| Tag | Content | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SG ID |
SG00002125 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
UniProt Accession |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Theoretical PI |
8.8
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Weight |
58886 Da
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Genbank Nucleotide ID |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Genbank Protein ID |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Name |
ER2 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Synonyms/Alias |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Name |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Synonyms/Alias |
SubName: Uncharacterized protein |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Organism |
Sus scrofa (Pig) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NCBI Taxonomy ID |
9823 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Chromosome Location |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function in Stage |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function in Cell Type |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Description |
Temporarily unavailable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The information of related literatures |
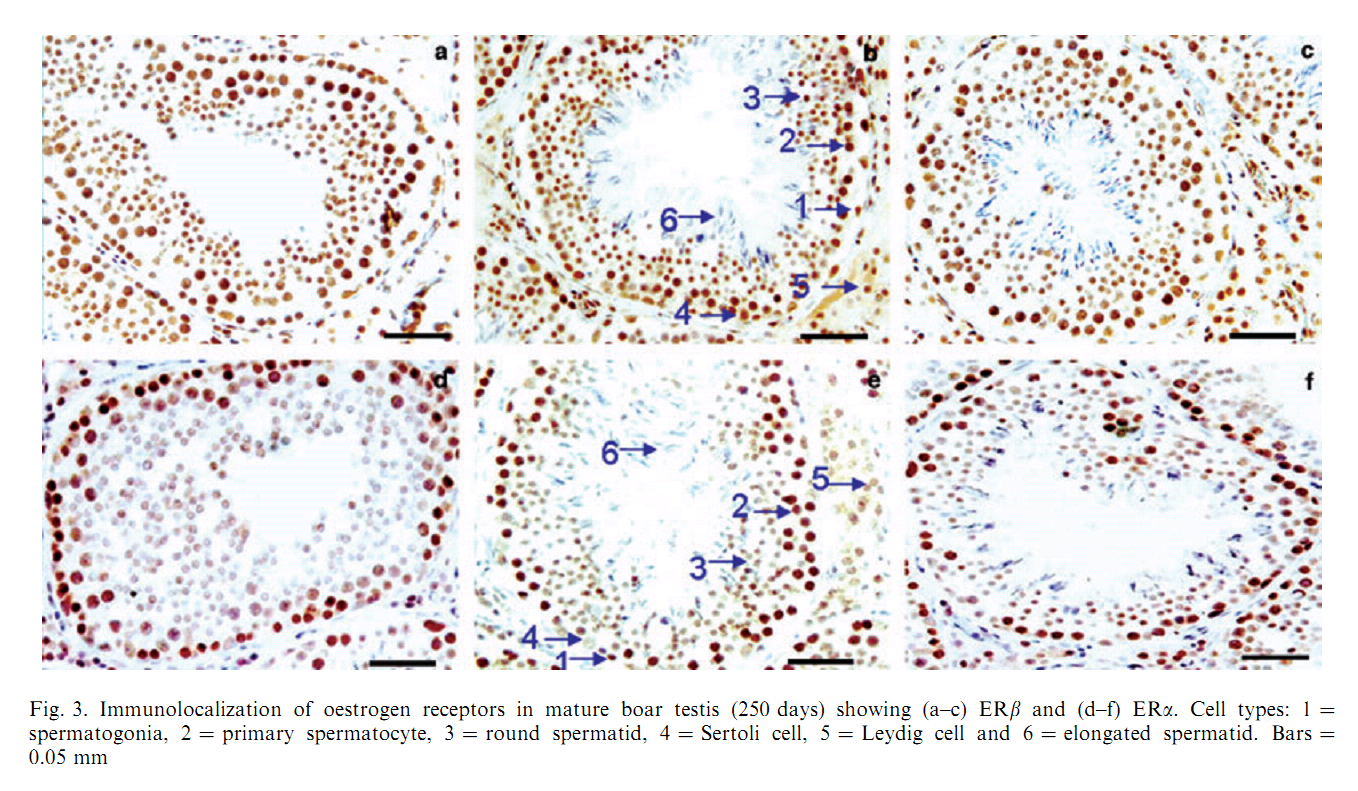
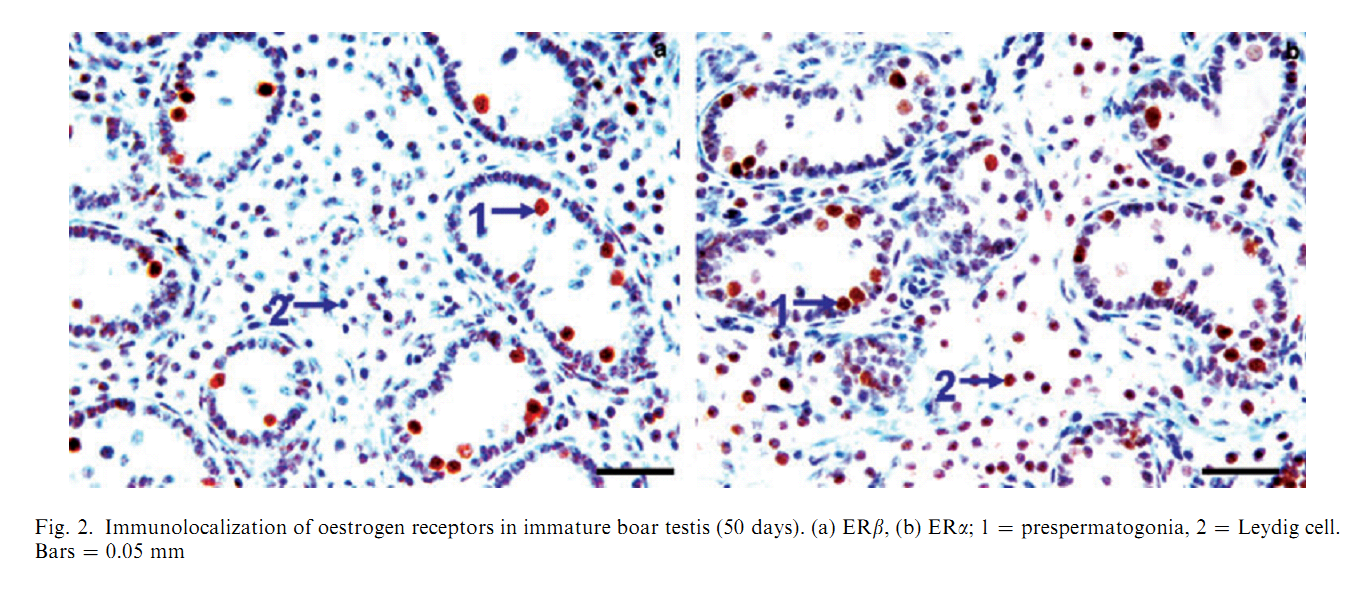
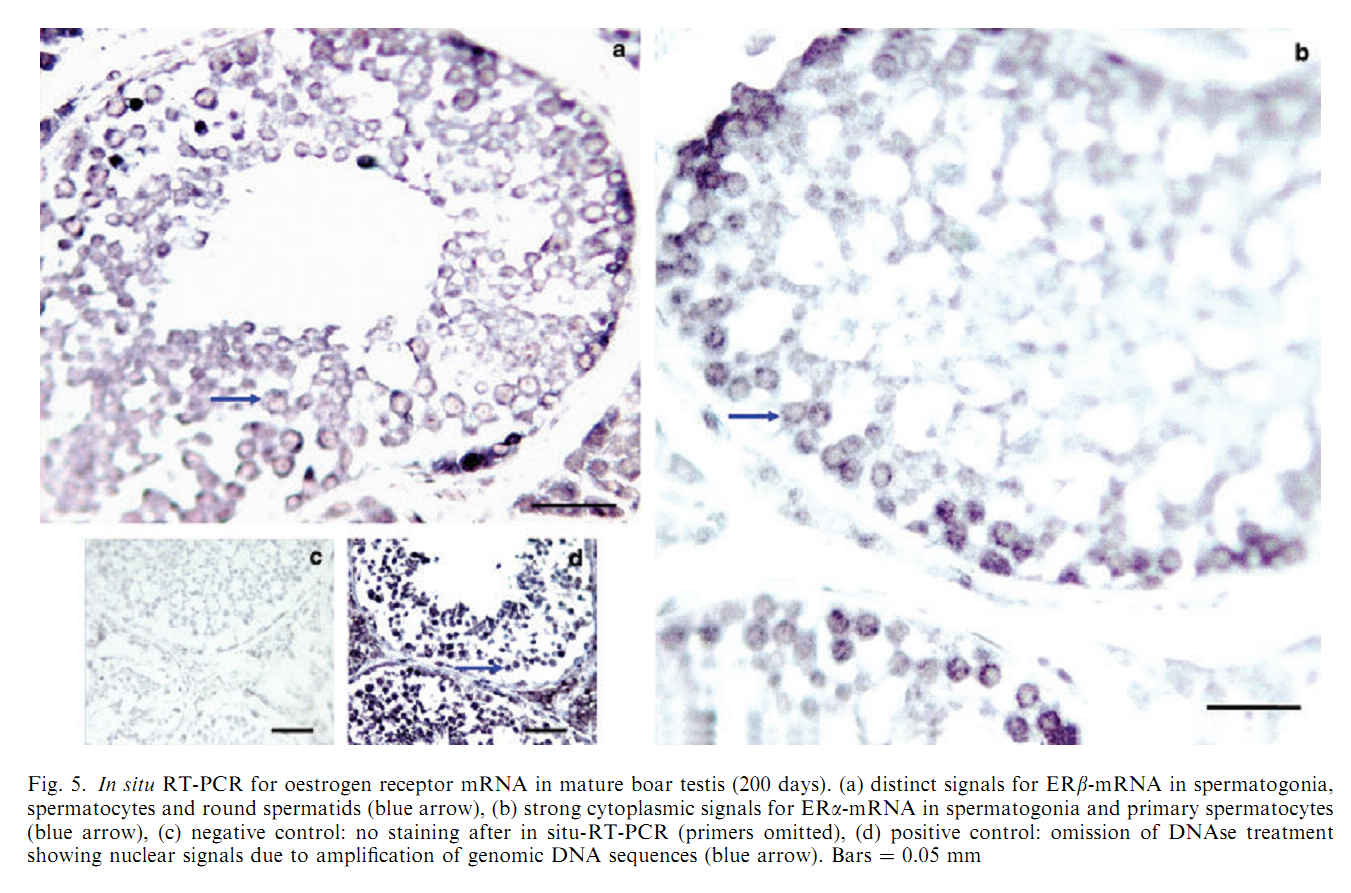
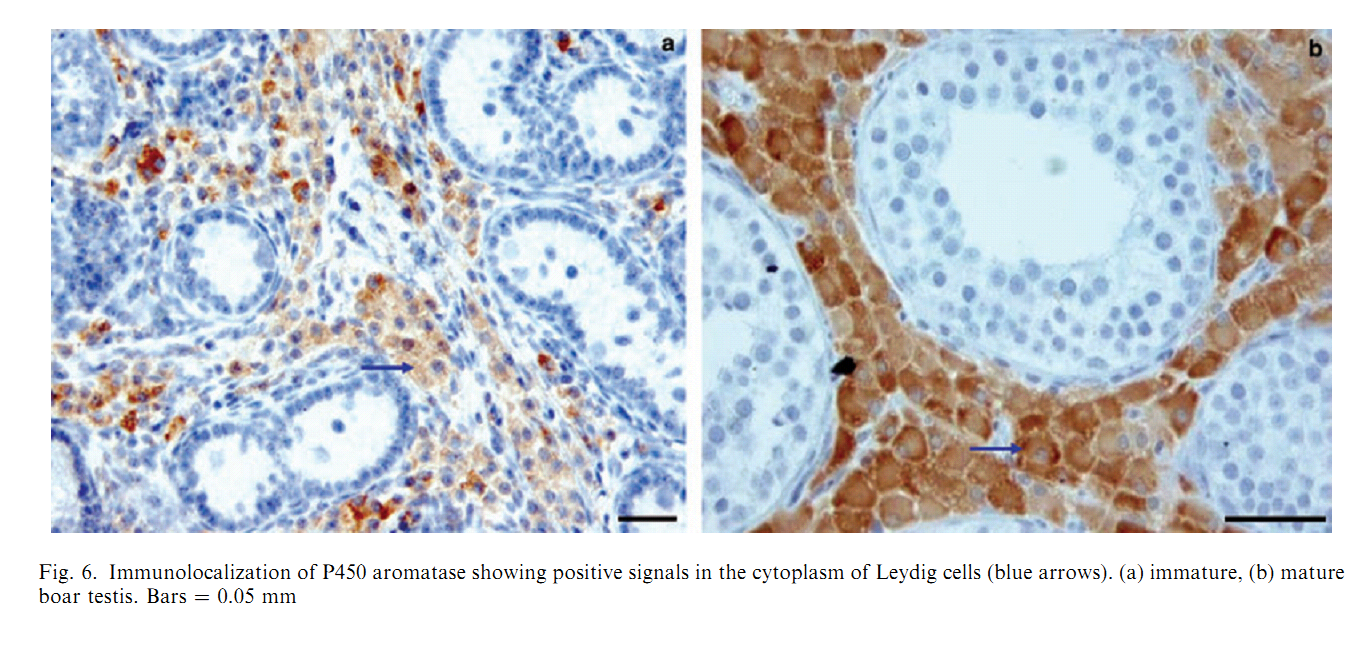
