| Tag | Content | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SG ID |
SG00002123 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
UniProt Accession |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Theoretical PI |
8.88
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Weight |
43077 Da
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Genbank Nucleotide ID |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Genbank Protein ID |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Name |
GJA1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Synonyms/Alias |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Name |
Gap junction protein |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Synonyms/Alias |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Organism |
Sus scrofa (Pig) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NCBI Taxonomy ID |
9823 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Chromosome Location |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function in Stage |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function in Cell Type |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Description |
Temporarily unavailable |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The information of related literatures |
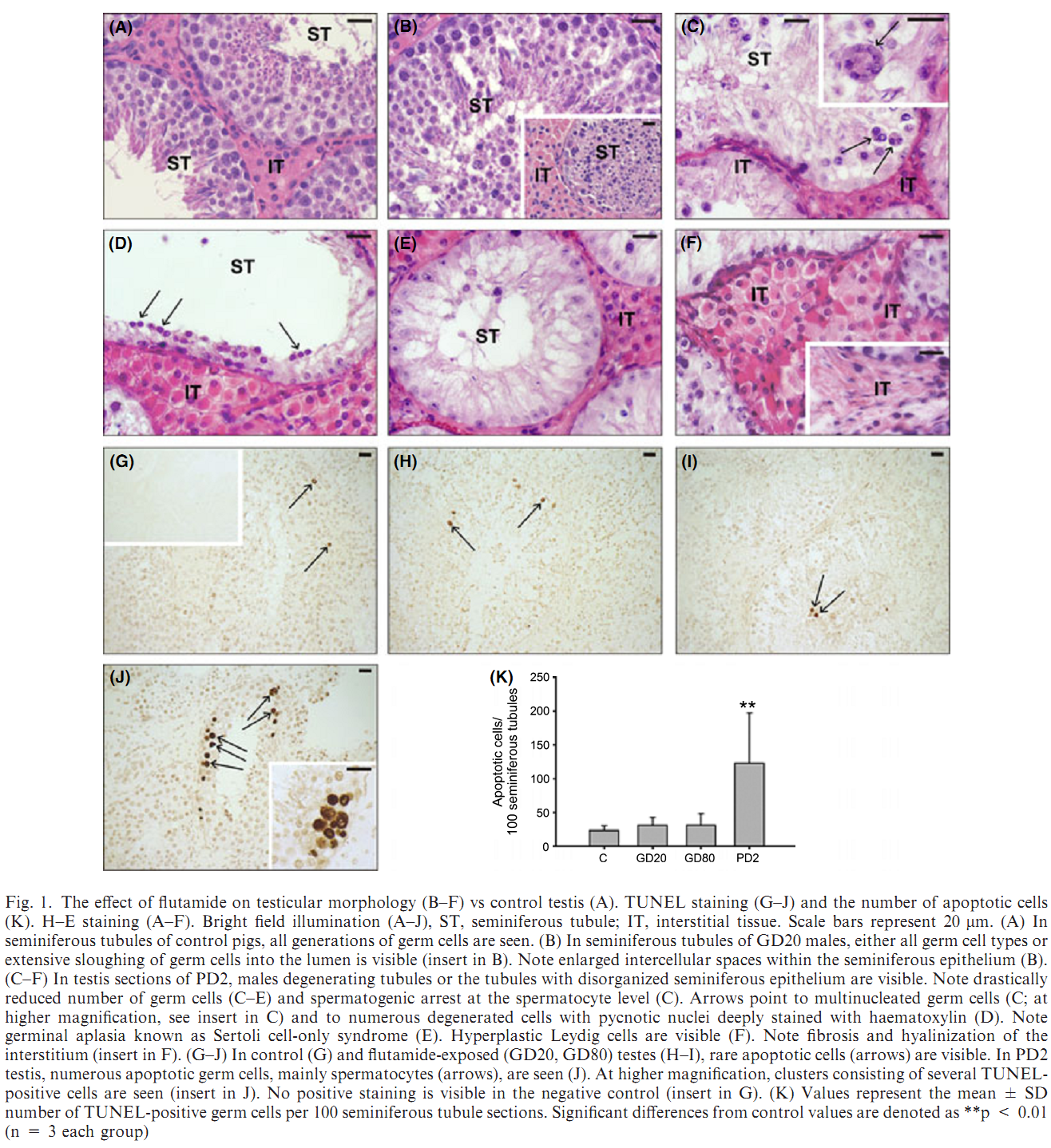
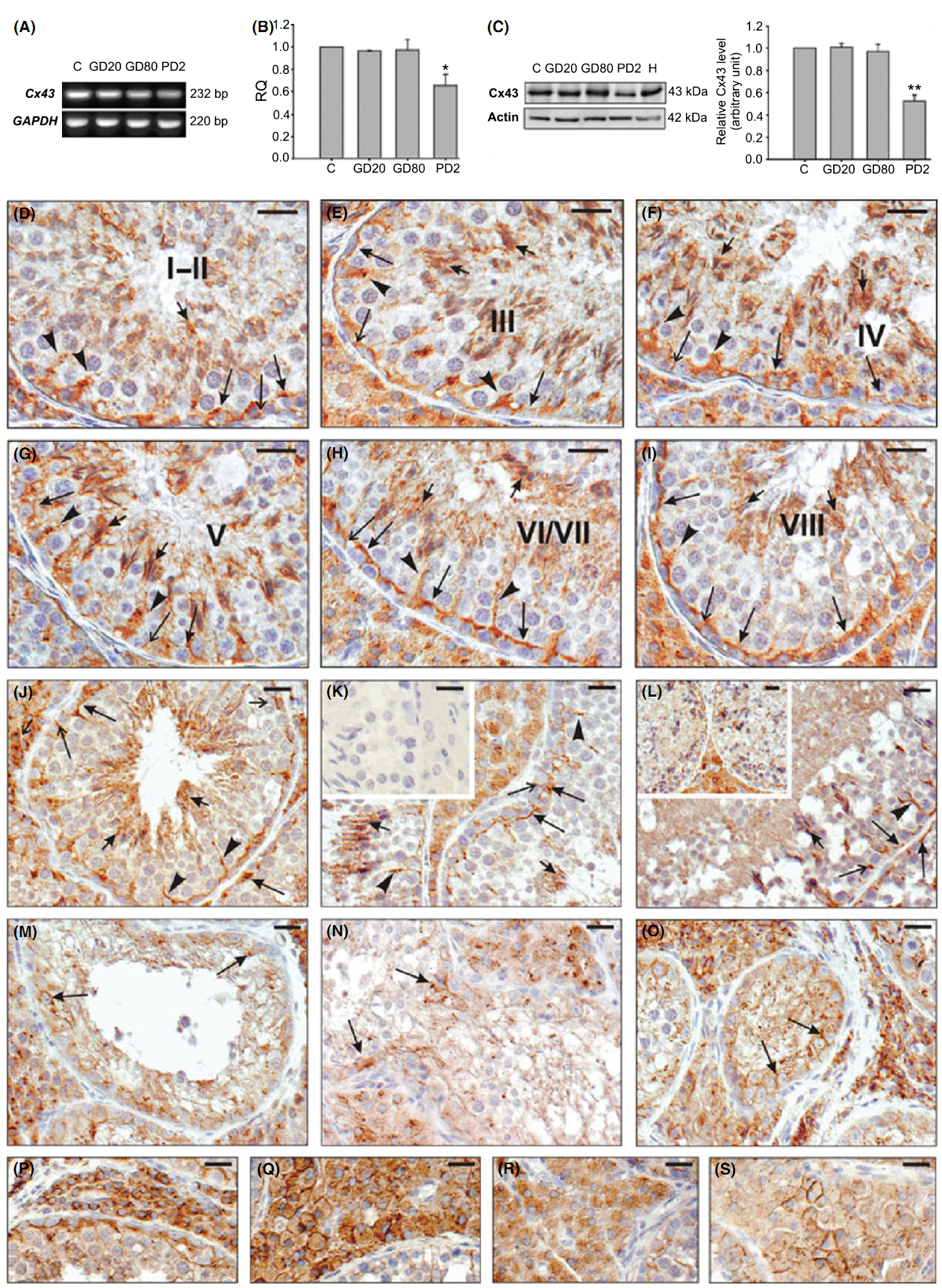
1. I. Kopera, M. Durlej, A. Hejmej, K. Knapczyk-Stwora, M. Duda, M. Slomczynska and B. Bilinska (2011) Differential expression of connexin 43 in adult pig testes during normal spermatogenic cycle and after flutamide treatment. Reprod Domest Anim 46(6): 1050-60. Abstract Evidence is mounting that the foetal and neonatal period of reproductive tract development is highly sensitive to hormonal disruption induced by various endocrine active compounds. Thus, we asked whether androgen withdrawal caused by prenatal (GD20, GD80) or neonatal (PD2) exposure to an anti-androgen flutamide alters Cx43 gene expression and may induce delayed effects on morphology and function of adult pig testes. Flutamide was given in five doses (50 mg/kg bw). Our histological analysis and TUNEL staining revealed varying degrees of seminiferous tubules abnormalities in all experimental pigs. Testes of pigs exposed to flutamide in utero exhibited moderate alterations of the spermatogenic process, whereas those of exposed neonatally were severely impaired. The most striking effects were spermatogenic arrest, germ cell detachment and a statistically significant increase in the frequency of germ cell apoptosis (p<0.01). Moreover, all pigs exposed to flutamide displayed Leydig cell hyperplasia. Because the