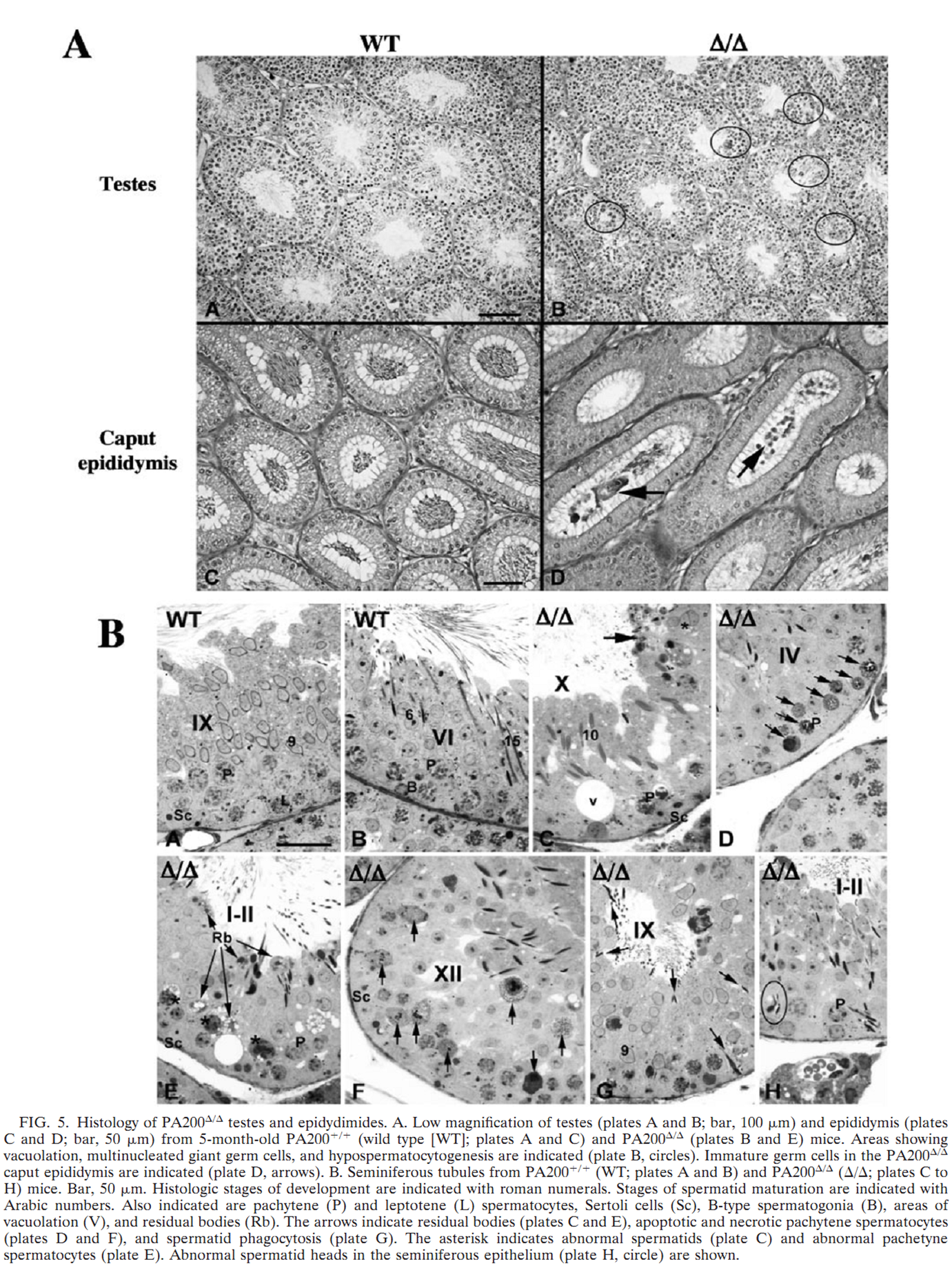
 B. Khor, A. L. Bredemeyer, C. Y. Huang, I. R. Turnbull, R. Evans, L. B. Maggi, Jr., J. M. White, L. M. Walker, K. Carnes, R. A. Hess and B. P. Sleckman (2006) Proteasome activator PA200 is required for normal spermatogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 26(8): 2999-3007. PMID: [16581775]
B. Khor, A. L. Bredemeyer, C. Y. Huang, I. R. Turnbull, R. Evans, L. B. Maggi, Jr., J. M. White, L. M. Walker, K. Carnes, R. A. Hess and B. P. Sleckman (2006) Proteasome activator PA200 is required for normal spermatogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 26(8): 2999-3007. PMID: [16581775]
 B. Khor, A. L. Bredemeyer, C. Y. Huang, I. R. Turnbull, R. Evans, L. B. Maggi, Jr., J. M. White, L. M. Walker, K. Carnes, R. A. Hess and B. P. Sleckman (2006) Proteasome activator PA200 is required for normal spermatogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 26(8): 2999-3007. PMID: [16581775]
B. Khor, A. L. Bredemeyer, C. Y. Huang, I. R. Turnbull, R. Evans, L. B. Maggi, Jr., J. M. White, L. M. Walker, K. Carnes, R. A. Hess and B. P. Sleckman (2006) Proteasome activator PA200 is required for normal spermatogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 26(8): 2999-3007. PMID: [16581775]