1. O. Lekhkota, R. Brehm, R. Claus, A. Wagner, R. M. Bohle and M. Bergmann (2006) Cellular localization of estrogen receptor-alpha (ERalpha) and -beta (ERbeta) mRNA in the boar testis. Histochem Cell Biol 125(3): 259-64. Abstract Boar testes synthesize high amounts of estrogens which are known to stimulate several male sexual functions in a variety of extragonadal target tissues. Possible effects within the testis depend on the existence of the estrogen receptor subtypes alpha and beta (ERalpha, ERbeta). The precise cellular localization of these subtypes within the testis was, so far, based mainly on protein expression studies using different antibodies in several species including boars shows contradictory results. Therefore, we investigated the ERalpha and ERbeta gene expression using RT-PCR of testis homogenates and RT-PCR after UV-single cell microdissection combined with in-situ hybridization of four fertile boars with an average age of 32 weeks. Both ERalpha and ERbeta mRNA were found in testis homogenates. Using in-situ hybridization and UV-single cell microdissection ERalpha mRNA was present in type A and type B spermatogonia up to mid-pachytene primary spermatocytes in stage V-VIII and stage I of the seminiferous epithelial cycle, but not in other cells. ERbeta mRNA was found only in Sertoli cells. Interstitial Leydig cells revealed neither ERalpha nor ERbeta mRNA. The data suggest a direct impact of estrogen in the boar on Sertoli cell function via ERbeta and germ cell formation via ERalpha. PMID: [16249893] 2. H. M. Mutembei, S. Pesch, G. Schuler and B. Hoffmann (2005) Expression of oestrogen receptors alpha and beta and of aromatase in the testis of immature and mature boars. Reprod Domest Anim 40(3): 228-36. Abstract The boar testis secretes high