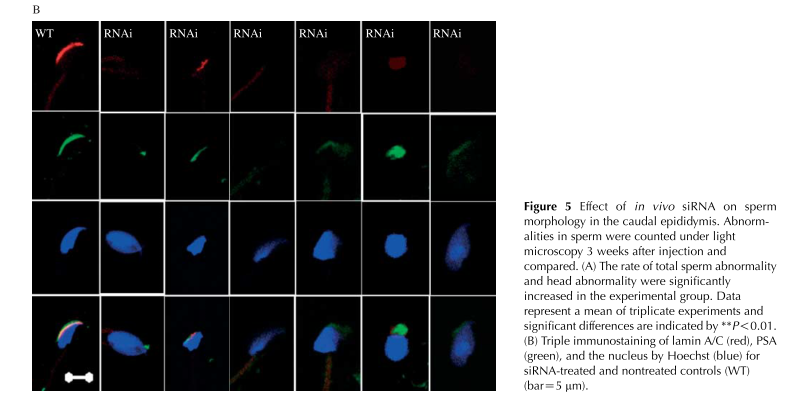
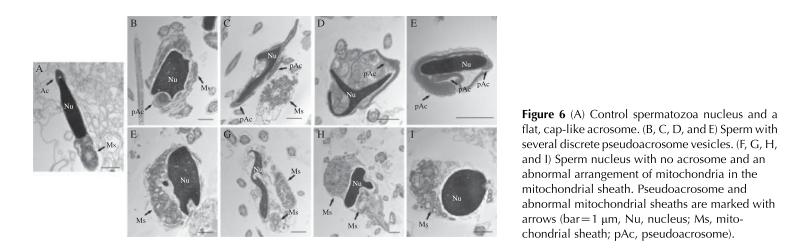
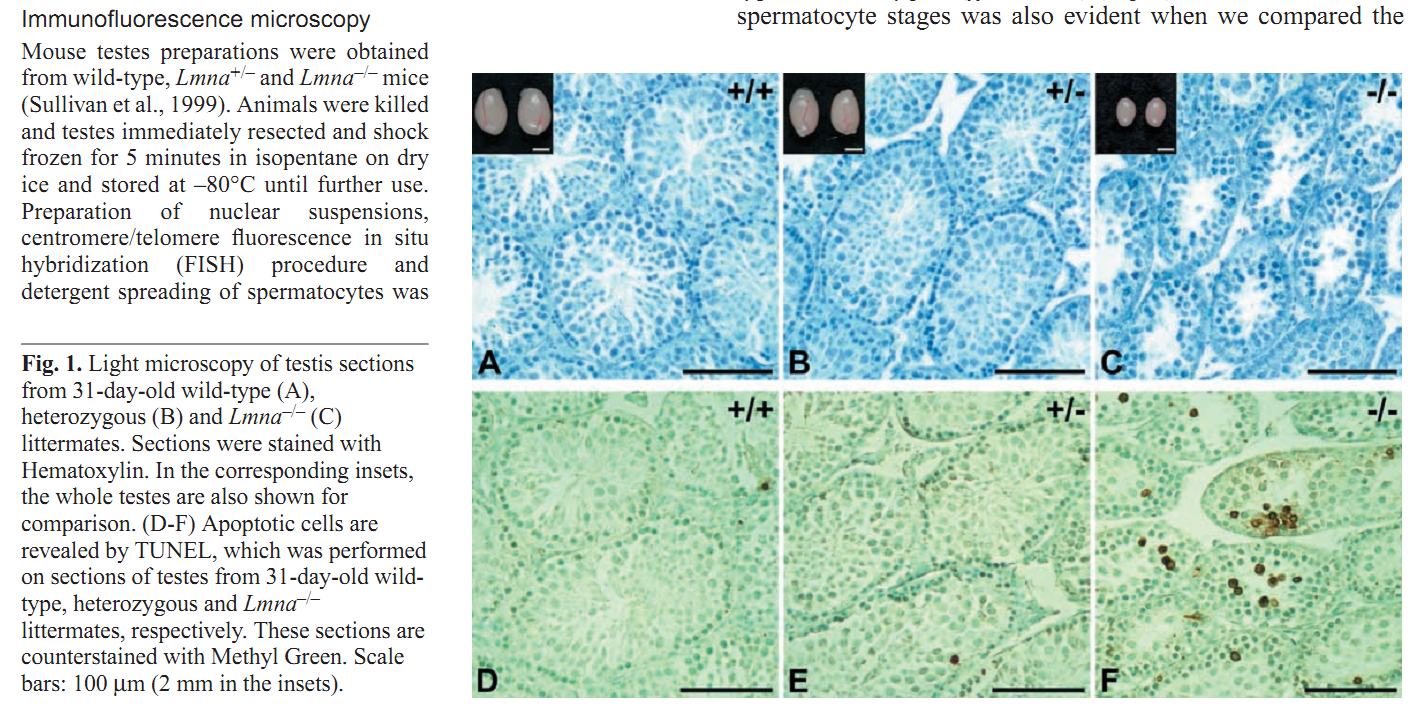
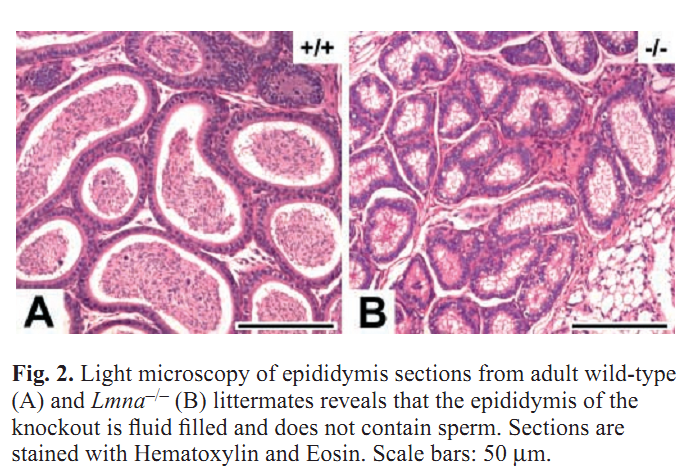
General information
| SG000258 | |||||||||||||||||
| Lmna | |||||||||||||||||
| Dhe | |||||||||||||||||
| Mus musculus | |||||||||||||||||
| 10090 | |||||||||||||||||
| ENSMUSG00000028063 | |||||||||||||||||
| ENSMUSP00000029699 ENSMUSP00000113093 ENSMUSP00000040265 ENSMUSP00000120784 | |||||||||||||||||
Lamin A [Mus musculus(house mouse) ] | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Reviewed functional gene |
Functional information
| meiotic postmeiotic | |
| Spermatid Spermatocyte | |
|
1. Abstract 2. Abstract 3. Abstract | |
| |
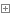
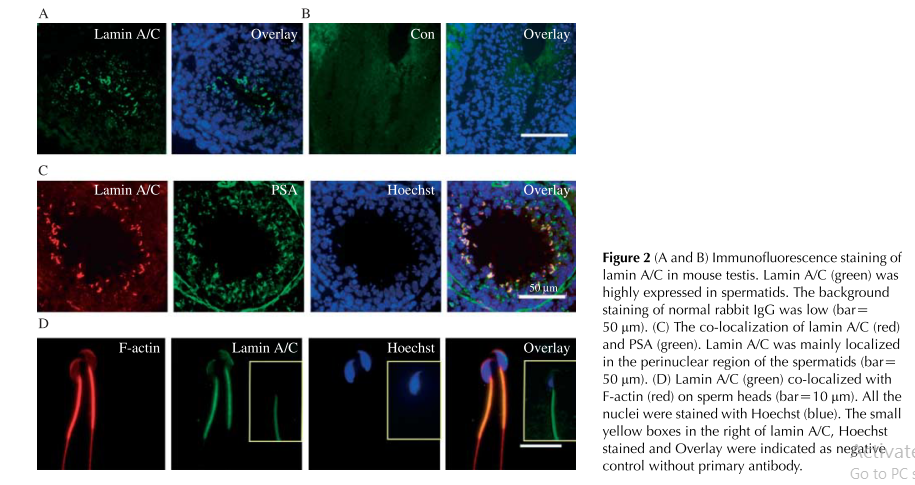
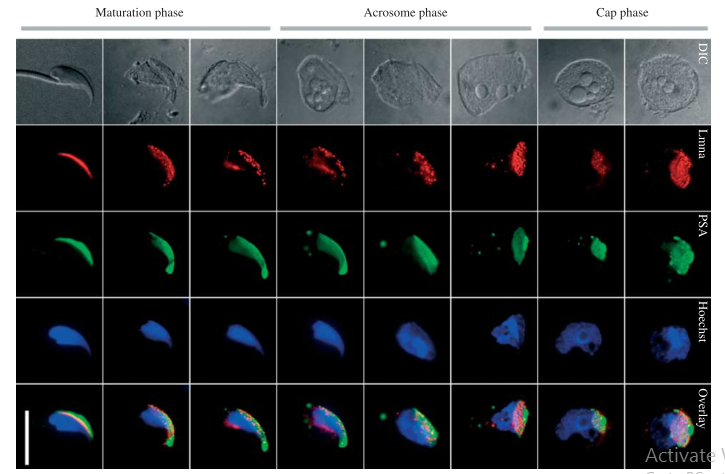
| Lamin A/C belongs to A-type lamins and is derived by differential splicing from the LMNA gene. Mutation in the LMNA gene appears to be responsible for several inherited disorders in humans, including Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD), Dunnigan-type familial partial lipodystrophy (FPLD), and Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. Lamin A/C was expressed in the mouse testis throughout the different stages of spermatogenesis and in mature sperm. Lamin A/C was also expressed in mouse haploid germ cells andwas found to be localized to the acroplaxome in spermiogenesis, from round spermatids until mature spermatozoa | |
|
ReactomeID: R-MMU-8862803 Deregulated CDK5 triggers multiple neurodegenerative pathways in Alzheimer's disease models | |
| N/A |
Expression and location
| Expressed highest in gallbladder | |
| Expressed highest in spermatogonium | |
| View detail | |
| View detail | |
| Nucleus. Nucleus envelope. Nucleus lamina |
Mutation in human orthology
|
1000G (Phase 3): 1469 ESP6500 (SI-V2): 111 ExAC (r0.3.1): 652 dbSNP(Build 147): 3795 |
|||||||
|
Chinese health control (254): 14 European health control (283): 13 Chinese patients (168): |
|||||||
|
Other information
|
Click the right sign for more information
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P48678 |