. Although Syk kinases were identified in some invertebrates, their role in this group of animals has not yet been elucidated. Since SmTK4 is the first Syk kinase from a parasitic helminth, shown to be predominantly expressed in the testes and ovary of adult worms, we investigated its function. To unravel signaling cascades in which SmTK4 is involved, yeast two-/three-hybrid library screenings were performed with either the tandem SH2-domain, or with the linker region including the tyrosine kinase domain of SmTK4. Besides the Src kinase SmTK3 we identified a new Src kinase (SmTK6) acting upstream of SmTK4 and a MAPK-activating protein, as well as mapmodulin acting downstream. Their identities and colocalization studies pointed to a role of SmTK4 in a signaling cascade regulating the proliferation and/or differentiation of cells in the gonads of schistosomes. To confirm this decisive role we performed biochemical and molecular approaches to knock down SmTK4 combined with a novel protocol for confocal laser scanning microscopy for morphological analyses. Using the Syk kinase-specific inhibitor Piceatannol or by RNAi treatment of adult schistosomes in vitro, corresponding phenotypes were detected in the testes and ovary. In the Xenopus oocyte system it was finally confirmed that Piceatannol suppressed the activity of the catalytic kinase domain of SmTK4. Our findings demonstrate a pivotal role of SmTK4 in gametogenesis, a new function for Syk kinases in eukaryotes. PMID: [20169182] Back to Top |
|||||||||
Figures for illustrating the function of this protein/gene |
|
|||||||||
Function |
||||||||||
Subcellular Location |
||||||||||
Tissue Specificity |
||||||||||
Gene Ontology |
|
|||||||||
Interpro |
||||||||||
Pfam |
||||||||||
SMART |
||||||||||
PROSITE |
PS00107; PROTEIN_KINASE_ATP; 1. PS50011; PROTEIN_KINASE_DOM; 1. PS00109; PROTEIN_KINASE_TYR; 1. Back to Top |
|||||||||
PRINTS |
||||||||||
Created Date |
18-Oct-2012 |
|||||||||
Record Type |
Experiment identified |
|||||||||
Protein sequence Annotation |
||||||||||
Nucleotide Sequence |
Length: bp Go to nucleotide: FASTA |
|||||||||
Protein Sequence |
Length: 766 bp Go to amino acid: FASTA |
|||||||||
The verified Protein-Protein interaction information |
| |||||||||
Other Protein-Protein interaction resources |
String database |
|||||||||
View Microarray data |
Temporarily unavailable |
|||||||||
Comments |
||||||||||