amounts of oestrogens. In order to test for a likely local significance, we investigated the expression of oestrogen receptors (ER) in immature and mature boar testes using immunohistochemistry (IHC), in vitro and in situ reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Samples were from 25 boars castrated at ages of 50, 100, 150, 200 and 250 days. Mouse monoclonal primary antibodies against porcine ERalpha (clone HT227), human ERbeta1 (clone PPG5/10) and human P450 aromatase (clone SM1671P) were used. Expression of the mRNA was tested utilizing primers specific for the respective porcine mRNA sequences. ER immunoreactivity was exclusively localized to the nuclei. In immature boars, 90.6 +/- 1.2% of prespermatogonia and 71.0 +/- 2.6% of the Leydig cells showed a strong staining for ERalpha; 95.5 +/- 3.5% of the prespermatogonia but none of the Leydig and Sertoli cells were ERbeta-positive. In mature boars a strong staining for the ERbeta was observed in virtually all Sertoli, Leydig and germ cells, except for the elongating/ed spermatids, which were clearly negative; for the ERalpha, strong immunoreaction signals were restricted to spermatogonia and primary spermatocytes with 93.6 +/- 2.7% of these cells being positive; distinctly less intensive signals were observed in 51.4 +/- 0.27% of the secondary spermatocytes, round spermatids and Leydig cells. In vitro RT-PCR was positive for both receptors and results of in situ RT-PCR matched those obtained by IHC. P450 aromatase immunoreaction was restricted to the cytoplasm of Leydig cells. These findings suggest that testicular ER may be important factors contributing to onset and maintenance of spermatogenesis in the boar. PMID: [15943697] Back to Top |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Figures for illustrating the function of this protein/gene |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Subcellular Location |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tissue Specificity |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Ontology |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interpro |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pfam |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SMART |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PROSITE |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PRINTS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Created Date |
18-Oct-2012 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Record Type |
Experiment identified |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein sequence Annotation |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nucleotide Sequence |
Length: bp Go to nucleotide: FASTA |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein Sequence |
Length: 526 bp Go to amino acid: FASTA |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The verified Protein-Protein interaction information |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other Protein-Protein interaction resources |
String database |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
View Microarray data |
Temporarily unavailable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Comments |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||