network of cell-cell communication provided by gap junction channels plays an essential role in the regulation and maintenance of spermatogenesis, the physiological significance of Cx43-based gap junctions with regards to the gonadal impairment was evaluated by analysis of its expression using immunohistochemical, Western blot and qRT-PCR approaches. Significantly, lower Cx43 expression was found when flutamide was administered neonatally, which has coincided with severe disruption of spermatogenesis. Our data suggest that neonatal exposure to flutamide induces long-term effects on the spermatogenic capacity of the pig testis through alterations of Cx43-mediated intercellular communication and permanent alteration of both Sertoli and Leydig cell functions. PMID: [21457361] Back to Top |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figures for illustrating the function of this protein/gene |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function |
One gap junction consists of a cluster of closely packedpairs of transmembrane channels, the connexons, through whichmaterials of low MW diffuse from one cell to a neighboring cell(By similarity). Back to Top |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Subcellular Location |
Membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein (Bysimilarity). |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tissue Specificity |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Ontology |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interpro |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pfam |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SMART |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PROSITE |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PRINTS |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Created Date |
18-Oct-2012 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Record Type |
Experiment identified |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein sequence Annotation |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nucleotide Sequence |
Length: bp Go to nucleotide: FASTA |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Sequence |
Length: 382 bp Go to amino acid: FASTA |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The verified Protein-Protein interaction information |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other Protein-Protein interaction resources |
String database |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
View Microarray data |
Temporarily unavailable |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Comments |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||