General information
| SG000102 | |||||||||||||||||
| Zbtb16 | |||||||||||||||||
| AI467657, PLZF, Zfp145, lu | |||||||||||||||||
| Mus musculus | |||||||||||||||||
| 10090 | |||||||||||||||||
| ENSMUSG00000066687 | |||||||||||||||||
| ENSMUSP00000091374 ENSMUSP00000150887 | |||||||||||||||||
Zinc finger and BTB domain containing 16 [Mus musculus (house mouse)] | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Reviewed functional gene |
Functional information
| premeiotic | |
| Spermatogonia | |
|
1. Abstract 2. Abstract 3. Abstract 4. Abstract | |
| |
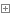
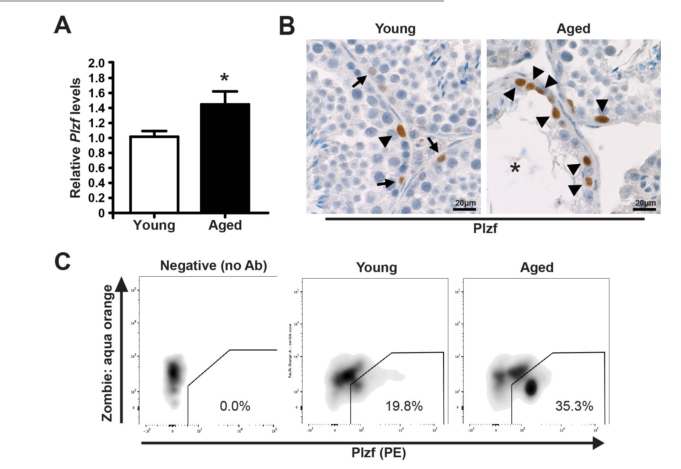
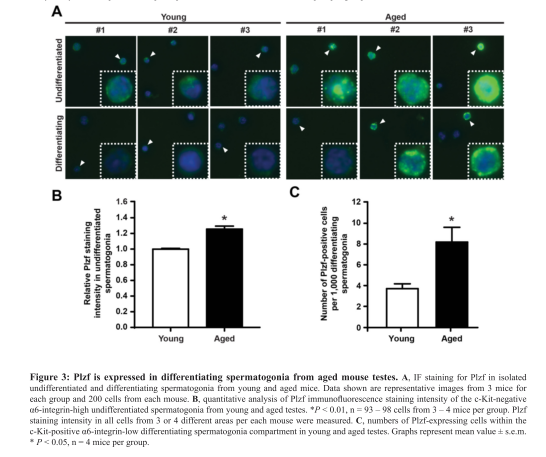
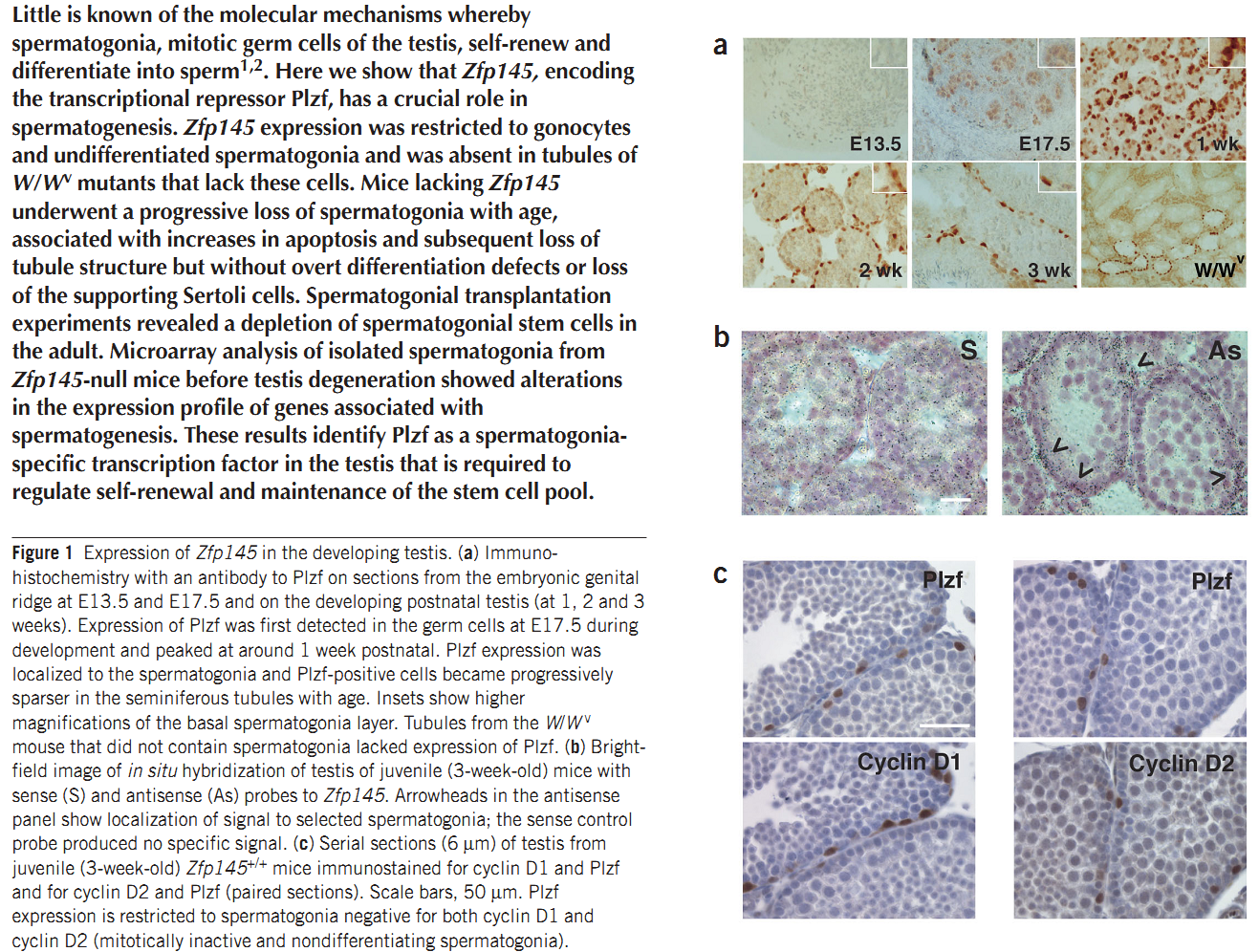
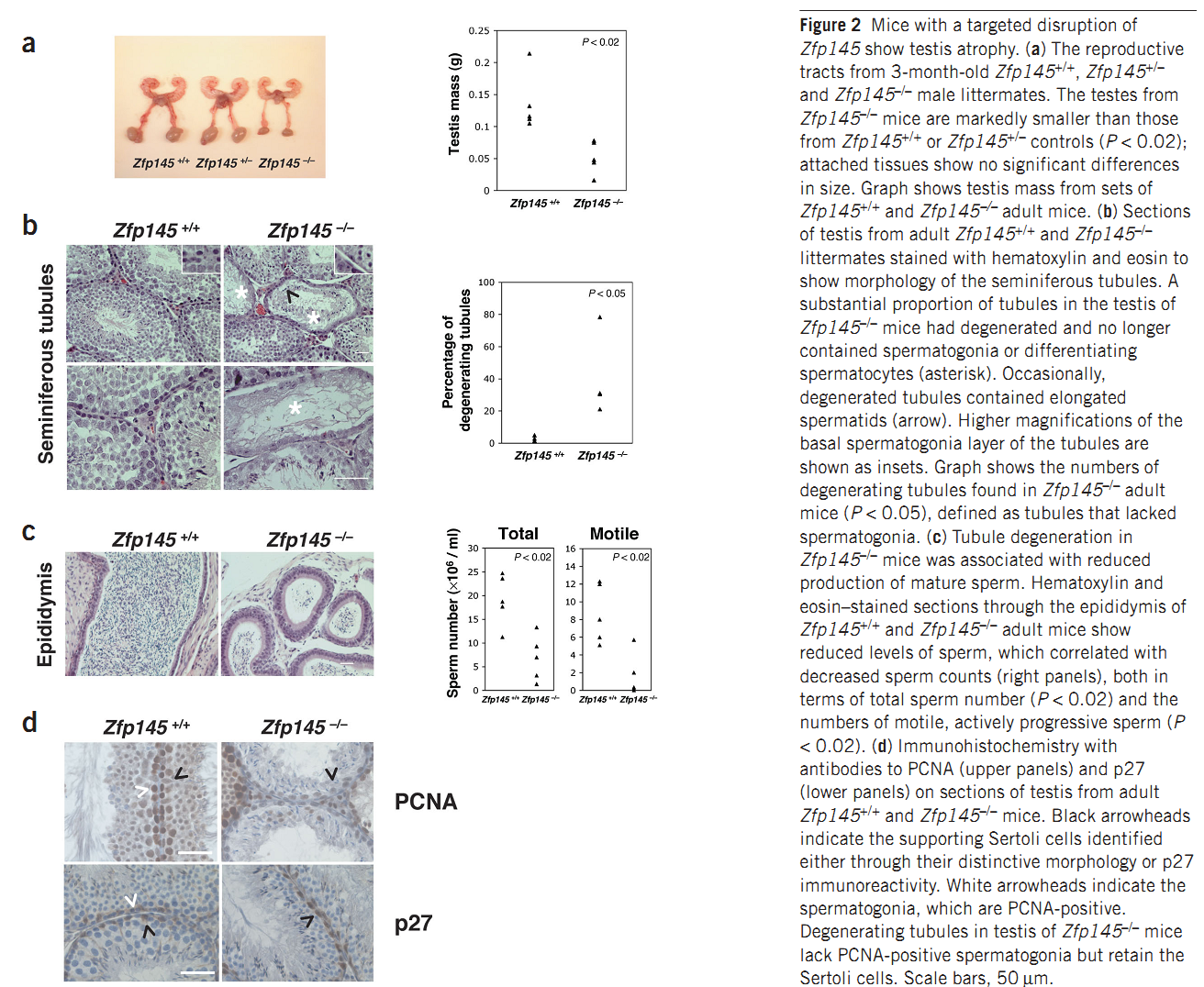
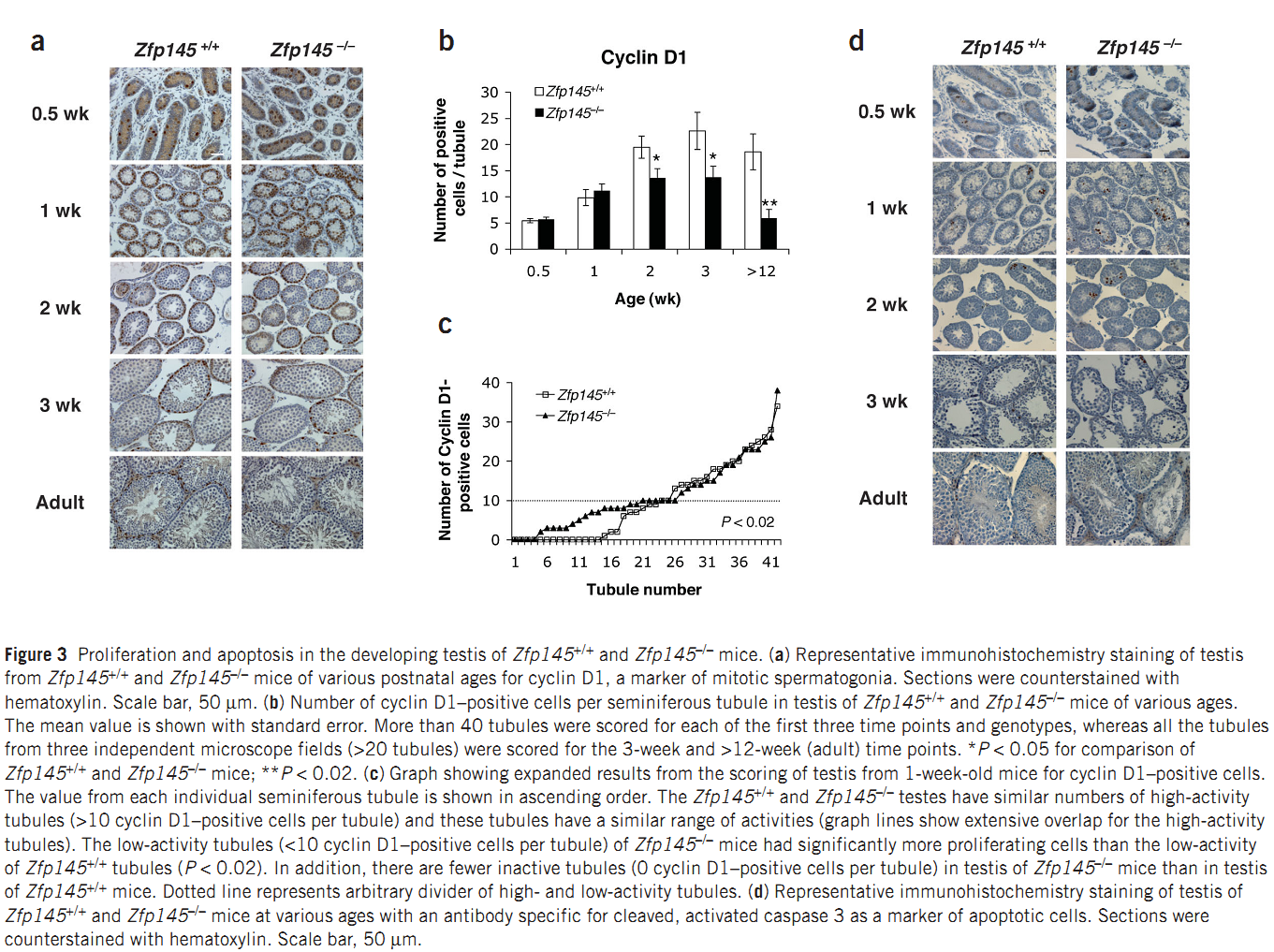
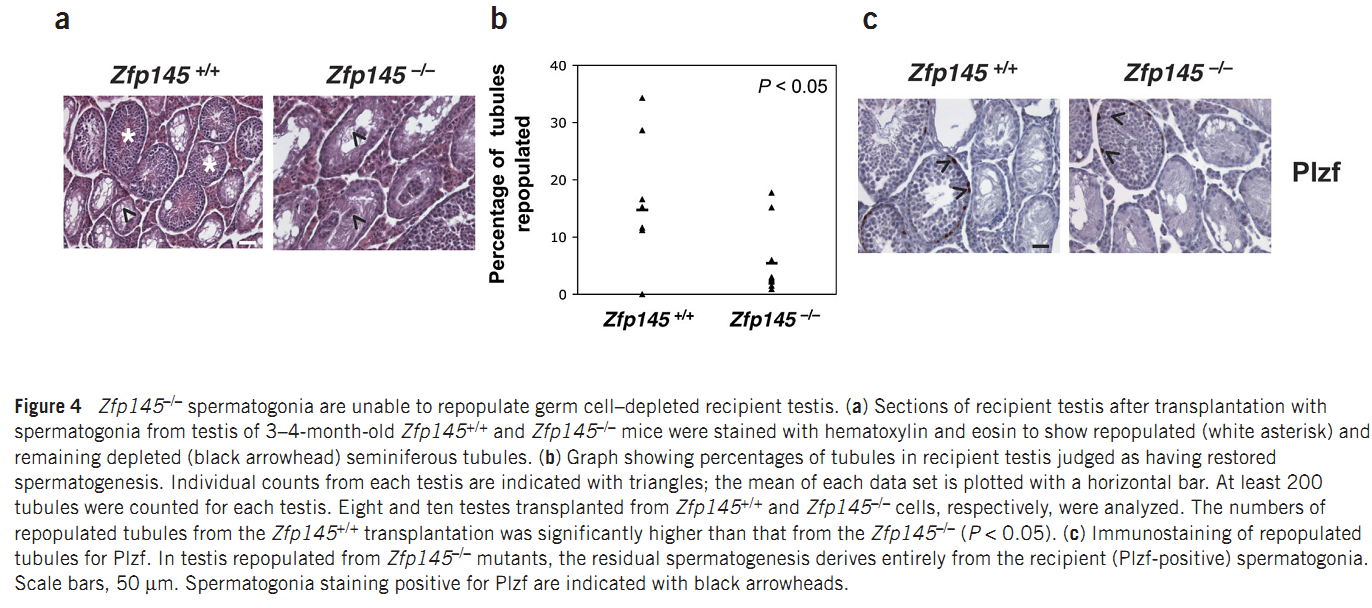
| Promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger (Plzf), encoded by Zbtb16, is specifically expressed at the spermatogonia stage during spermatogenesis in mouse and human. It plays an essential role in spermatogonia maintenance by preventing their differentiation and age-related increase in Plzf expression represents a novel molecular signature of spermatogonia aging by functionally arresting their differentiation|The transcription factors promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger (PLZF; also known as ZBTB16) ) is known to be required for normal SSC function. Loss of PLZF results in progressive depletion of SSCs after the first wave of spermatogenesis leading to eventual spermatogenic arrest, apparently the result of a shift in the balance in SSC fate away from self-renewal and towards differentiation | |
|
ReactomeID: R-MMU-8951664 Neddylation | |
| SCO |
Expression and location
| Expressed highest in ovary | |
| Expressed highest in spermatogonium | |
| View detail | |
| View detail | |
| - |
Mutation in human orthology
|
1000G (Phase 3): 4704 ESP6500 (SI-V2): 71 ExAC (r0.3.1): 381 dbSNP(Build 147): 9184 |
|||||||
|
Chinese health control (254): 11 European health control (283): 10 Chinese patients (168): |
|||||||
|
Other information
|
Click the right sign for more information
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q3UQ17 |